Abstract
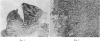
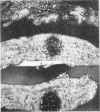
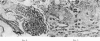
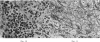
Pigs were subjected to active anaphylactic shock using egg albumin and to reversed passive anaphylaxis using Escherichia coli (O138). The symptoms and lesions closely resembled those of oedema disease and haemorrhagic gastroenteritis. Catarrhal enteritis was also observed. There was a relationship between the character of the lesions which were produced and the severity and duration of the anaphylactic symptoms. Further evidence confirmed earlier observations that clinically normal pigs may develop a hypersensitivity to those serotypes of E. coli which are associated with these conditions. The results are discussed in relation to the pathogenesis of these diseases, and it is considered that oedema disease and haemorrhagic gastro-enteritis develop from an anaphylactic type of hypersensitivity to E. coli rather than from a direct toxaemia arising from the sudden absorption of increased quantities of bacterial polysaccharide.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GARVEY J. S., CAMPBELL D. H. The in vivo stability of antibody. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:355–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDGRABER M. B., KIRSNER J. B. The Arthus phenomenon in the colon of rabbits; a serial histological study. AMA Arch Pathol. 1959 May;67(5):556–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSNER J. B., ELCHLEPP J. G., GOLDGRABER M. B., ABLAZA J., FORD H. Production of an experimental ulcerative "colitis" in rabbits. Arch Pathol. 1959 Oct;68:392–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMONT H. G., LUKE D., GORDON W. A. M. Some pig diseases. Vet Rec. 1950 Dec 9;62(49):737–747. doi: 10.1136/vr.62.49.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITT M. Studies in experimental eosinophilia. III. The induction of peritoneal eosinophilia by the passive transfer of serum antibody. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:522–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORE R. H., MOVAT H. Z. Cellular and intercellular changes in the Arthus phenomenon. AMA Arch Pathol. 1959 Jun;67(6):679–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAVIN H. A., ROWLEY D., JENKINS C., FINE J. On the absorption of bacterial endotoxin from the gastro-intestinal tract of the normal and shocked animal. J Exp Med. 1960 Nov 1;112:783–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.5.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIMONEY J. F. Oedema disease of swine. Vet Rec. 1950 Dec 9;62(49):748–756. doi: 10.1136/vr.62.49.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE R. G. Observations on the formation and nature of Russell bodies. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Aug;35(4):365–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]