Abstract
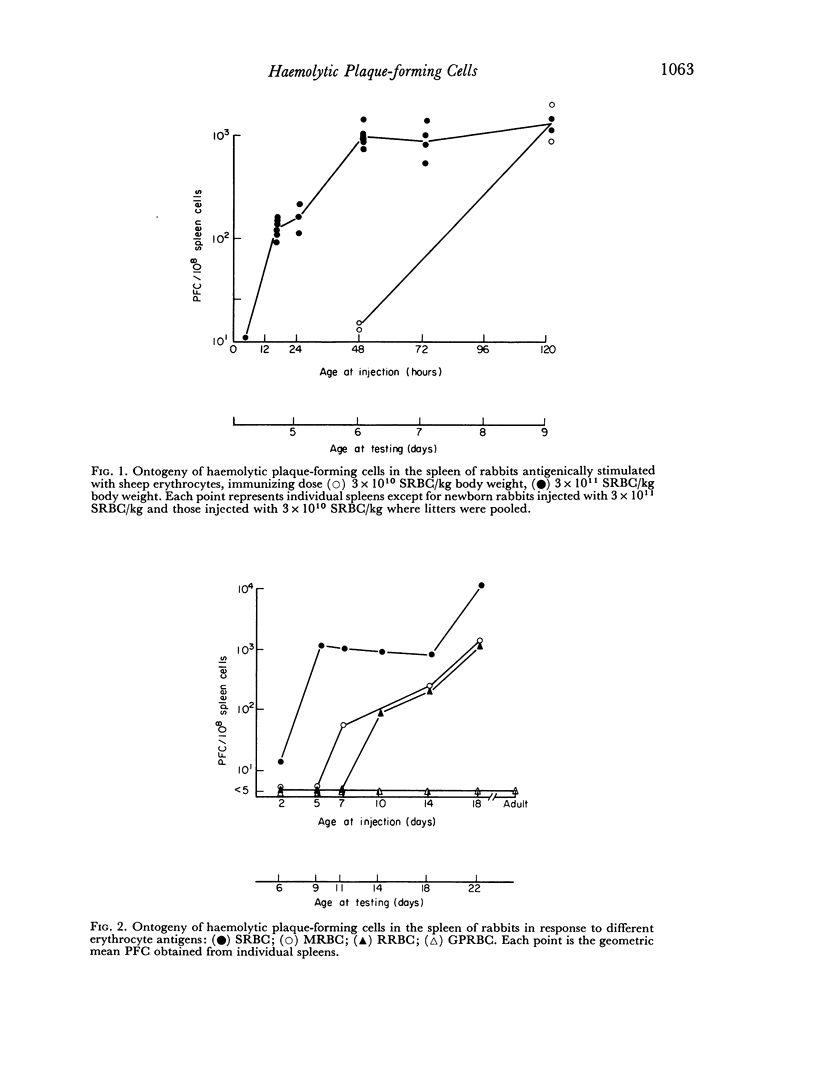
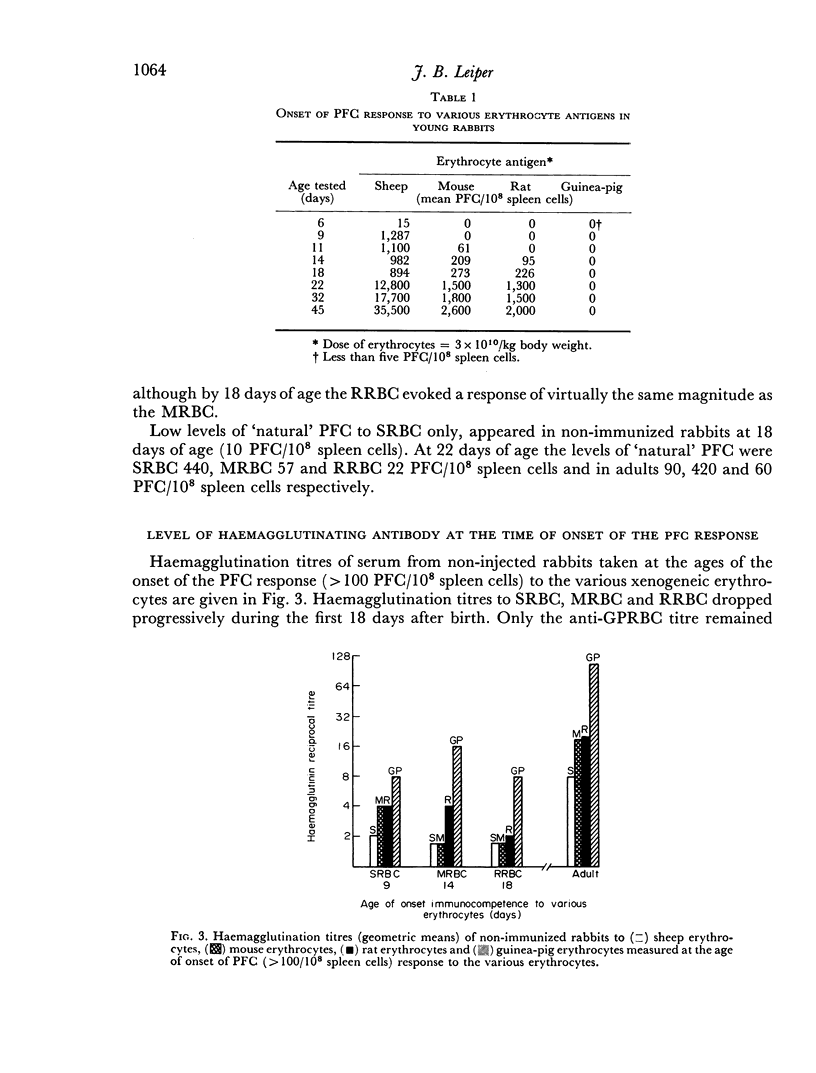
The ability of rabbits to respond to relatively high doses of sheep erythrocytes appears within 5 days after birth. Young rabbits exhibited an apparent sequential maturation of responsiveness to sheep, mouse, rat and guinea-pig erythrocyte antigens. The delay in response to these antigens can be correlated with different levels of specific haemagglutinin, presumably of maternal origin, in the circulation of young rabbits.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AITKEN I. D. DEVELOPMENT OF NATURAL ANTI-FORSSMAN HEMOLYSIN IN YOUNG RABBITS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Apr;114:174–178. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.2.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman G. A., Hostetler J. R. Morphological studies of the embryonic rabbit thymus: the in situ epithelial versus the extrathymic derivation of the initial population of lymphocytes in the embryonic thymus. Anat Rec. 1970 Jan;166(1):27–45. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091660103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra D., Gery I., Davies A. M. Specificity of blast transformation. II. Studies with erythrocyte antigens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):488–495. doi: 10.1159/000230378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERY I., DAVIES A. M. PATTERNS OF IMMUNE REACTION OF RATS INJECTED WITH HETEROLOGOUS ERYTHROCYTES. Vox Sang. 1963 Sep-Oct;8:634–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1963.tb04193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargis B. J., Malkiel S. Production of hypersensitivity in the neonatal mouse. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):942–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H. Strain differences in the immune response of mice. I. The neonatal response to sheep red cells. Immunology. 1968 Jul;15(1):35–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN A. M., UHR J. W., KRANER K. L., LUKES R. J. Fetal response to antigenic stimulus. II. Antibody production by the fetal lamb. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:799–812. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B., Leiper J., Reid T. M. Ontogeny of haemolytic plaque-forming cells in the hamster; the response to sheep and mouse erythrocytes. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):63–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B., Riddell G. S., Whyte D. F. Specific immunosuppressive delay of the plaque-forming response by trace amounts of antibody of maternal origin in young rats injected with mouse or sheep erythrocytes. Immunology. 1972 Feb;22(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B. Unification of foetal and neonatal immunology. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):895–897. doi: 10.1038/227895a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAINER A., ROBBINS J., BELLANTI J., EITZMAN D., SMITH R. T. Synthesis of gamma-globulin in the newborn rabbit. Nature. 1963 May 4;198:487–488. doi: 10.1038/198487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


