Abstract
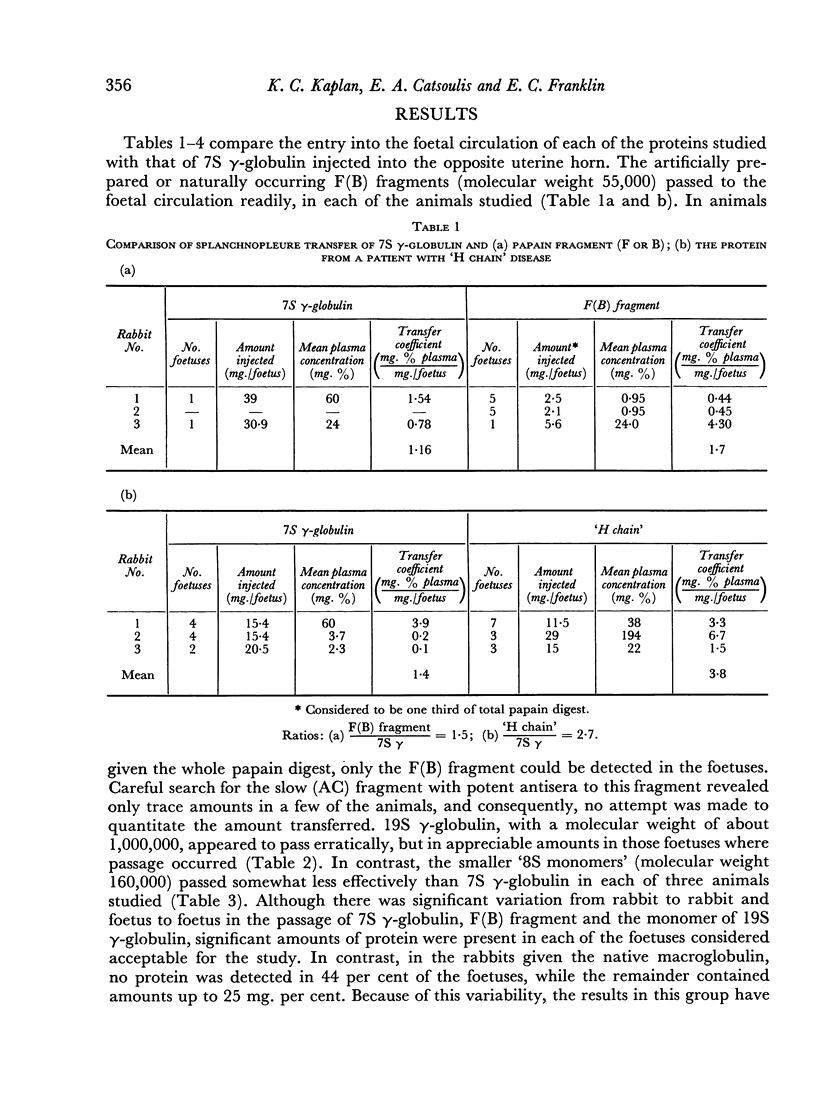
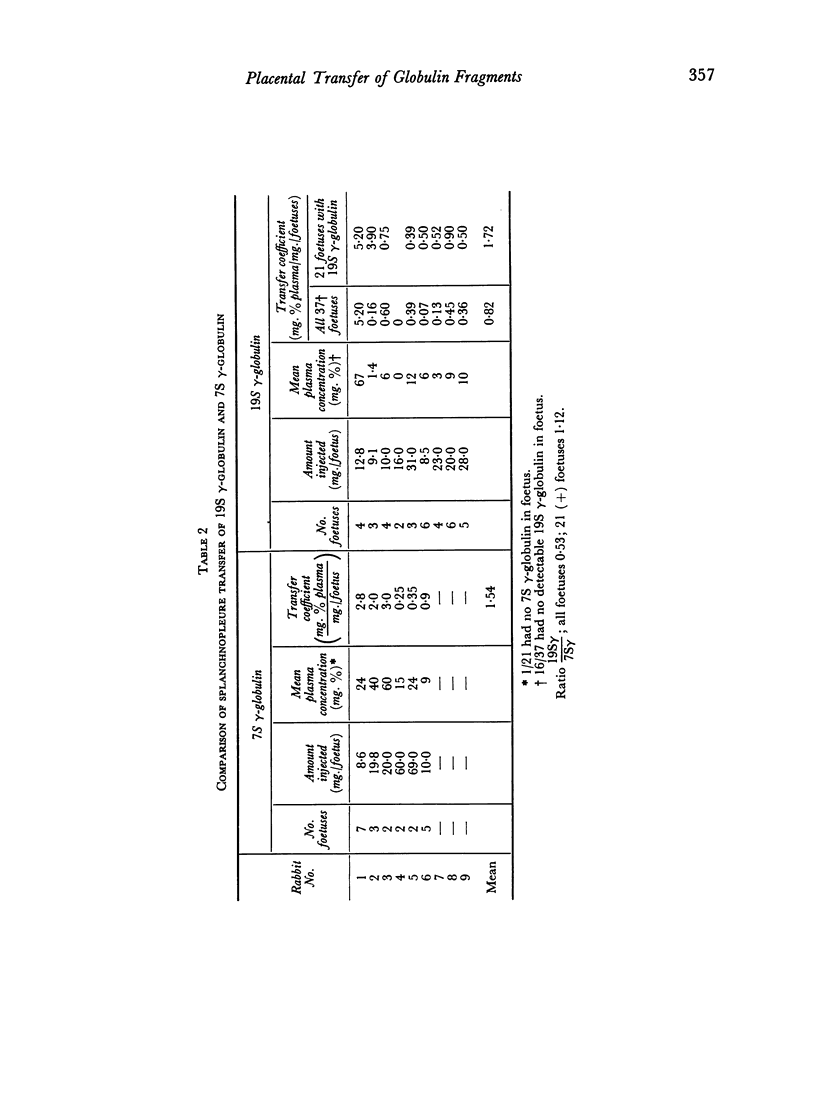
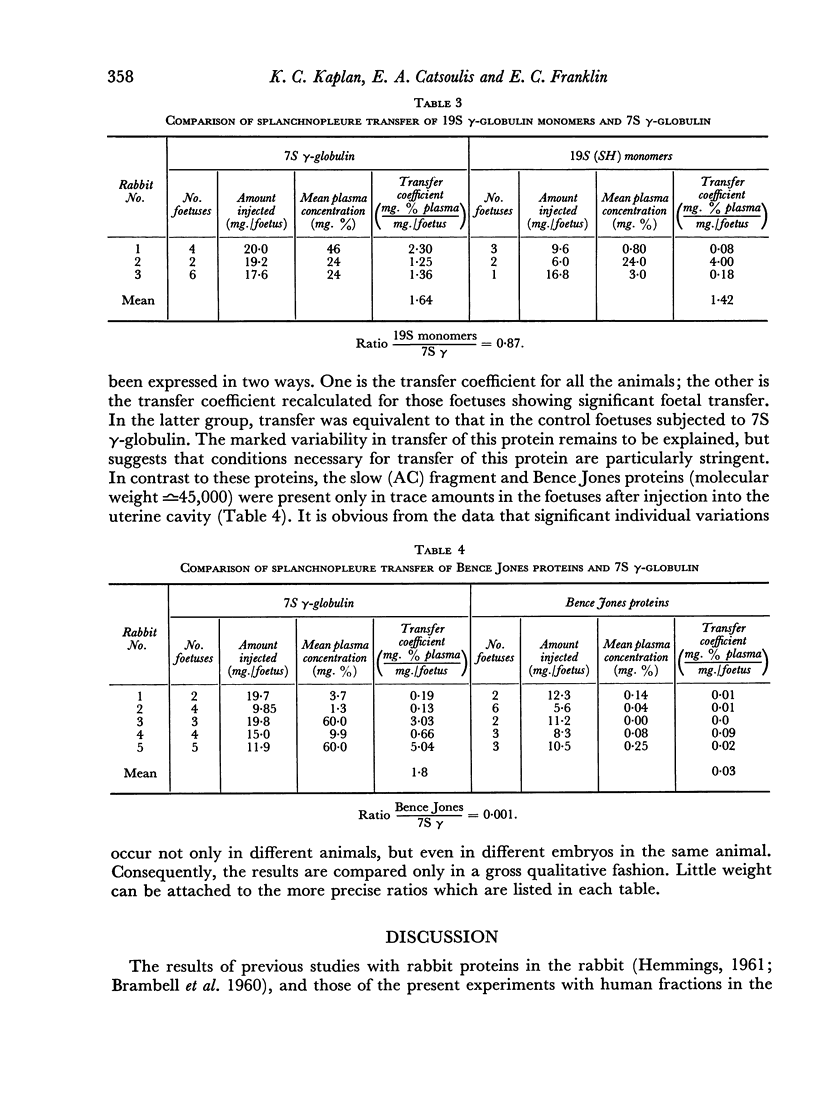
Studies of the ability of human 7S and 19S γ-globulins and some of their structural units to pass from the maternal to the foetal circulation in the rabbit have demonstrated that 7Sγ, 19Sγ, the `8S' units of the 19S γ-globulin and the artificially and naturally occurring F(B) fragments enter the foetal circulation readily. On the other hand, the slow (AC) papain fragment and Bence Jones proteins enter the foetal circulation poorly or not at all.
It would appear that some structure associated with the `H chain' and found in the F(B) fragment of 7S γ-globulin is essential for the active process involved in the transfer of proteins across the rabbit splanchnopleure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAMBELL F. W. R., HEMMINGS W. A., HENDERSON M., ROWLANDS W. T. The selective admission of antibodies to the foetus by the yolk-sac splanchnopleur in rabbits. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1950 Jul 24;137(887):239–252. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1950.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMBELL F. W., HEMMINGS W. A., OAKLEY C. L., PORTER R. R. The relative transmission of the fractions of papain hydrolyzed homologous gamma-globulin from the uterine cavity to the foetal circulation in the rabbit. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1960 Mar 1;151:478–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1960.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMBELL F. W. RESEMBLANCES BETWEEN PASSIVE ANAPHYLACTIC SENSITIZATION AND TRANSMISSION OF PASSIVE IMMUNITY. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1164–1166. doi: 10.1038/1991164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C., KUNKEL H. G. Comparative levels of high molecular weight (19S) gamma globulin in maternal and umbilical cord sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Nov;52(5):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C., LOWENSTEIN J., BIGELOW B., MELTZER M. HEAVY CHAIN DISEASE- A NEW DISORDER OF SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULINS : REPORT OF THE FIRST CASE. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:332–350. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELL P. G. Immunological analysis of abnormalities in the human serum proteins by a gel-diffusion method. J Clin Pathol. 1955 Nov;8(4):269–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEMMINGS W. A., BRAMBELL F. W. Protein transfer across the foetal membranes. Br Med Bull. 1961 May;17:96–101. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F., TAKATSUKI K. CLINICAL AND IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF FOUR CASES OF HEAVY (H-GAMMA-2) CHAIN DISEASE. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:351–373. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., KARUSH F. Studies on the immunologic mechanism of anaphylaxis. II. Sensitizing and combining capacity in vivo of fractions separated from papain digests of antihapten antibody. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:146–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISNER C. A., FRANKLIN E. C. Studies of mercaptoethanol-dissociated normal human 19 S gamma-globulin and pathologic macroglobulins from patients with macroglobulinemia. J Immunol. 1961 Dec;87:654–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARANTA A., FRANKLIN E. C. Complement fixation by antibody fragments. Science. 1961 Dec 15;134(3494):1981–1982. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3494.1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


