Abstract
Purification of the aspermatogenic factor of guinea-pig testes has resulted in an antigen capable of inducing circulating antibody, delayed skin reactivity and a testis lesion on injection of as little as 5 μg into guinea-pigs.
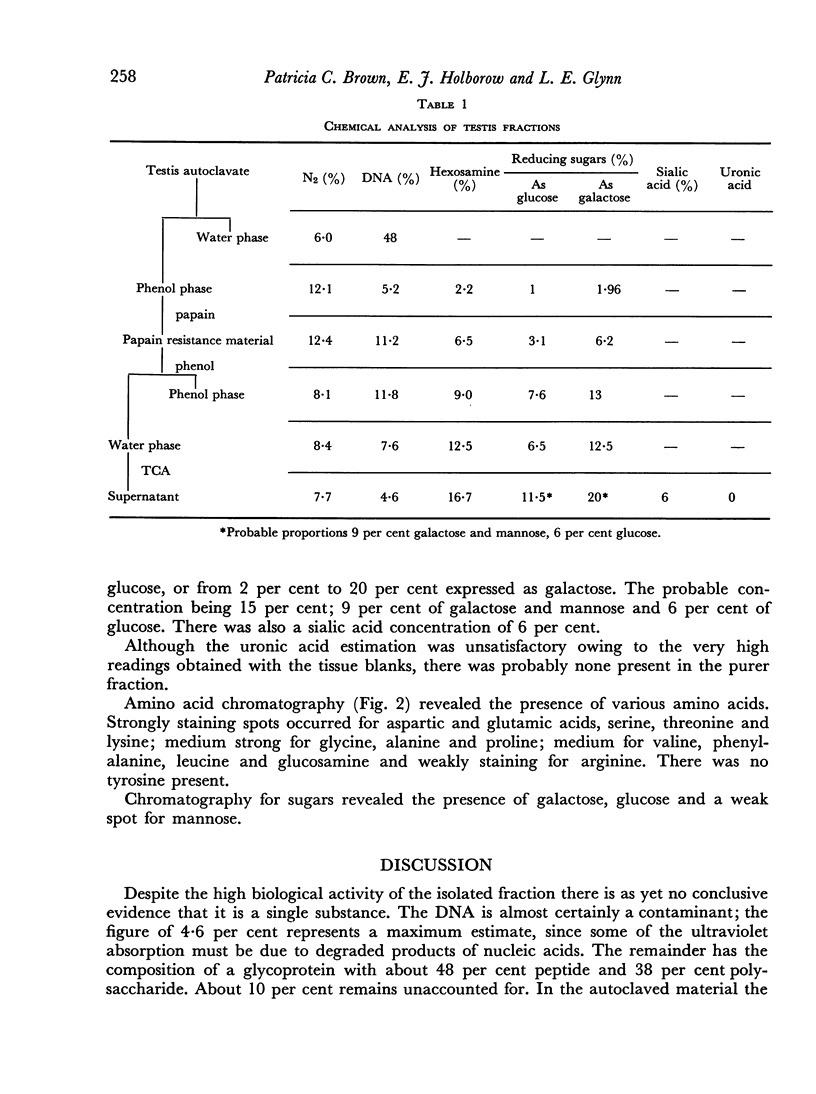
Chemical analysis of the fraction revealed a nitrogen content of 7.7 per cent and a polysaccharide content of 38 per cent.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNISON E. F., MORGAN W. T. J. Studies in immunochemistry. X. The isolation and properties of Lewis (Lea) human blood group substance. Biochem J. 1952 Feb;50(4):460–471. doi: 10.1042/bj0500460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANNISON E. F., MORGAN W. T. J. Studies in immunochemistry. XI. The isolation and properties of the human blood-group H substance. Biochem J. 1952 Oct;52(2):247–258. doi: 10.1042/bj0520247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., ABBOTT V., TSAI T. Relationship of colominic acid (poly N-acetylneuraminic acid) to bacteria which contain neuraminic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Oct;29:335–352. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN P. C., GLYNN L. E., HOLBOROW E. J. THE PATHOGENESIS OF EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ORCHITIS IN GUINEA-PIGS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:505–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUTNA J., RYCHLIKOVA M. PREVENTION AND SUPPRESSION OF EXPERIMENTAL AUTOIMMUNE ASPERMATOGENESIS IN ADULT GUINEA PIGS. Folia Biol (Praha) 1964;10:177–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson L. A., Morgan W. T. A colorimetric method for the determination of glucosamine and chondrosamine. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1824–1828. doi: 10.1042/bj0271824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT J. K. The semi-micro Kjeldahl method for the determination of nitrogen. J Med Lab Technol. 1954 Jan;12(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUND J., THOMPSON G. E., LIPTON M. M. Aspermatogenesis, anaphylaxis, and cutaneous sensitization induced in the guinea pig by homologous testicular extract. J Exp Med. 1955 Jun 1;101(6):591–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.6.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. A., MORGAN W. T. Studies in immunochemistry. 14. The isolation and properties of substances of human origin possessing blood-group B specificity. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):283–295. doi: 10.1042/bj0570283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLBOROW E. J., LOEWI G. The immune response to bloodgroup substances. Immunology. 1962 Mar;5:278–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. W., MARSHALL J. D., Jr, EVELAND W. C. Use of contrasting fluorescent dye as counterstain in fixed tissue preparations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:179–181. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]