Abstract
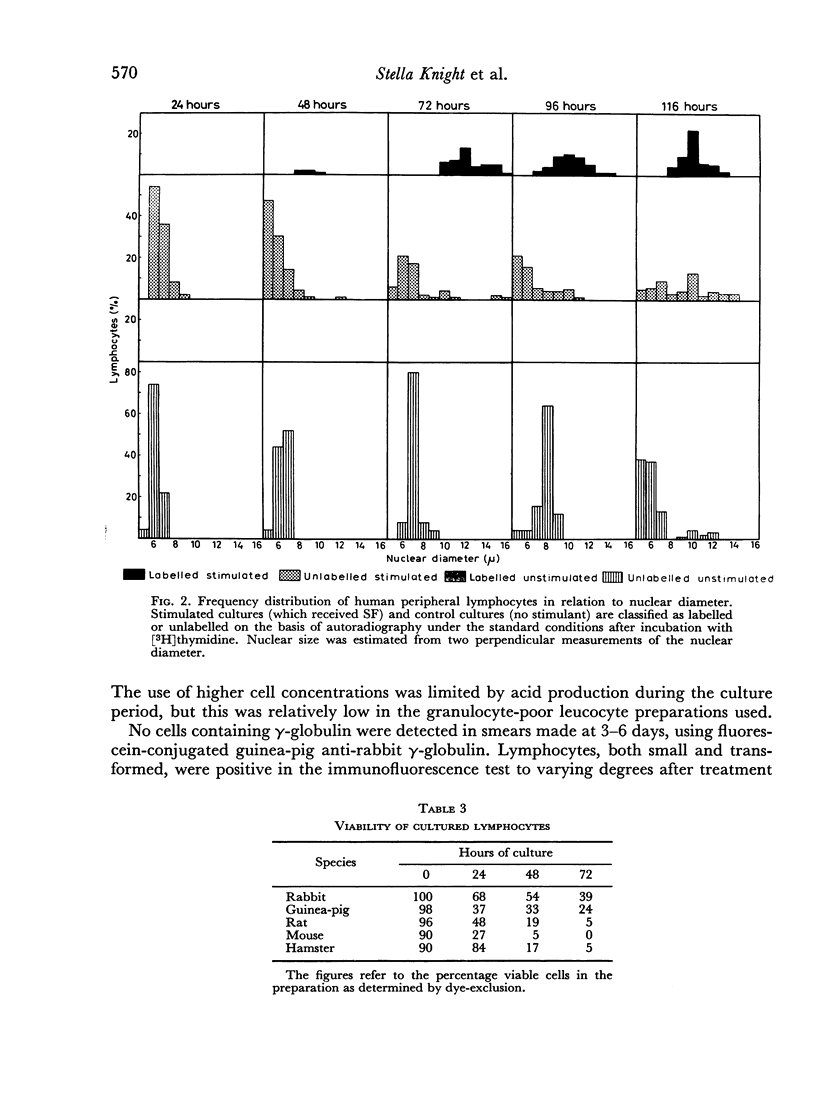
The peripheral lymphocytes of monkeys, rabbits, guinea-pigs, hamsters, rats and mice were transformed in culture by phytohaemagglutinin and staphylococcal filtrate. The response was most marked with the peripheral lymphocytes of monkeys and rabbits and least marked with rat and mouse lymphocytes. The response occurred earlier with rabbit and guinea-pig than human lymphocytes.
The short life span in vitro of rat and mouse lymphocytes adversely affected their response. The tritiated thymidine uptake of the stimulated lymphocytes of the various species was also limited by their rate of survival over the culture period.
Attempts to obtain antigen-specific stimulation of peripheral rabbit and guinea-pig lymphocytes were unsuccessful.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASPEGREN N., RORSMAN H. SHORT-TERM CULTURE OF LYMPHOCYTES FROM GUINEA-PIGS ALLERGIC TO TUBERCULIN. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1964;24:119–123. doi: 10.1159/000229450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON P. F., VULLIAMY D. G., TAUBMAN J. O. Congenital hemihypertrophy and malignancy. Lancet. 1963 Mar 2;1(7279):468–469. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK L., BERENBAUM M. C. FACTORS AFFECTING THE DYE EXCLUSION TEST FOR CELL VIABILITY. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jun;35:9–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN N. D., PARKHOUSE R. M., DUTTON R. W. ANTIGEN STIMULATED PROLIFERATION IN LYMPHOID AND MYELOID TISSUES FROM IMMUNIZED RABBITS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:708–711. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWLING D. C., QUAGLINO D., DAVIDSON E. CHANGES INDUCED BY TUBERCULIN IN LEUCOCYTE CULTURES. Lancet. 1963 Nov 23;2(7317):1091–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92860-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTON R. W., EADY J. D. AN IN VITRO SYSTEM FOR THE STUDY OF THE MECHANISM OF ANTIGENIC STIMULATION IN THE SECONDARY RESPONSE. Immunology. 1964 Jan;7:40–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUDE W. D., UPTON A. C., ODELL T. T., Jr Giemsa staining of autoradiograms prepared with stripping film. Stain Technol. 1955 Jul;30(4):161–162. doi: 10.3109/10520295509114458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., HUSBAND E. M. SPECIFIC AND NON-SPECIFIC STIMULATION OF PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES. Lancet. 1964 Feb 15;1(7329):363–365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., SPICER E., JAMES K., WILLIAMSON N. THE ACTIVATION OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES BY PRODUCTS OF STAPHYLOCOCCI. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jul;11:421–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYCETTE R. R., PEARMAIN G. E. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON ANTIGEN-INDUCED MITOSIS. Lancet. 1963 Aug 24;2(7304):386–386. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)93063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYNIHAN P. C., JACKSON J. F., HARDY J. D. LYMPHOCYTE TRANSFORMATION AS AN IN-VITRO HISTOCOMPATIBILITY TEST. Lancet. 1965 Feb 27;1(7383):453–455. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OXNARD C. E. SOME VARIATIONS IN THE AMOUNT OF VITAMIN B12 IN THE SERUM OF THE RHEUSUS MONKEY. Nature. 1964 Mar 21;201:1188–1191. doi: 10.1038/2011188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARMAIN G., LYCETTE R. R., FITZGERALD P. H. Tuberculin-induced mitosis in peripheral blood leucocytes. Lancet. 1963 Mar 23;1(7282):637–638. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. H. TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES OF THE HUMAN LYMPHOCYTE. Science. 1964 Dec 25;146(3652):1648–1654. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3652.1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERS P. C., HUMASON G. L. CULTURE AND SLIDE PREPARATION OF LEUKOCYTES FROM BLOOD OF MACACA. Stain Technol. 1964 Jul;39:209–213. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHREK R. In vitro longevity and radiosensitivity of lymphocytes of man and other species. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Feb;31(2):112–116. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/31.2.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHREK R., RABINOWITZ Y. Effects of phytohemagglutinin on rat and normal and leukemic human blood cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 May;113:191–194. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEE J. C. Myelosclerosis: an autoimmune disease. Lancet. 1963 Apr 6;1(7284):773–773. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91599-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]