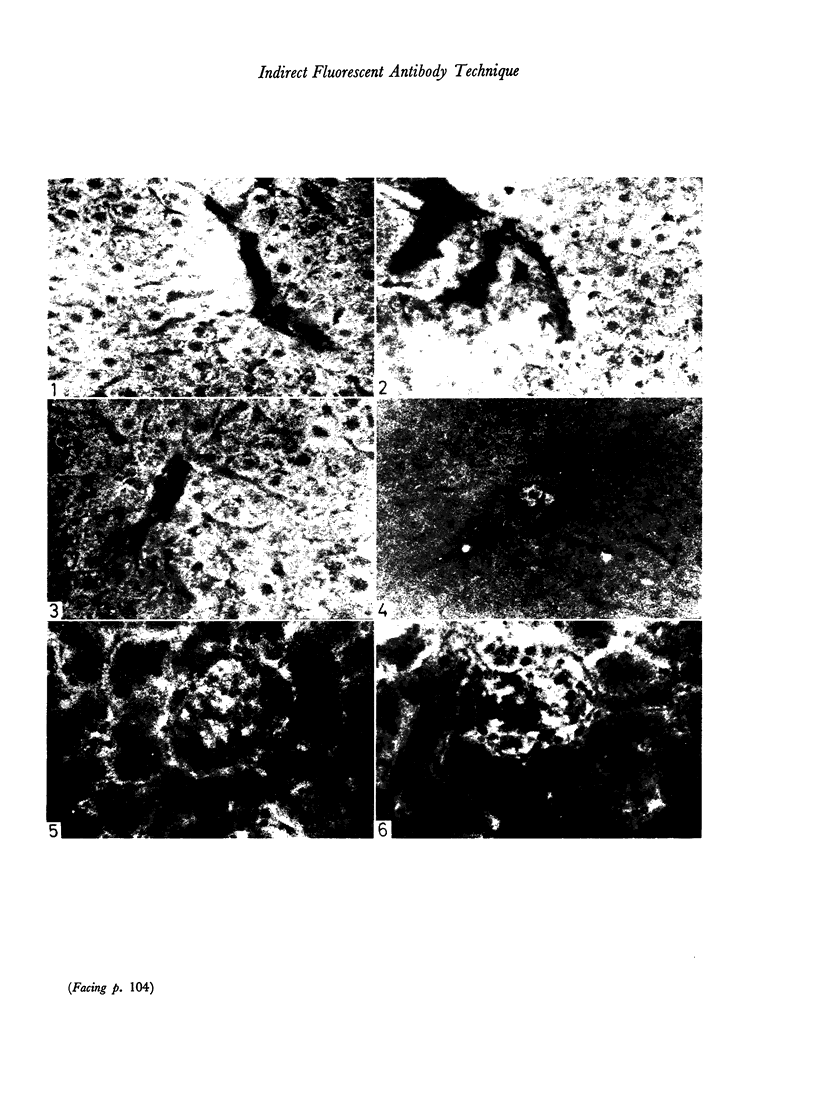
Abstract
Two antisera were compared with their γ-globulin fractions for their effectiveness as the middle or unlabelled layer in the indirect fluorescent antibody technique. The γ-globulin fraction did not produce better results in either case than the equivalent concentration of whole serum. Control sections were prepared with normal rabbit serum substituted for the whole antiserum and with normal rabbit γ-globulin substituted for the γ-globulin fraction of the antiserum. The control sections with γ-globulin showed considerably more non-specific fluorescence than those with whole serum. In one case the non-specific fluorescence in the γ-globulin control interfered with interpretation of the experimental section.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. W., METZGER J. F., HOGGAN M. D. Immunofluorescence as applied to pathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;38:26–42. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/38.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAN E. M., KAPLAN M. H. IMMUNOLOGICAL RELATION OF BASEMENT MEMBRANE AND A SERUM BETA GLOBULIN IN THE MOUSE. DEMONSTRATION OF RENAL BASEMENT MEMBRANE ALTERATION IN MICE INJECTED WITH STREPTOLYSIN S. Immunology. 1963 Jul;6:331–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody studies with agents of varicella and herpes zoster propagated in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Aug-Sep;86(4):789–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]