Abstract
Mixed haemadsorption should be regarded as an application of the mixed antiglobulin reaction to situations where the antigen is sessile on a glass surface. Antibody attached to the antigen when exposing the latter to an antiserum is traced by red cells carrying an antiglobulin layer which makes them adsorb to the antibody.
The indicator cells are prepared by coating them first with a layer of γ-globulin from the animal species, the antibody globulin of which they are intended to trace, and then with a layer of the corresponding antiglobulin. The most effective indicator cells were obtained by attaching antibody to natural receptors on the red cells to achieve their first coating of γ-globulin.
The preparation of indicator cells for tracing antibodies from a number of species, including human, is described.
The mixed haemadsorption technique is highly specific and has a sensitivity which is comparable to that of the most sensitive serological techniques.
Test procedures adapted for different purposes are outlined and a number of applications to experimental and clinical problems are reviewed.
Full text
PDF
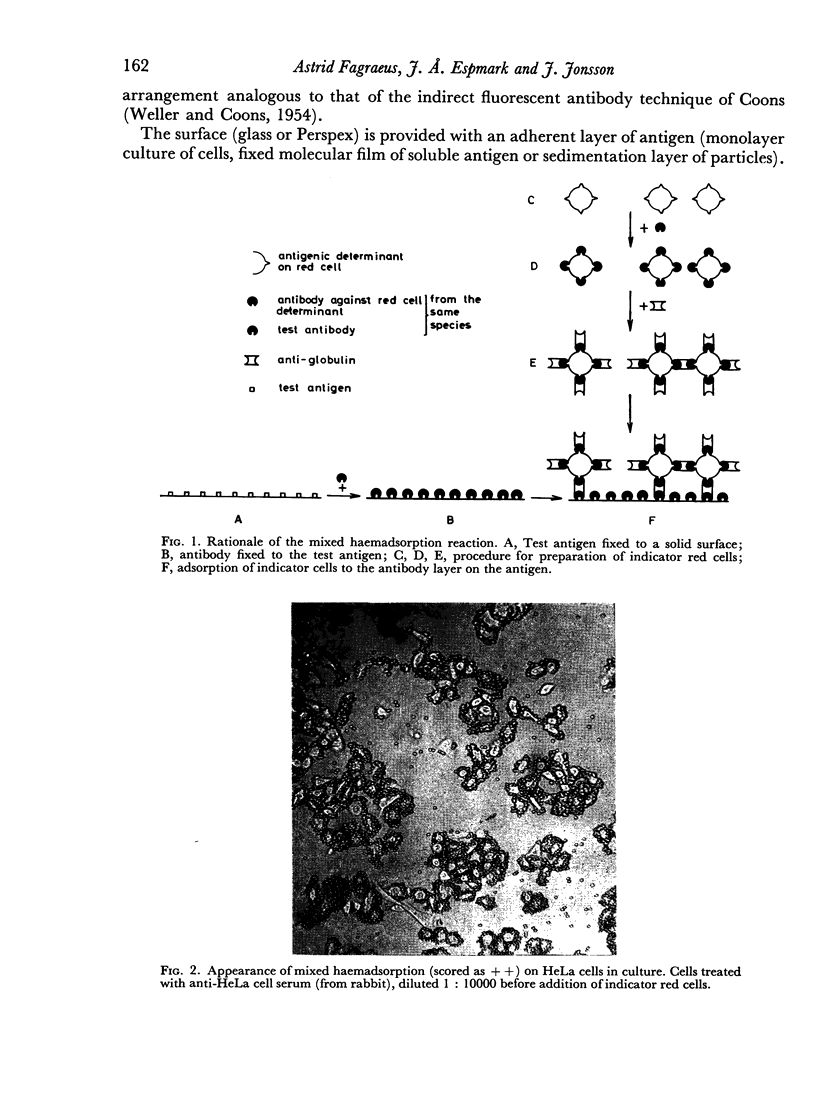





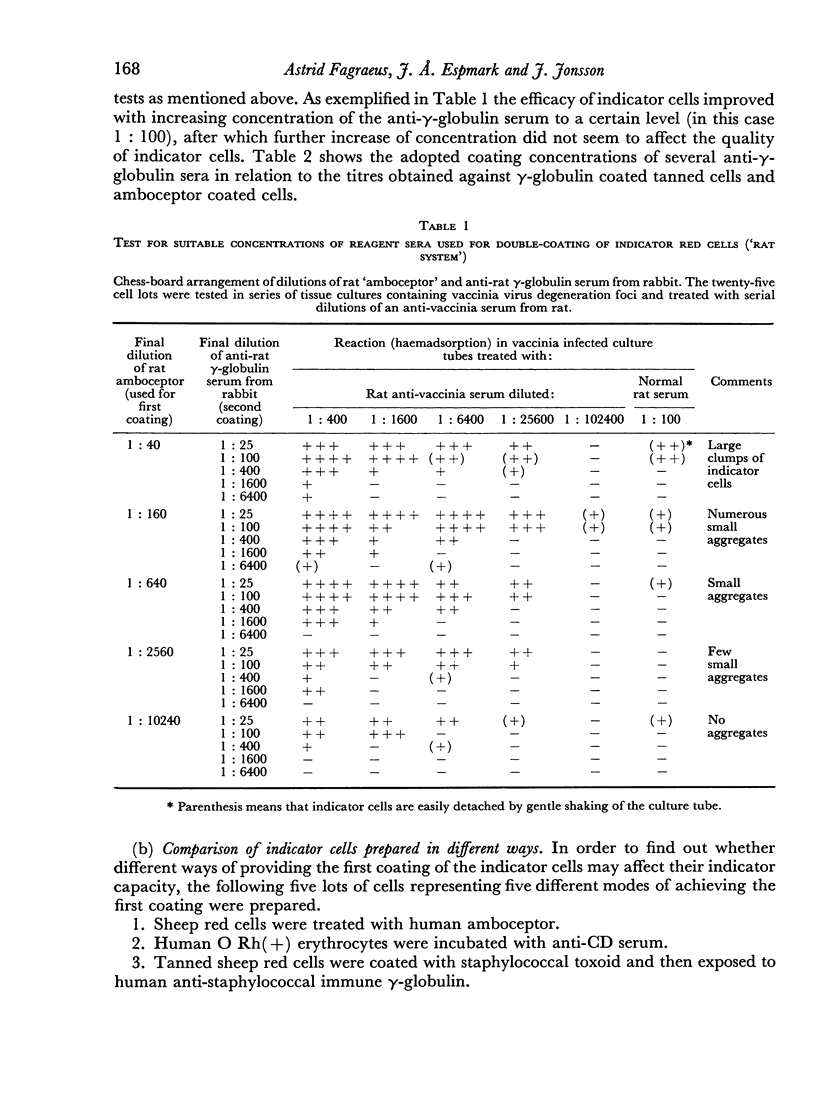
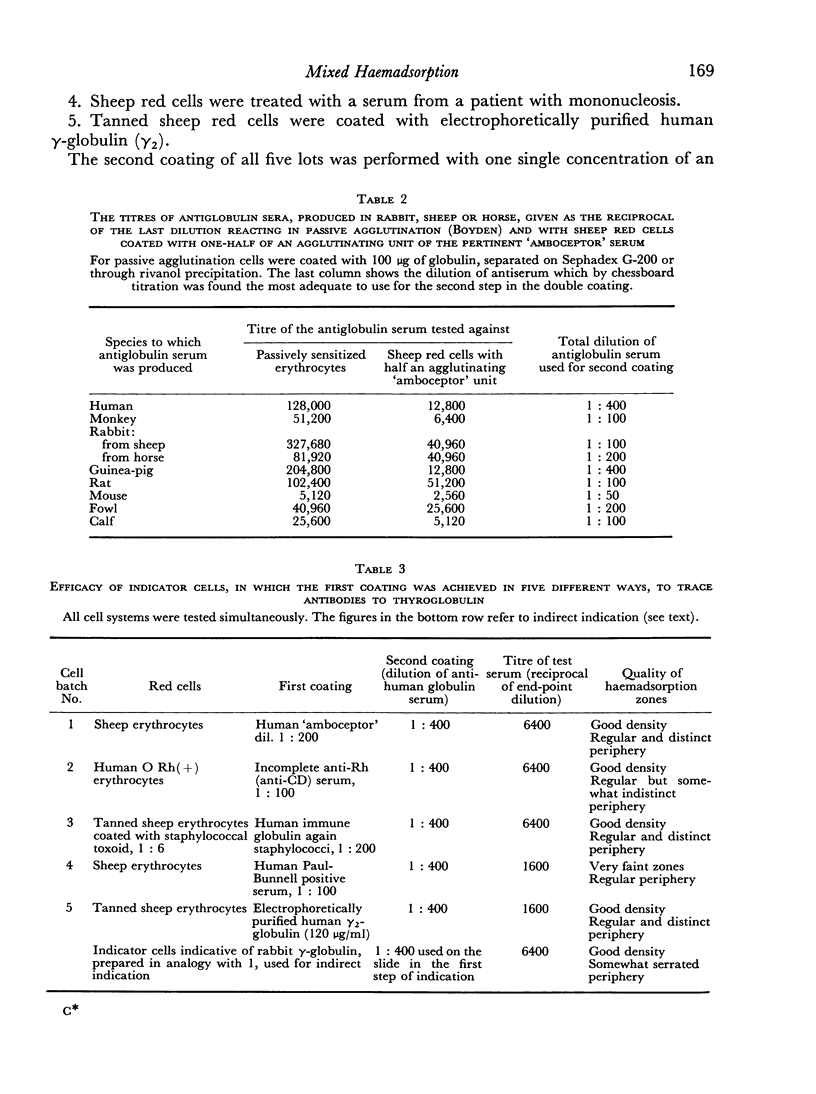






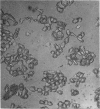
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHO K., HARBOE M., LEIKOLA J. STUDIES OF THE ANTIBODY NATURE OF THE RHEUMATOID FACTOR. REACTION OF THE RHEUMATOID FACTOR WITH SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES SENSITIZED WITH HUMAN ANTI-SHEEP CELL ANTIBODIES AND WITH O RH POSITIVE CELLS SENSITIZED WITH INCOMPLETE ANTI-RH ANTIBODIES. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:403–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRON A. L., MILGROM F., KARZON D. T., WITEBSKY E. DEMONSTRATION OF HUMAN MEASLES ANTIBODY BY MIXED AGGLUTINATION. J Immunol. 1963 Jun;90:908–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BJORKLUND B., HELLSTROM L. Studies on the effect of anti-bone-marrow-serum. Acta Med Scand. 1951;139(2):122–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHALMERS D. G., COOMBS R. R., GURNER B. W., DAUSSET J. The mixed antiglobulin reaction in the detection of human isoantibodies against leucocytes, platelets and HeLa cells. Br J Haematol. 1959 Jul;5:225–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1959.tb04030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS R. R. A., STOKER M. G. P. Detection of Q fever antibodies by the anti-globulin sensitization test. Lancet. 1951 Jul 7;2(6671):15–17. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)93452-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS R. R., BEDFORD D., ROUILLARD L. M. A and B blood-group antigens on human epidermal cells demonstrated by mized agglutination. Lancet. 1956 Apr 21;270(6921):461–463. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS R. R., DANIEL M. R., GURNER B. W., KELUS A. Recognition of the species of origin of cells in culture by mixed agglutination. I. Use of antisera to red cells. Immunology. 1961 Jan;4:55–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS R. R., MARKS J., BEDFORD D. Specific mixed agglutination: mixed erythrocyte-platelet anti-globulin reaction for the detection of platelet antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1956 Jan;2(1):84–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1956.tb06689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESPMARK A., FAGRAEUS A. Detection of antigens in tissue culture with the aid of mixed hemadsorption. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1962;Suppl 154:258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAGRAEUS A., ESPMARK A. Use of a 'mixed haemadsorption' method in virus-infected tissue cultures. Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:370–371. doi: 10.1038/190370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGMAN C. The principle of mixed agglutination applied to tissue culture systems; a method for study of cell-bound blood-group antigens. Vox Sang. 1959 Feb;4(1):12–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1959.tb04307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANO K., MILGROM F. REACTIONS OF SERUM SICKNESS AND INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS SERA IN TISSUE CULTURES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:172–173. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS J. L., SEIWALD R. J., BURCKHALTER J. H., DOWNS C. M., METCALF T. G. Isothiocyanate compounds as fluorescent labeling agents for immune serum. Am J Pathol. 1958 Nov-Dec;34(6):1081–1097. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEFFEN C. Untersuchungen über die Verwendung der Antihumanglobulin-Ablenkungsmethode zum Nachweis von Thrombozytenantikörpern. Wien Z Inn Med. 1955 Jun;36(6):246–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOENDER O., MILGROM F., WITEBSKY E. MIXED AGGLUTINATION WITH TISSUE SECTIONS. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:265–274. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody studies with agents of varicella and herpes zoster propagated in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Aug-Sep;86(4):789–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]