Abstract
The formation of immunoglobulins by circulating lymphocytes was studied by three techniques: (1) Autoradiographic analysis of the immunoglobulins synthesized during the incubation of cell suspensions in a medium with radioactive amino acids; (2) direct immunofluorescent staining; and (3) examination of the cellular morphology.
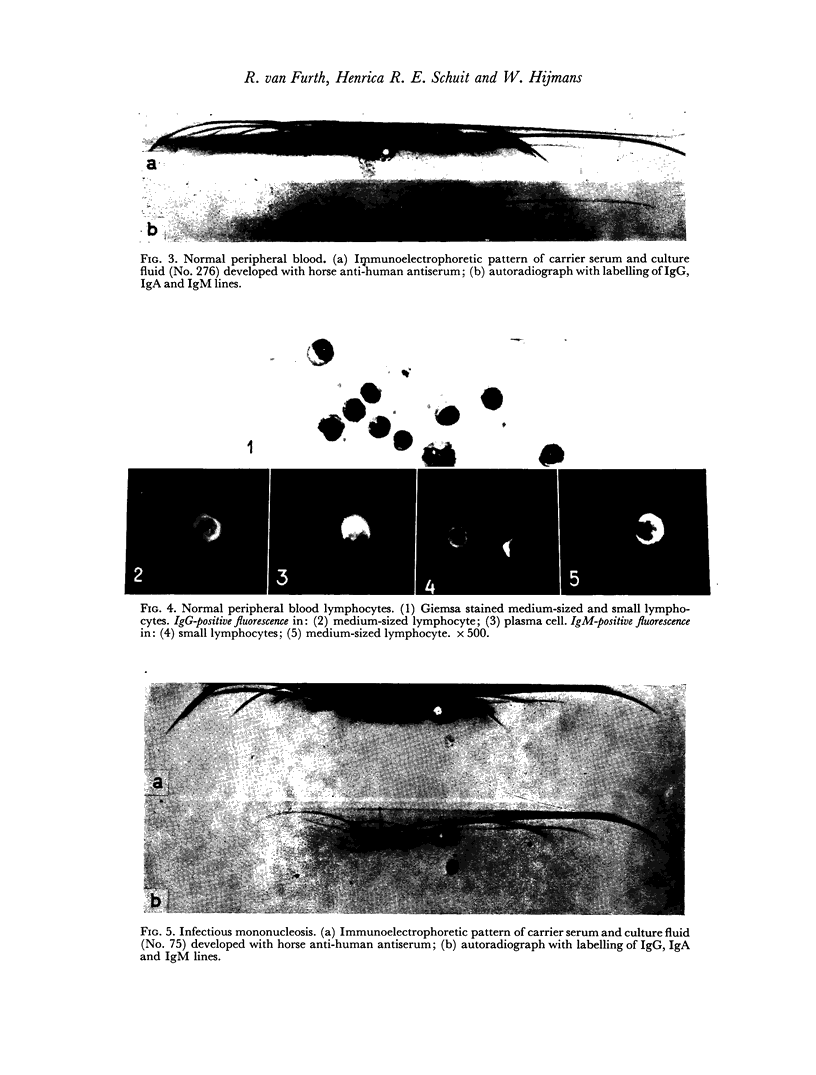
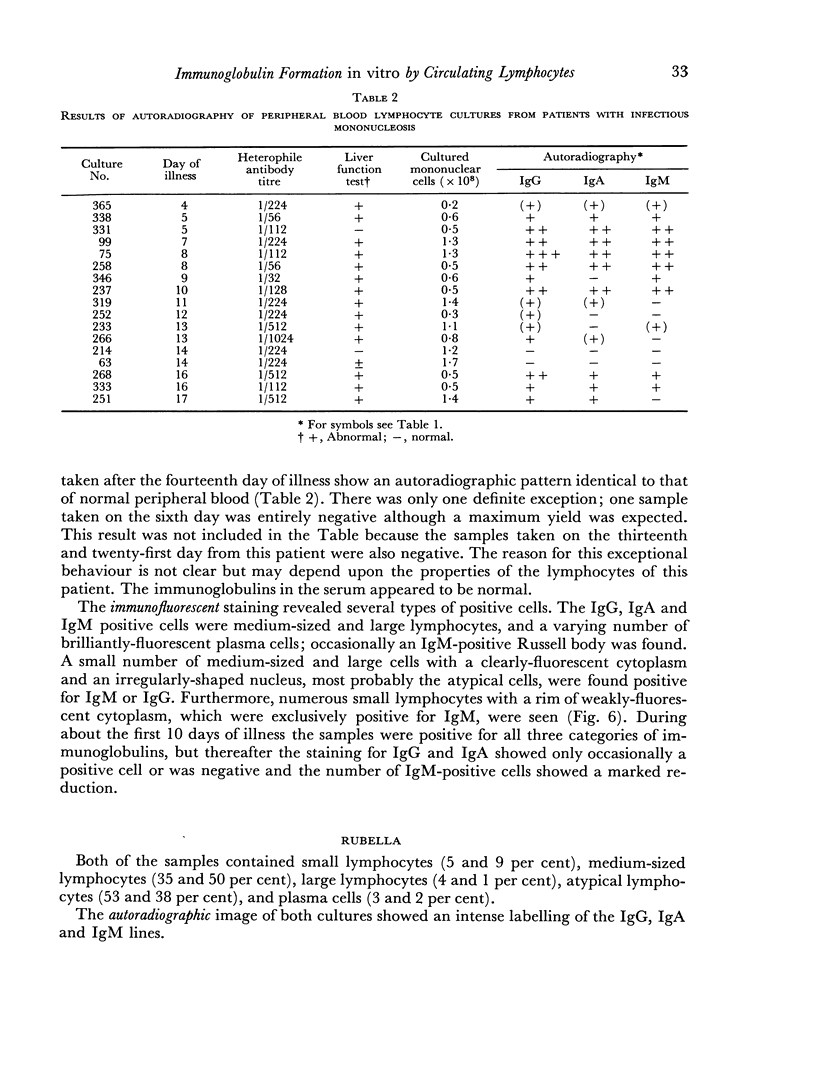
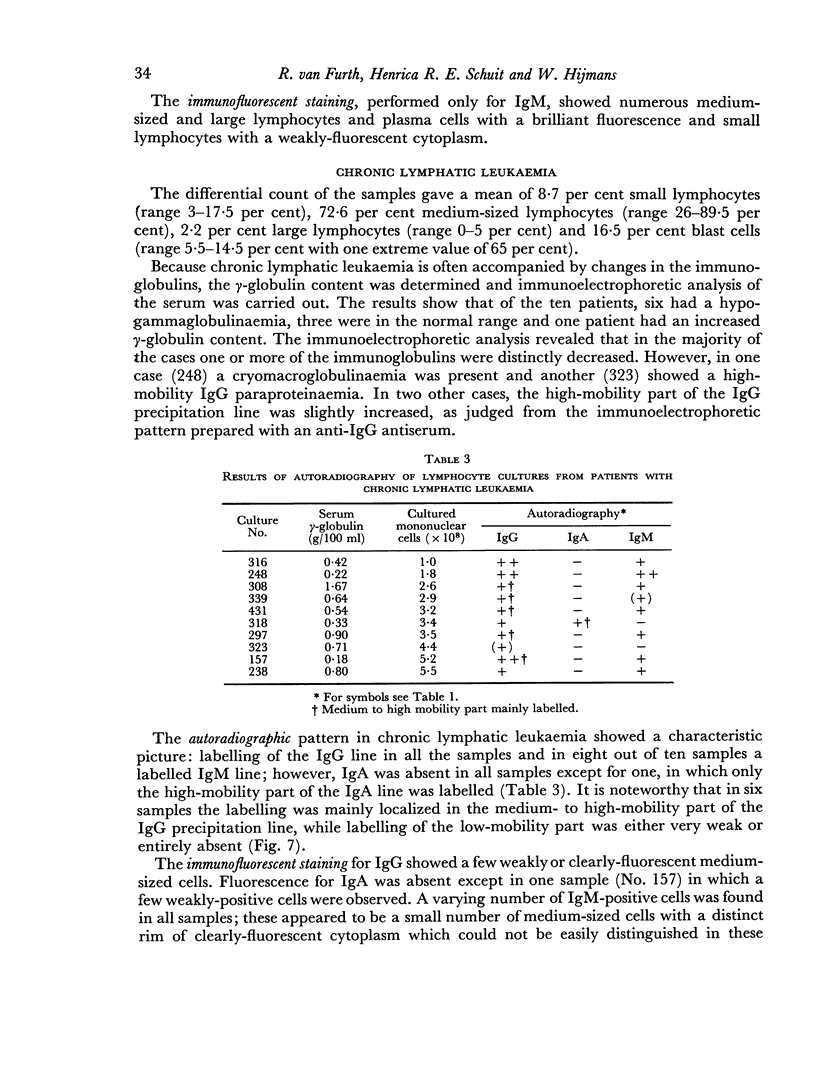
Lymphocytes of the normal peripheral blood were found to synthesize a distinct amount of IgG and smaller amounts of IgA and IgM. Cells of the thoracic-duct lymph synthesized distinct amounts of all three immunoglobulins. A similar pattern was found in infectious mononucleosis and rubella. In infectious mononucleosis the significantly increased synthesis of IgM during the first 10 days of illness led to the supposition that this result may be due to primary antigenic stimulation. The pattern in chronic lymphatic leukaemia is characterized by the consistent absence of IgA and the labelling of IgG, mainly the medium to high mobility part, and of IgM. In agammaglobulinaemia a trace of IgG and IgA was found in one case; the other was entirely negative.
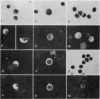
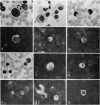
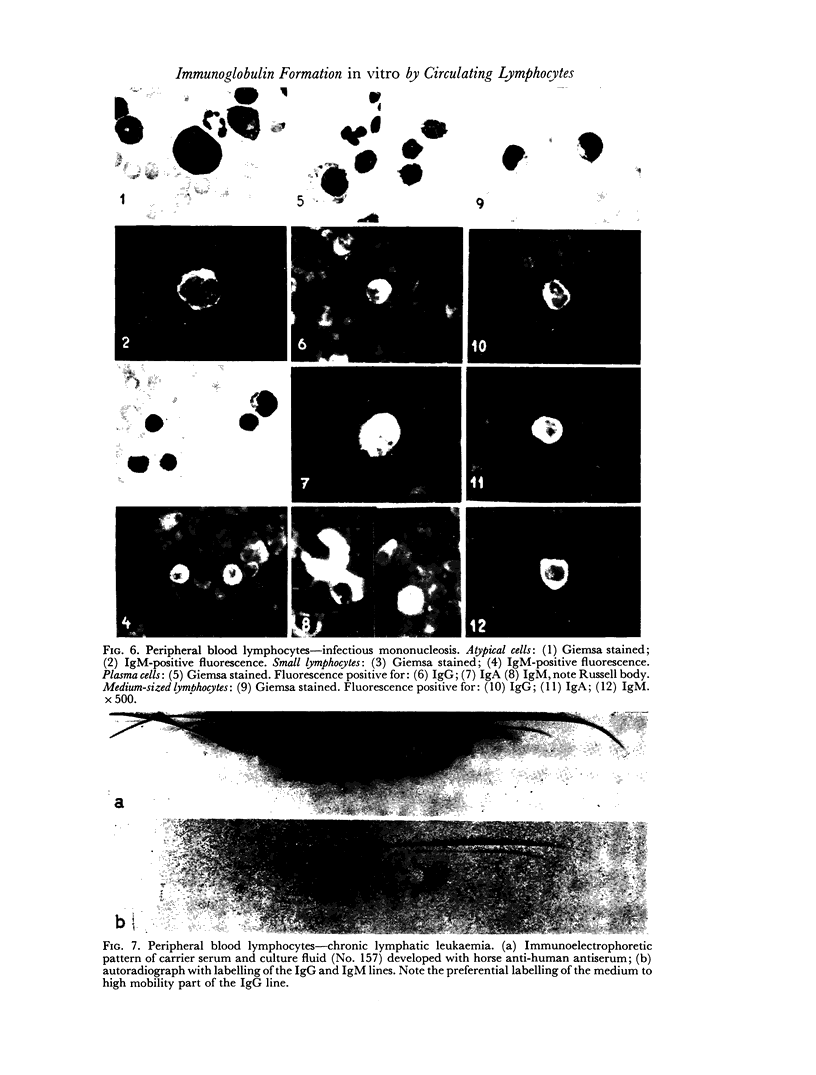
The immunofluorescent staining showed that in all samples some of the medium-sized lymphocytes contain IgG, IgA or IgM. Peripheral blood samples taken during an infectious mononucleosis or rubella infection and thoracic duct lymph revealed also positive large lymphocytes and plasma cells.
A remarkable observation was the weak fluorescence of small lymphocytes which were exclusively positive for IgM. It is postulated that these small lymphocytes indicate their initial synthesis of IgM antibodies when engaged in primary response.
Full text
PDF


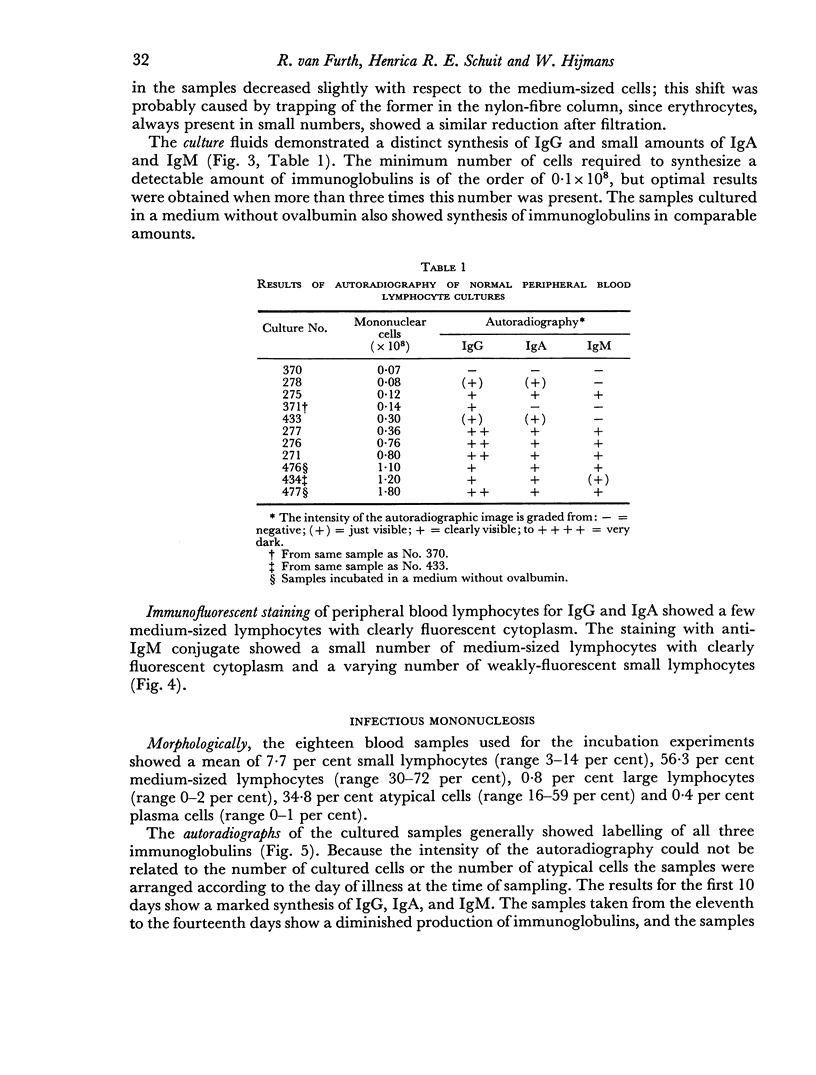
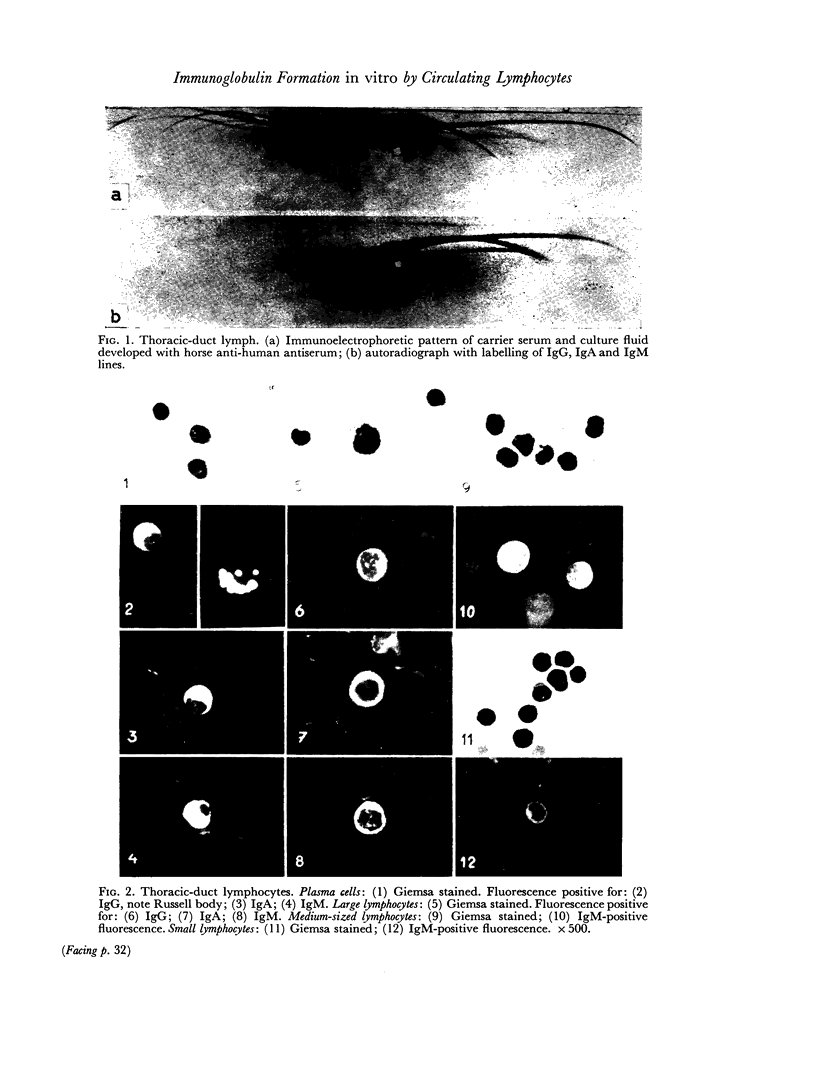






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN S. B. METABOLISM OF GAMMA-SS GLOBULIN IN SECONDARY HYPOGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA. Am J Med. 1963 Nov;35:708–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATTARDI G., COHN M., HORIBATA K., LENNOX E. S. ANTIBODY FORMATION BY RABBIT LYMPH NODE CELLS. II. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE BEHAVIOR OF SINGLE ANTIBODY-PRODUCING CELLS WITH RESPECT TO THEIR SYNTHETIC CAPACITY AND MORPHOLOGY. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:346–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACH F., HIRSCHHORN K. GAMMA-GLOBULIN PRODUCTION BY HUMAN LYMPHOCYTES IN VITRO. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Dec;32:592–595. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIN B., VAS M. R., LOWENSTEIN L. THE DEVELOPMENT OF LARGE IMMATURE MONONUCLEAR CELLS IN MIXED LEUKOCYTE CULTURES. Blood. 1964 Jan;23:108–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALFOUR B. M., COOPER E. H., ALPEN E. L. MORPHOLOGICAL AND KINETIC STUDIES ON ANTIBODY-PRODUCING CELLS IN RAT LYMPH NODES. Immunology. 1965 Mar;8:230–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARR M., FAIRLEY G. H. Circulating antibodies in reticuloses. Lancet. 1961 Jun 17;1(7190):1305–1310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTFELD H., JULIAR J. F. "IMMUNOLOGICAL ORGANISATION" AND ACTIVITY OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL WHITE-BLOOD-CELL CULTURES. Lancet. 1964 Oct 10;2(7363):767–769. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90555-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUER D. C., MATHIES M. J., STAVITSKY A. B. Sequences of synthesis of gamma-1 macroglobulin and gamma-2 globulin antibodies during primary and secondary responses to proteins, salmonella antigens, and phage. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:889–907. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer D. C., Stavitsky A. B. ON THE DIFFERENT MOLECULAR FORMS OF ANTIBODY SYNTHESIZED BY RABBITS DURING THE EARLY RESPONSE TO A SINGLE INJECTION OF PROTEIN AND CELLULAR ANTIGENS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct;47(10):1667–1680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONE L., UHR J. W. IMMUNOLOGICAL DEFICIENCY DISORDERS ASSOCIATED WITH CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA AND MULTIPLE MYELOMA. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2241–2248. doi: 10.1172/JCI105098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWLING D. C., QUAGLINO D., DAVIDSON E. CHANGES INDUCED BY TUBERCULIN IN LEUCOCYTE CULTURES. Lancet. 1963 Nov 23;2(7317):1091–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92860-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAIRLEY G. H., SCOTT R. B. Hypogammaglobulinaemia in chronic lymphatic leukaemia. Br Med J. 1961 Oct 7;2(5257):920–924. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5257.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN H. DISTRIBUTION OF ANTIBODY PLAQUE FORMING CELLS IN VARIOUS TISSUES OF SEVERAL STRAINS OF MICE INJECTED WITH SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:526–530. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASBECK R., NORDMAN C., DELACHAPELLE A. MITOGENIC ACTION OF ANTILEUCOCYTE IMMUNE SERUM ON PERIPHERAL LEUCOCYTES IN VITRO. Lancet. 1963 Aug 24;2(7304):385–386. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)93062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWALT T. J., GAJEWSKI M., McKENNA J. L. A new method for preparing buffy coat-poor blood. Transfusion. 1962 Jul-Aug;2:221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1962.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE A. J., COOPER E. H. DNA synthesis in infectious mononucleosis and acute leukaemia. Acta Haematol. 1963 May;29:257–266. doi: 10.1159/000207971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH R. B., FAIRLEY G. H., MALPAS J. S. PRODUCTION OF ANTIBODIES AGAINST VIRUSES IN LEUKAEMIA AND RELATED DISEASES. Br J Haematol. 1964 Jul;10:365–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., BACH F., KOLODNY R. L., FIRSCHEIN I. L., HASHEM N. IMMUNE RESPONSE AND MITOSIS OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD LYMPHOCYTES IN VITRO. Science. 1963 Nov 29;142(3596):1185–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3596.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND R. J. Diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. Blood. 1960 Jul;16:1045–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND R. J. The clinical manifestations of infectious mononucleosis: a report of two hundred cases. Am J Med Sci. 1960 Jul;240:55–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND R. J. The transmission of infectious mononucleosis. Am J Med Sci. 1955 Mar;229(3):262–272. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195503000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND P., MAUER A. M. DRUG-INDUCED IN-VITRO STIMULATION OF PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES. Lancet. 1964 Jun 20;1(7347):1368–1369. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLUB M. Potentialities of the small lymphocyte as revealed by homotransplantation and autotransplantation expriments in diffusion chambers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 24;99:477–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb45329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUDSON R. P., WILSON S. J. Hypogammaglobulinemia and chronic lymphatic leukemia. Cancer. 1960 Jan-Feb;13:200–204. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196001/02)13:1<200::aid-cncr2820130131>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLIGER L., SORKIN E. Synthesis of antibodies by blood leucocytes of the rabbit. Nature. 1963 Apr 20;198:299–299. doi: 10.1038/198299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JIM R. T. Serum gamma globulin levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Med Sci. 1957 Jul;234(1):44–47. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195707000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., HUSBAND E. M. SPECIFIC AND NON-SPECIFIC STIMULATION OF PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES. Lancet. 1964 Feb 15;1(7329):363–365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOSPALLUTO J., MILLER W., Jr, DORWARD B., FINK C. W. The formation of macroglobulin antibodies. I. Studies on adult humans. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jul;41:1415–1421. doi: 10.1172/JCI104596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKINNEY A. A., Jr, STOHLMAN F., Jr, BRECHER G. The kinetics of cell proliferation in cultures of human peripheral blood. Blood. 1962 Mar;19:349–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T., GOWANS J. L. THE MIGRATION OF LYMPHOCYTES THROUGH THE ENDOTHELIUM OF VENULES IN LYMPH NODES: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:283–290. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D. G., BUDINGER J. M., KARNOFSKY D. A. A clinical and pathological study of resistance to infection in chronic lymphatic leukemia. Cancer. 1962 Mar-Apr;15:307–329. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196203/04)15:2<307::aid-cncr2820150214>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOSSAL G. J., MAKELA O. Genetic aspects of antibody formation. Lab Invest. 1961 Nov-Dec;10:1094–1109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAEGLE R. D. Electron microscopic study of leukocytes in infectious mononucleosis. Blood. 1961 Jun;17:687–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARMAIN G., LYCETTE R. R., FITZGERALD P. H. Tuberculin-induced mitosis in peripheral blood leucocytes. Lancet. 1963 Mar 23;1(7282):637–638. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESSMAN D., YAGI Y., HIRAMOTO R. A comparison of fluorescein and I 131 as labels for determining the in vivo localization of anti-tissue antibodies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1958;12(3-4):125–136. doi: 10.1159/000228449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVEHAG S. E., MANDEL B. THE FORMATION AND PROPERTIES OF POLIOVIRUS-NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY. I. 19S AND 7S ANTIBODY FORMATION: DIFFERENCES IN KINETICS AND ANTIGEN DOSE REQUIREMENT FOR INDUCTION. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:1–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVEHAG S. E., MANDEL B. THE FORMATION AND PROPERTIES OF POLIOVIRUS-NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY. II. 19S AND 7S ANTIBODY FORMATION: DIFFERENCES IN ANTIGEN DOSE REQUIREMENT FOR SUSTAINED SYNTHESIS, ANAMNESIS, AND SENSITIVITY TO X-IRRADIATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:21–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UHR J. W., FINKELSTEIN M. S. Antibody formation. IV. Formation of rapidly and slowly sedimenting antibodies and immunological memory to bacteriophage phi-X 174. J Exp Med. 1963 Mar 1;117:457–477. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSLEN T. Studies on the rôle of lymphocytes in antibody production. Acta Derm Venereol. 1952;32(4):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The formation of immunoglobulins by human tissues in vitro. 3. Spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow and thymus. Immunology. 1966 Jul;11(1):19–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit R. E., Hijmans W. The formation of immunoglobulins by human tissues in vitro. I. The methods and their specificity. Immunology. 1966 Jul;11(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R. The formation of immunoglobulins by human tissues in vitro. II. Quantitative studies. Immunology. 1966 Jul;11(1):13–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]