Abstract
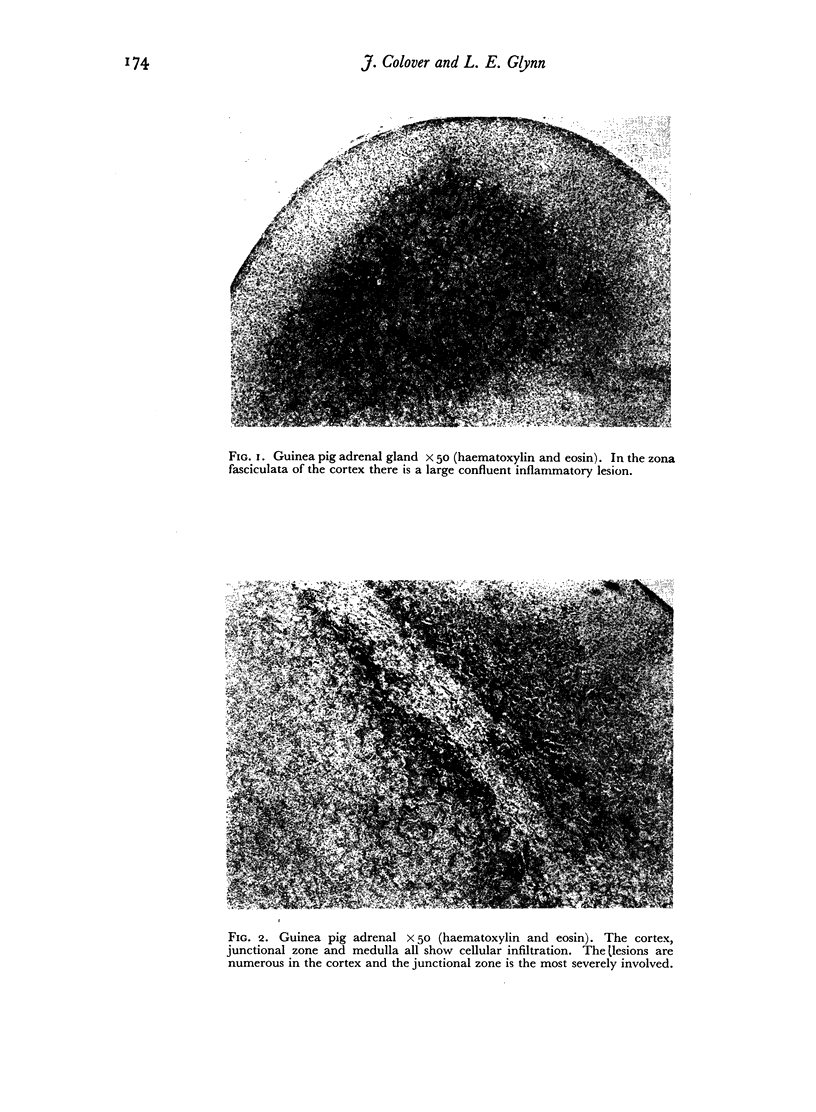
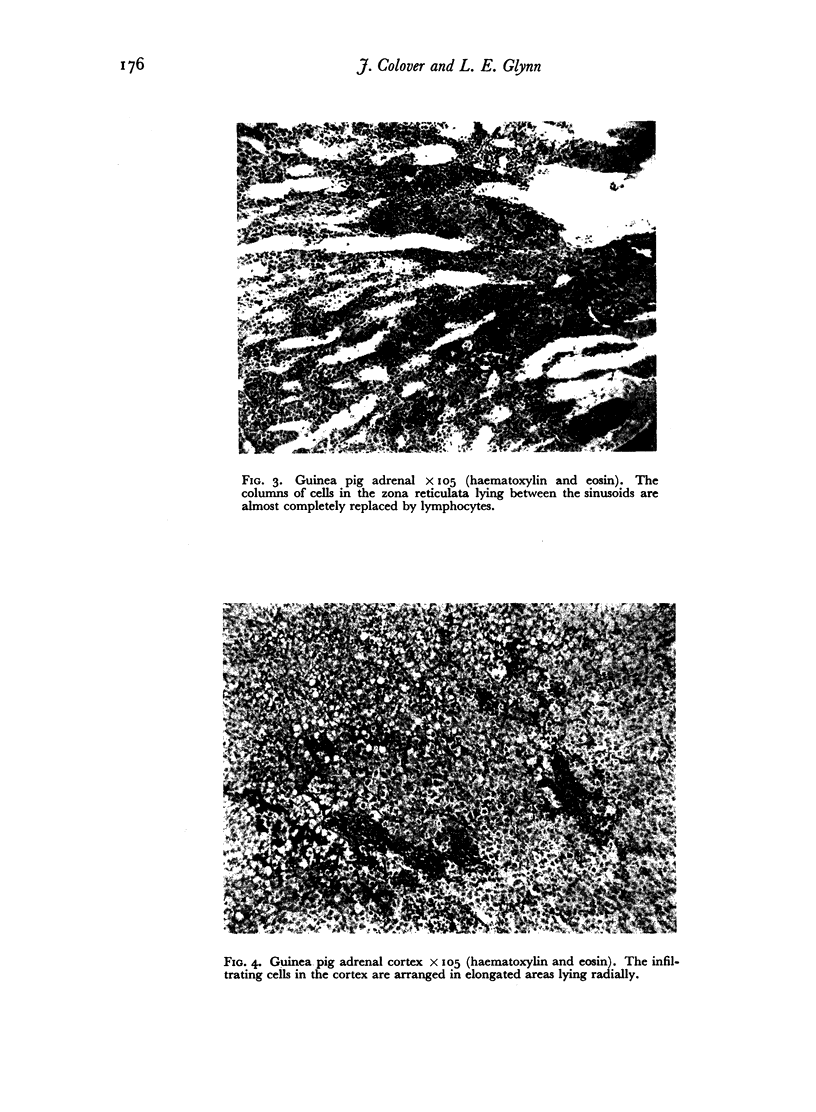
Lesions of the adrenal glands have been produced in guinea pigs by the intramuscular injection of homologous adrenal gland with a fraction made from heat-killed human tubercle bacilli incorporated in a water-in-oil emulsion.
Both the cortex and medulla were affected. Destruction and infiltration of the glandular tissues were observed histologically.
Control groups of animals, in some of which the same bacillary fraction and similar adrenal gland suspensions had been injected separately, failed to show the adrenal lesions.
This experimental adrenalitis has been compared and contrasted with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: it is believed both are caused by a similar process, immunological in nature.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLOVER J. Tubercle bacillus fractions in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Brain. 1954;77(3):435–447. doi: 10.1093/brain/77.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE N. R., WITEBSKY E. Studies on organ specificity. V. Changes in the thyroid glands of rabbits following active immunization with rabbit thyroid extracts. J Immunol. 1956 Jun;76(6):417–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]