Abstract
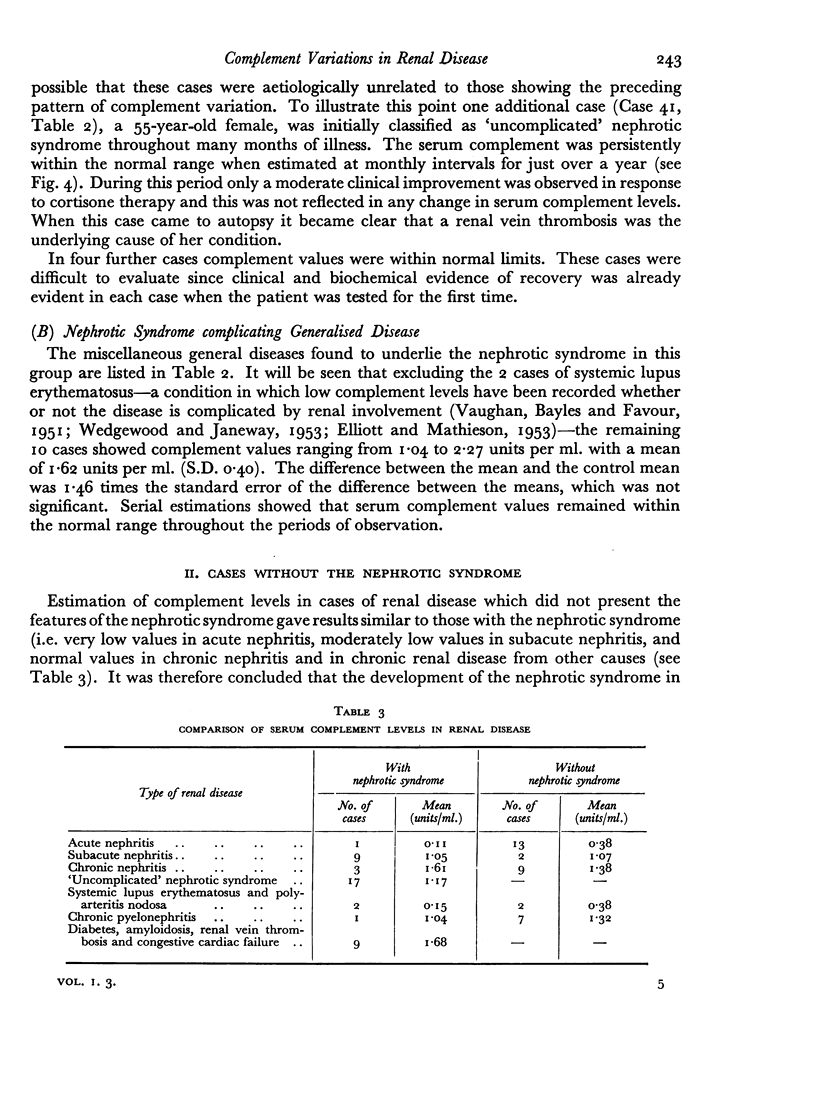
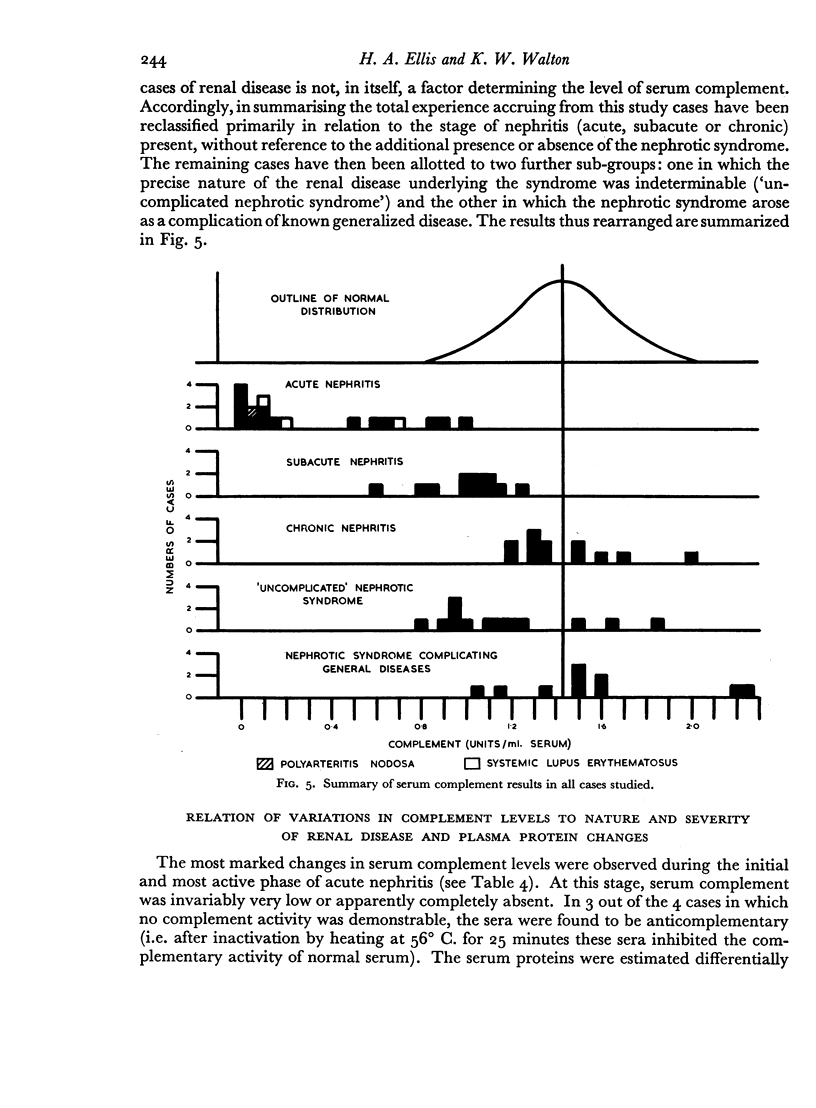
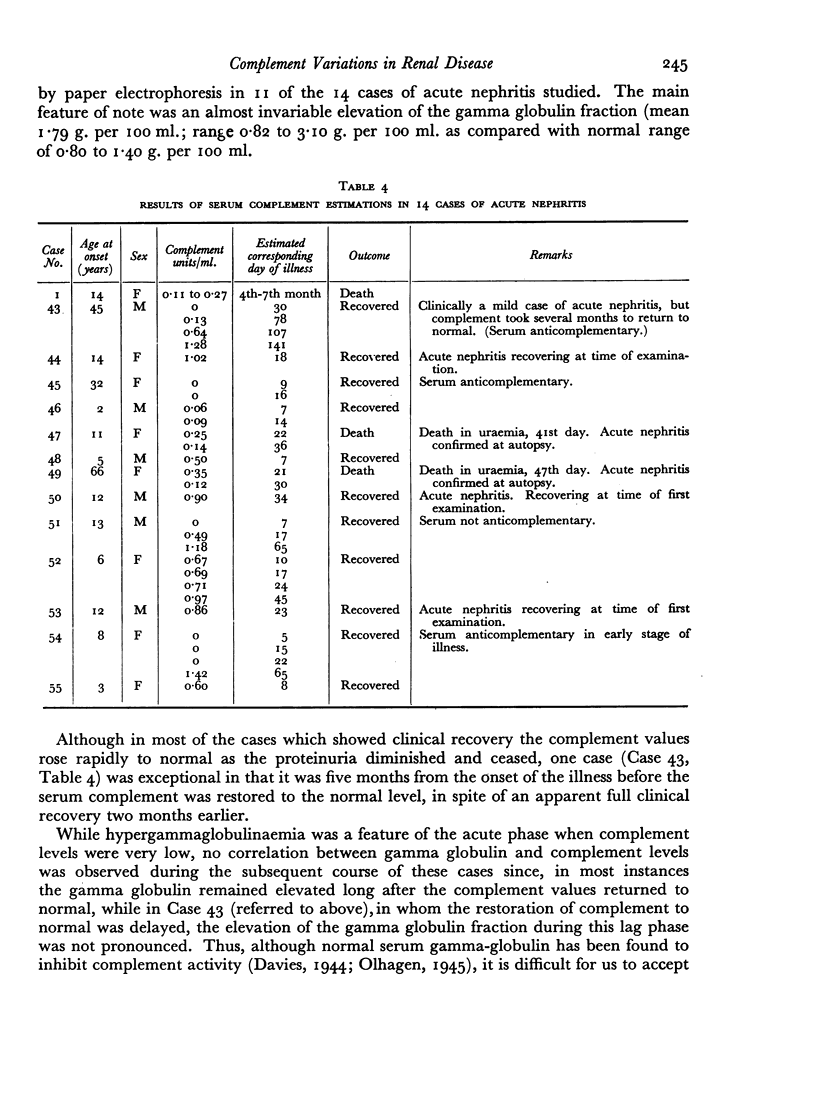
Serial complement determinations have been carried out in 75 patients suffering from various forms of renal disease. Very low serum complement levels were found during the early active stage of acute nephritis, but these low values returned to normal in most cases in parallel with clinical recovery. Moderately depressed complement levels were found in subacute nephritis. These values returned to normal whether clinical recovery occurred or whether the patient progressed to chronic nephritis with or without terminal renal failure. Cases of chronic nephritis, chronic pyelonephritis or of chronic renal damage from other causes gave normal complement values.
Serum complement values were similar when cases with and without the nephrotic syndrome were matched, as far as possible, according to the underlying disease process. Cases of the nephrotic syndrome of undetermined aetiology were divisible into a group with subnormal values and a group with persistently normal values. It is suggested on the basis of the foregoing observations that these two groups may be aetiologically distinct.
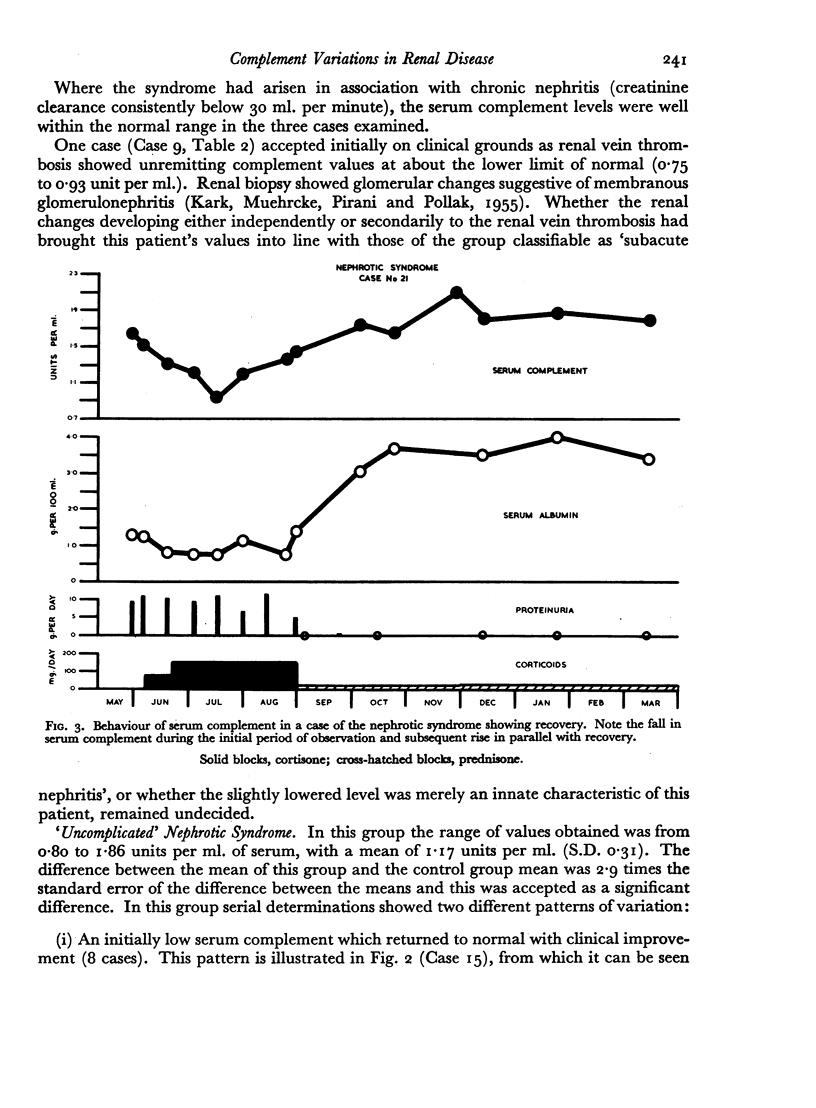
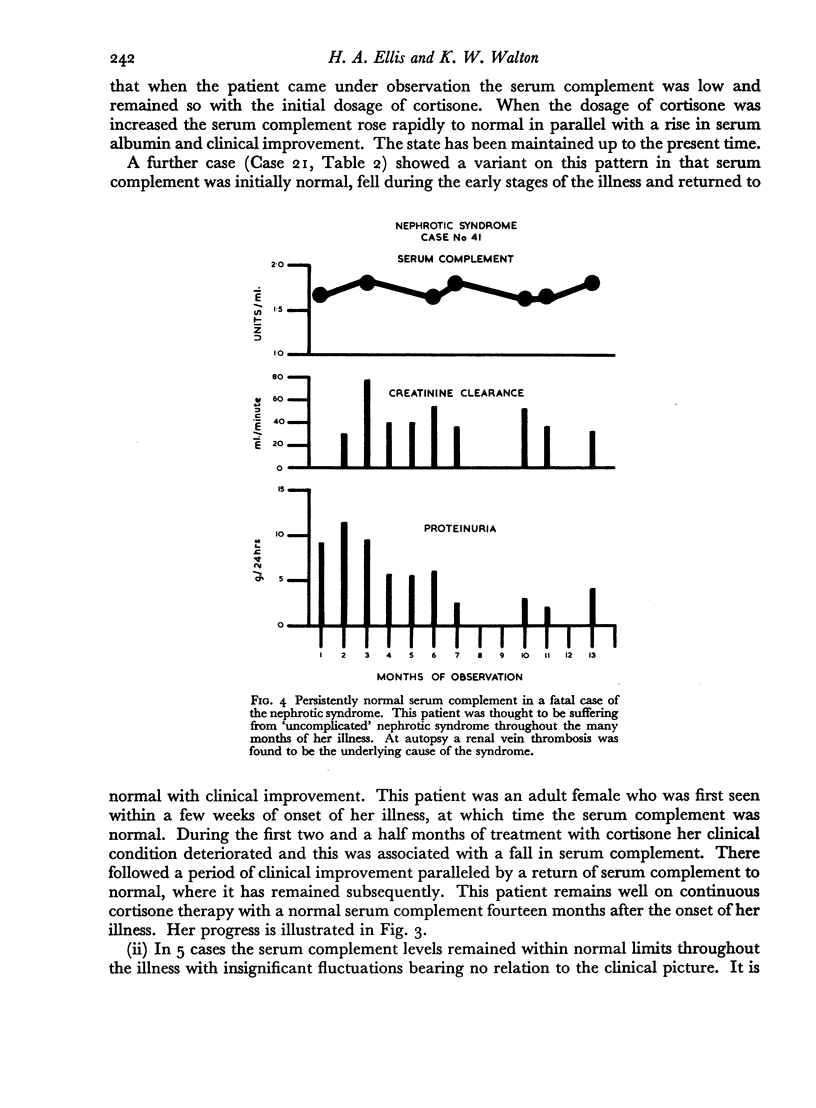
The values of serial complement determinations as aids to diagnosis, the control of therapy (especially corticosteroid therapy) and prognosis in renal disease is appraised.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAINEY J. D. High protein diets in the treatment of the nephrotic syndrome. Clin Sci. 1954 Nov;13(4):567–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARK R. M., MUEHRCKE R. C., PIRANI C. L., POLLAK V. E. The clinical value of renal biopsy. Ann Intern Med. 1955 Oct;43(4):807–847. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-43-4-807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGE K., GRAIG F., OBERMAN J., SLOBODY L., OGUR G., LoCASTO F. Changes in serum complement during the course and treatment of glomerulonephritis. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1951 Oct;88(4):433–445. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1951.03810100017002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGE K., STRANG R., SLOBODY L. B., WENK E. J. The treatment of the nephrotic syndrome with steroids in children and adults. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1957 May;99(5):760–770. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1957.00260050088011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGE K., WENK E. J. Complement components in the sera and urines of patients with severe proteinurias. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Oct;228(4):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGE K., WENK E. J. Investigations into the site of complement loss in experimental glomerulonephritis. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Oct;228(4):454–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUEHRCKE R. C., KARK R. M., PIRANI C. L. Technique of percutaneous renal biopsy in the prone position. J Urol. 1955 Sep;74(3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)67279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN J. A., IGGO B., SCANDRETT F. J., STEWART C. P. The determination of creatinine in plasma or serum, and in urine; a critical examination. Biochem J. 1954 Nov;58(3):426–437. doi: 10.1042/bj0580426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESSMAN D. The zone of localization of antibodies; the in vivo disposition of anti-mouse-kidney serum and anti-mouse-plasma serum as determined by radioactive tracers. J Immunol. 1949 Dec;63(4):375–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROYER P., LESTRADET H., SEYNAEVE A. Le taux du complément du sérum dans les néphropathies de l'enfant. Sem Hop. 1956 Jan 22;32(5/1):259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SQUIRE J. R., BLAINEY J. D., HARDWICKE J. The nephrotic syndrome. Br Med Bull. 1957 Jan;13(1):43–52. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SQUIRE J. R. The nephrotic syndrome. Br Med J. 1953 Dec 26;2(4851):1389–1399. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4851.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN J. H., BAYLES T. B., FAVOUR C. B. The response of serum gamma globulin level and complement titer to adrenocorticotropic hormone therapy in lupus erythematosus disseminatus. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 May;37(5):698–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEDGWOOD R. J. P., JANEWAY C. A. Serum complement in children with collagen diseases. Pediatrics. 1953 Jun;11(6):569–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


