Abstract
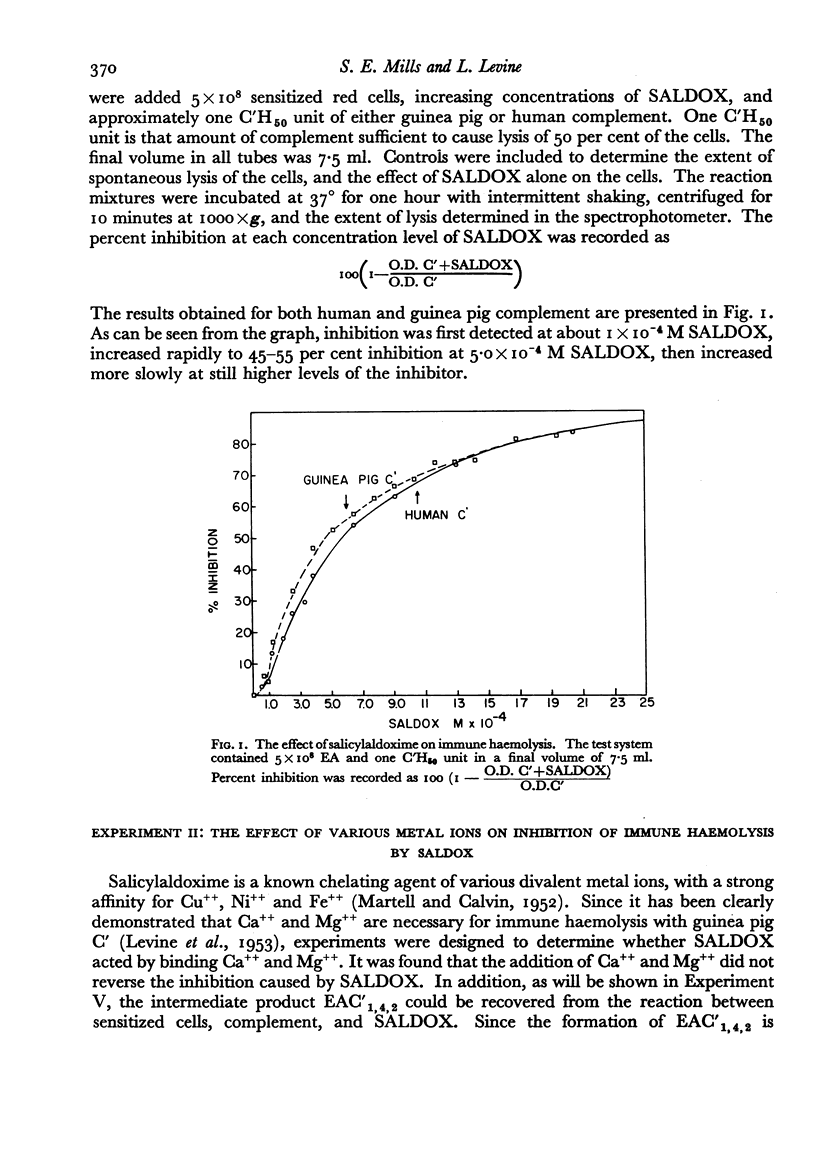
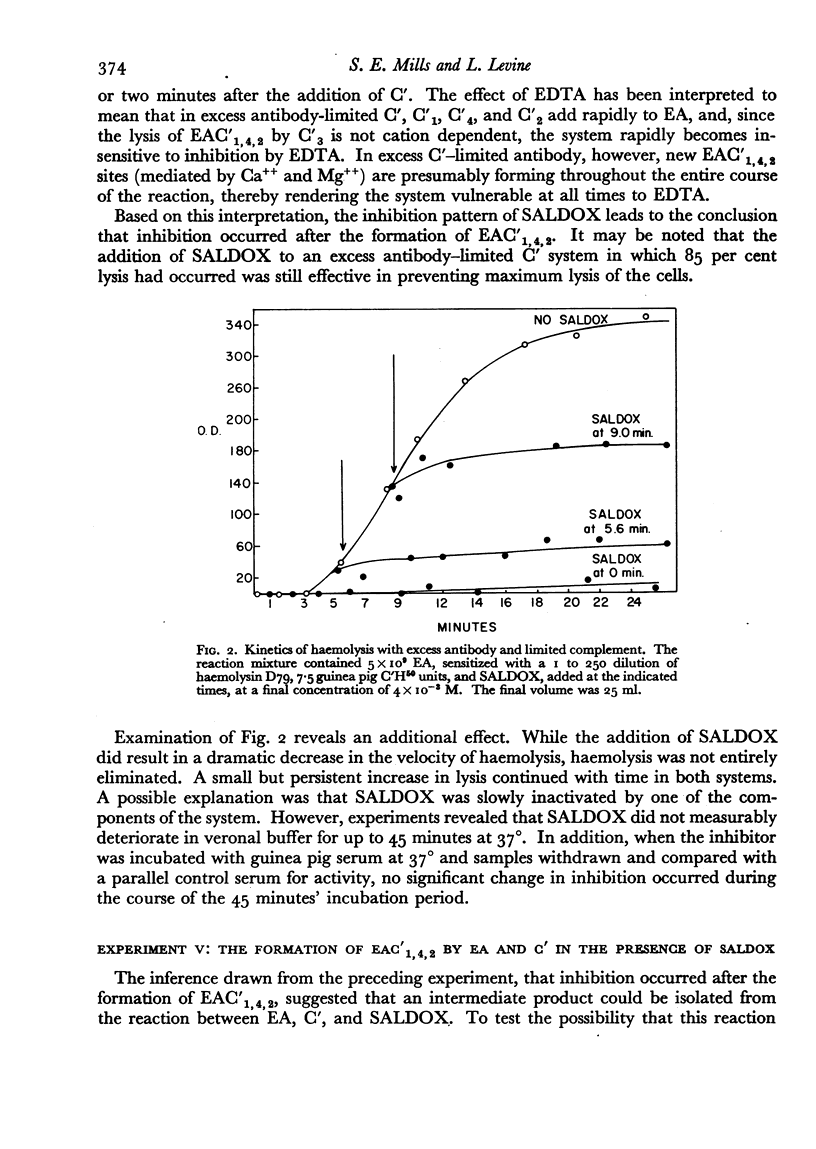
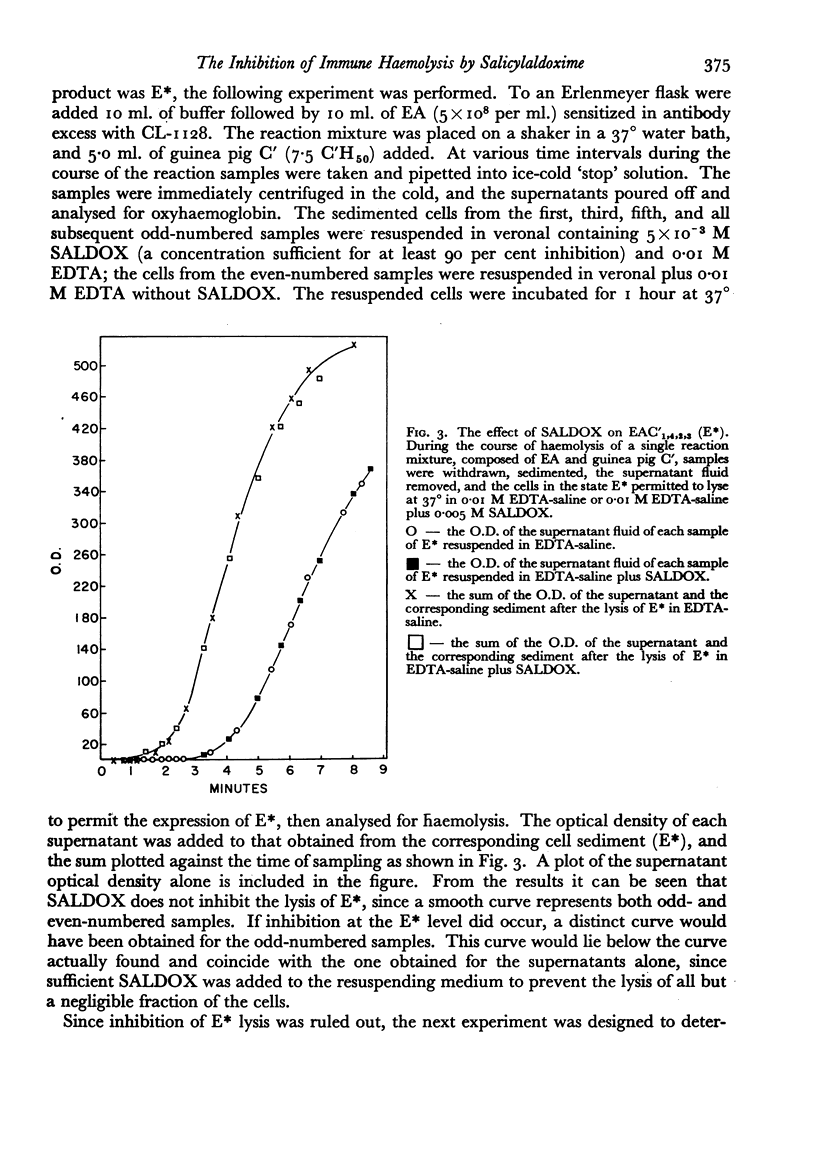
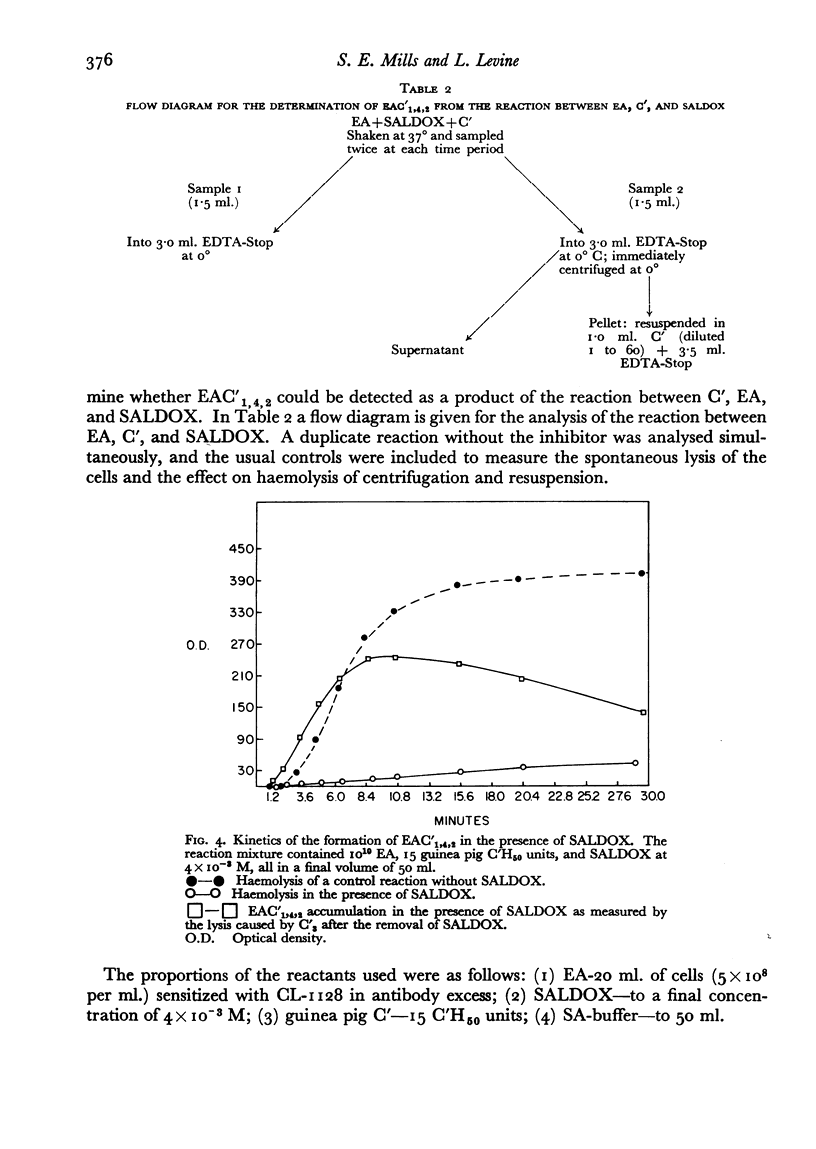
It has been shown that haemolysis of sheep erythrocytes by antibody and either guinea pig or human complement is inhibited by salicylaldoxime (0-hydroxybenzaldoxime.) Salicylaldoxime differs in its action on immune haemolysis from such previously described inhibitors as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and diisopropylfluorophosphate in that it specifically inhibits the reaction between the intermediate complex EAC′1,4,2 and C′3. The inhibition does not appear to be reversible by divalent cations. To be effective the inhibitor must be present during the course of the reaction, since haemolysis proceeds unimpaired if the inhibitor is added to complement and removed by dialysis, or if added to either red cells or EAC′1,4,2 and removed by centrifugation. The experimental evidence suggests that salicylaldoxime acts by preventing the effective combination of C′3 with EAC′1,4,2, and not by the destruction of C′3.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMIRAIAN K., PLESCIA O. J., CAVALLO G., HEIDELBERGER M. Complex nature of the step in immune hemolysis involving third component of complement. Science. 1958 Jan 31;127(3292):239–240. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3292.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER E. L. Concerning the mechanism of complement action. I. Inhibition of complement activity by diisopropyl fluophosphate. J Immunol. 1956 Dec;77(6):462–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER M. M. Studies on the mechanism of hemolysis by antibody and complement. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:215–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP H. J. Mechanism of immune hemolysis: recognition of two steps in the conversion of EAC' 1,4,2 to E. Science. 1958 Jan 31;127(3292):234–236. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3292.234-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


