Abstract
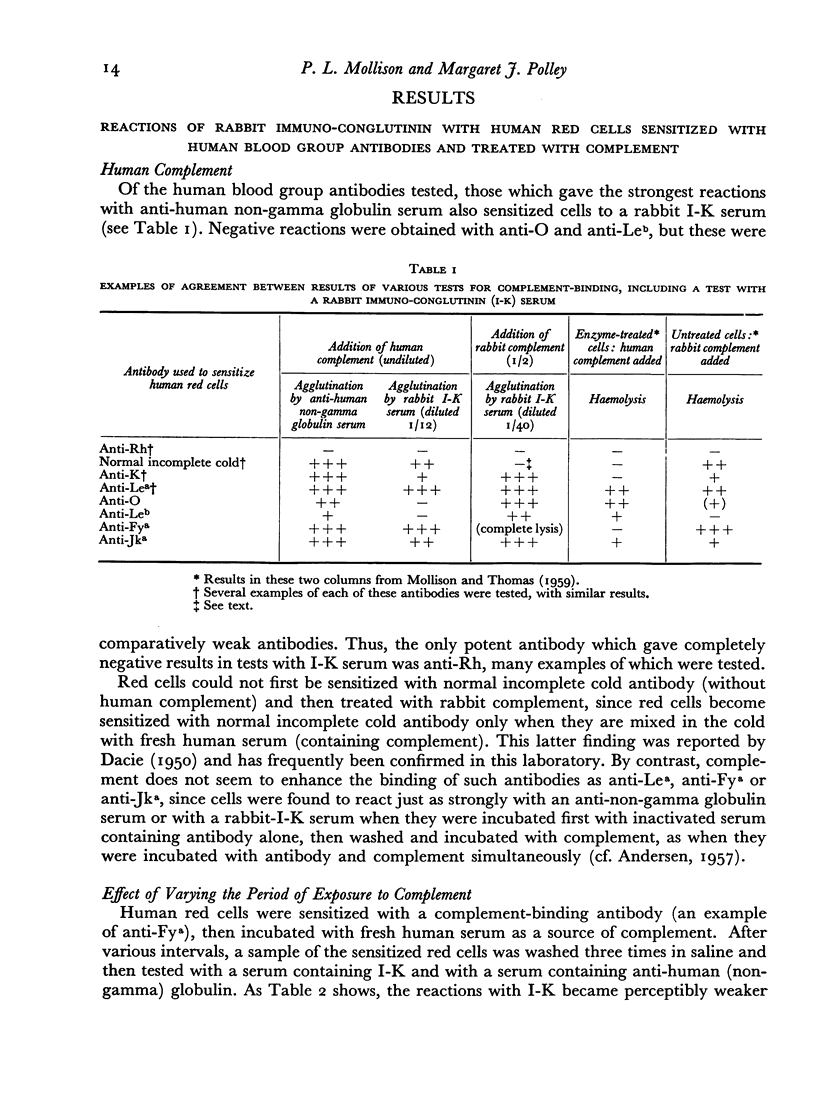
The value of sera containing immuno-conglutinin or conglutinin in demonstrating complement-binding by human blood group iso-antibodies was investigated. Provided that a suitable complement was used, positive results were obtained with all human sera which had been shown by other methods to contain complement-binding antibodies.
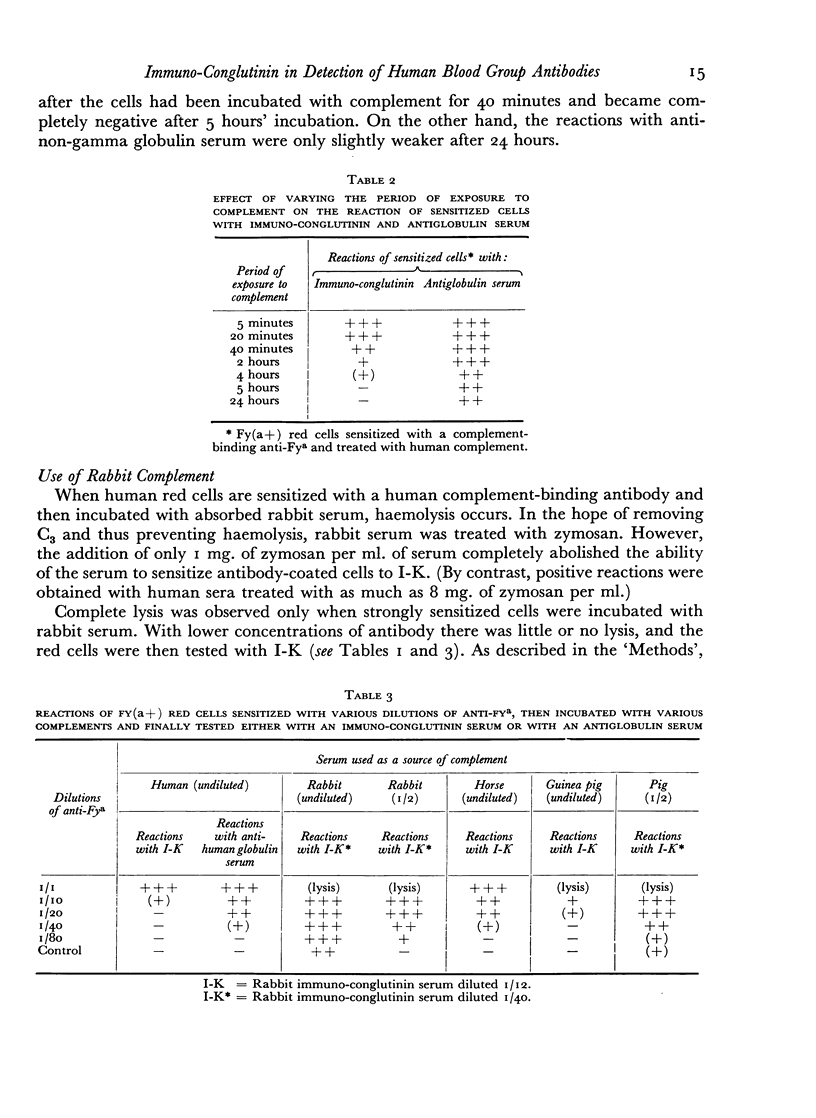
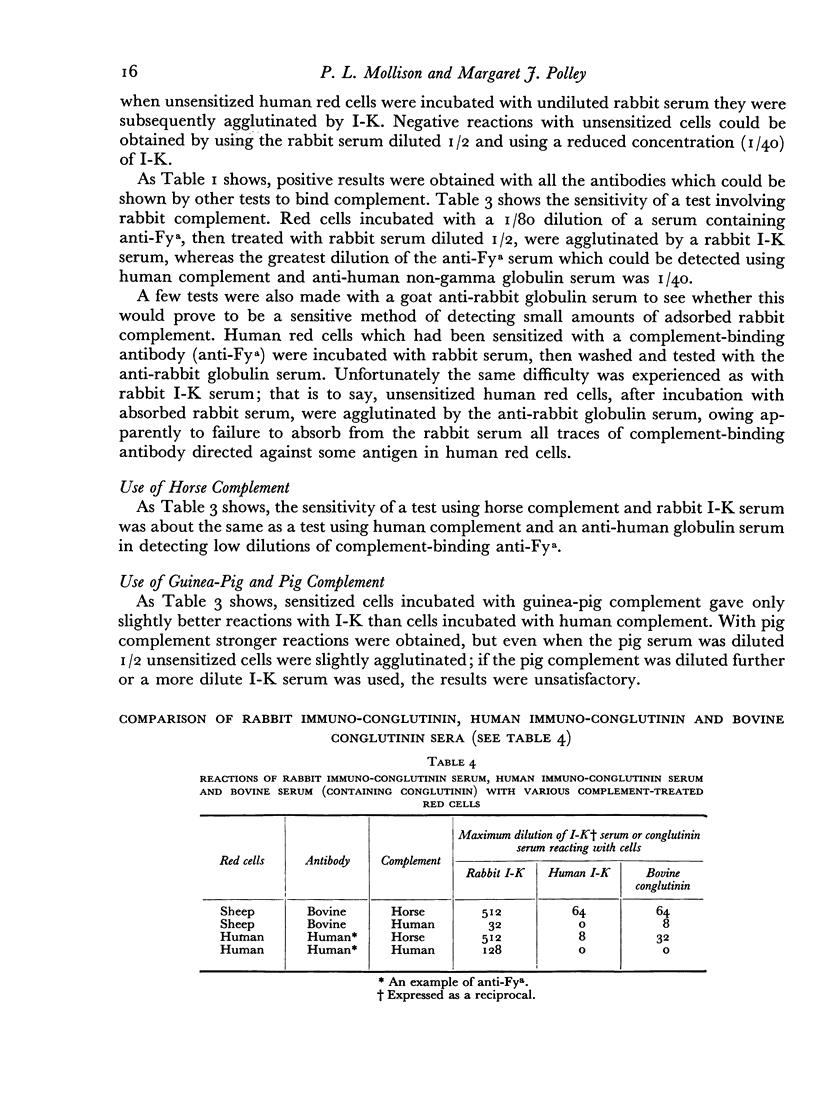
When human red cells were sensitized with human complement-binding blood group antibody and then treated with horse serum as a source of complement, the strongest reactions were obtained with rabbit immuno-conglutinin; the reactions with bovine serum (containing conglutinin) were distinctly weaker, and the reactions with human sera containing immuno-conglutinin were weaker still. When rabbit complement was used instead of horse complement, stronger reactions were obtained, but it was difficult to avoid `false positive' reactions. When human complement was used, good reactions were obtained with rabbit immuno-conglutinin, but the reactions with bovine conglutinin and human immuno-conglutinin were completely negative.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN J. Fixation of thermolabile serum globulin (complement) to sensitized red blood cells; demonstrated by Coombs' test. Dan Med Bull. 1957 Aug;4(5):137–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DACIE J. V., CROOKSTON J. H., CHRISTENSON W. N. Incomplete cold antibodies role of complement in sensitization to antiglobulin serum by potentially haemolytic antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jan;3(1):77–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DACIE J. V. Occurrences in normal human sera of 'incomplete' forms of 'cold' auto-antibodies. Nature. 1950 Jul 1;166(4209):36–36. doi: 10.1038/166036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER M. M., LEVINE L., RAPP H. J., MARUCCI A. A. Kinetic studies on immune hemolysis. VII. Decay of EAC'1, 4, 2, fixation of C'3, and other factors influencing the hemolytic action of complement. J Immunol. 1954 Dec;73(6):443–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


