Abstract
Two fluorochromes of contrasting colour, fluorescein and lissamine rhodamine B200 have been used in an application of Coons's immuno-histochemical technique to a comparison of the reactions with their antigens in tissue sections of anti-human-glomerulus antisera and anti-human-synovium antisera.
A uniform redistribution of labelled antibodies took place when tissue sections pre-treated with fluorescein labelled anti-glomerulus globulin were exposed to anti-glomerulus globulin labelled with lissamine rhodamine B200.
In sections pre-treated with an anti-human-glomerulus conjugate and exposed to an anti-human-synovium conjugate labelled contrastingly, and vice versa, the redistribution of antibodies did not occur to the same extent in every situation.
The findings can be explained by the hypothesis that there is a difference in the stability of union between certain connective tissue antigens and antibodies present in anti-glomerulus conjugates, on the one hand, and anti-synovium conjugates on the other.
The results of these experiments and of others in which anti-glomerulus and anti-synovium conjugates labelled contrastingly were allowed to react with tissue sections simultaneously, indicate that splenic reticulin is antigenically dissimilar to fibrils in vascular adventitia.
Full text
PDF




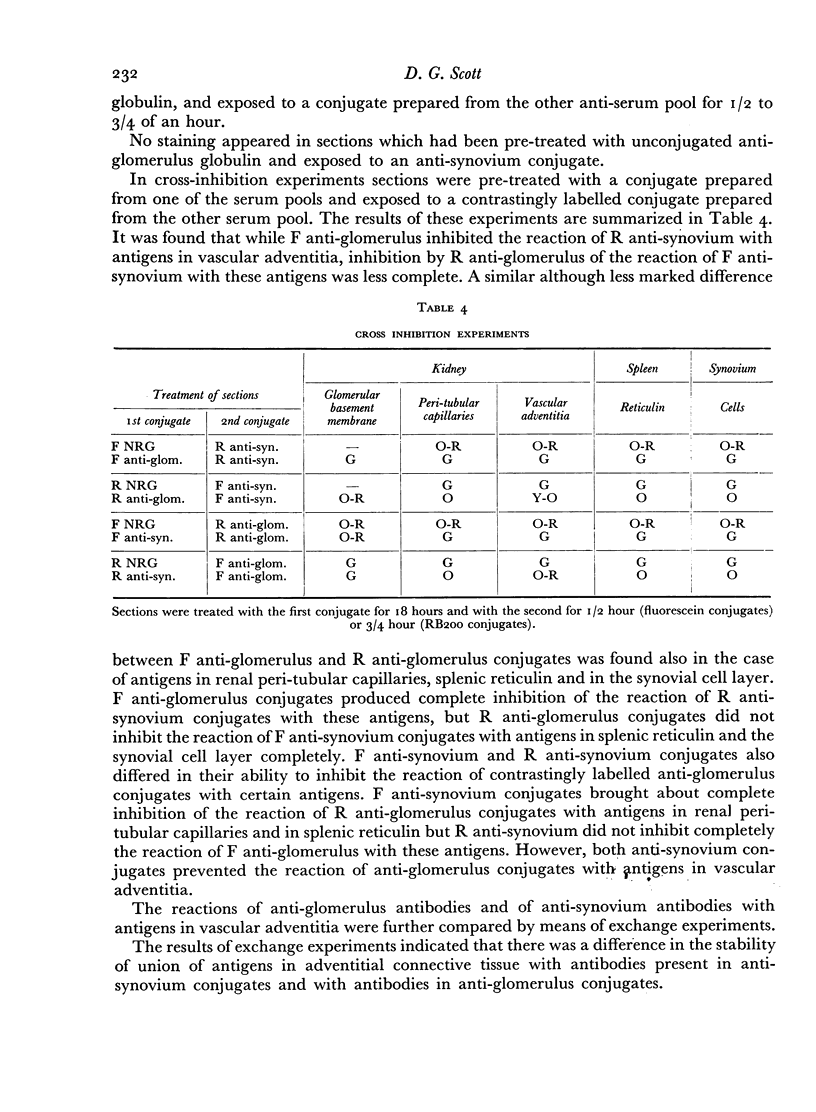
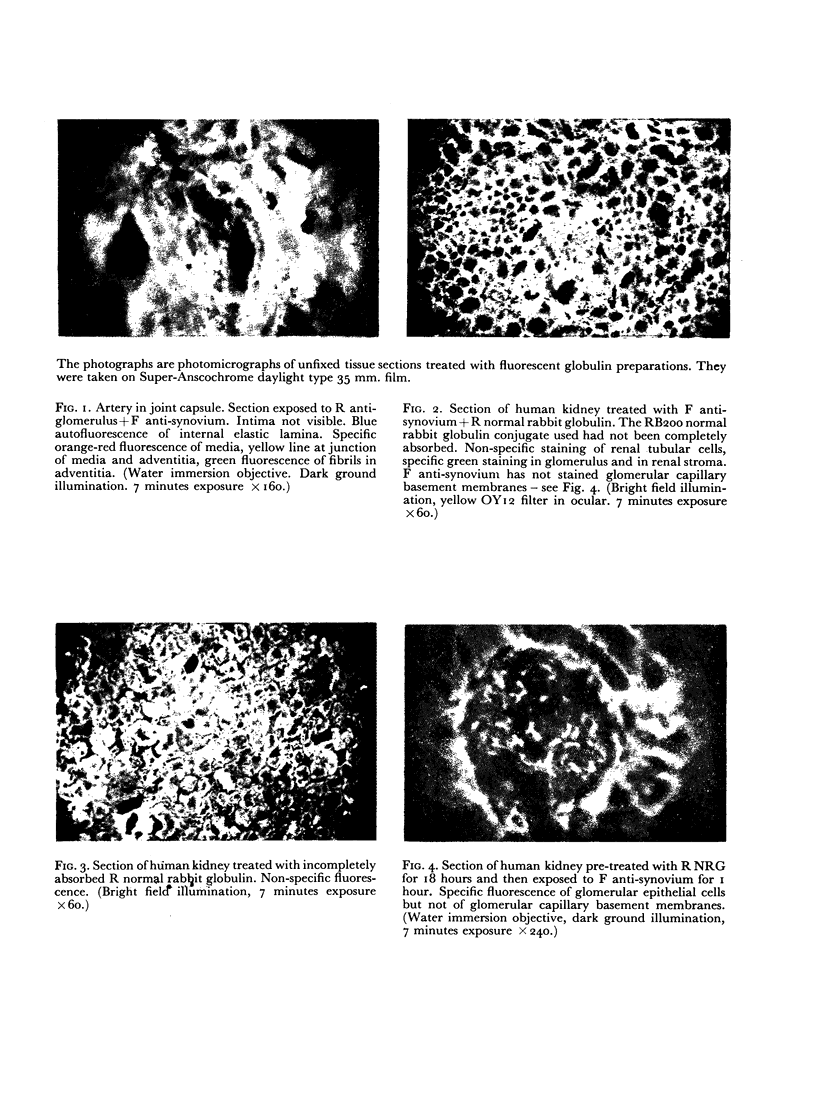
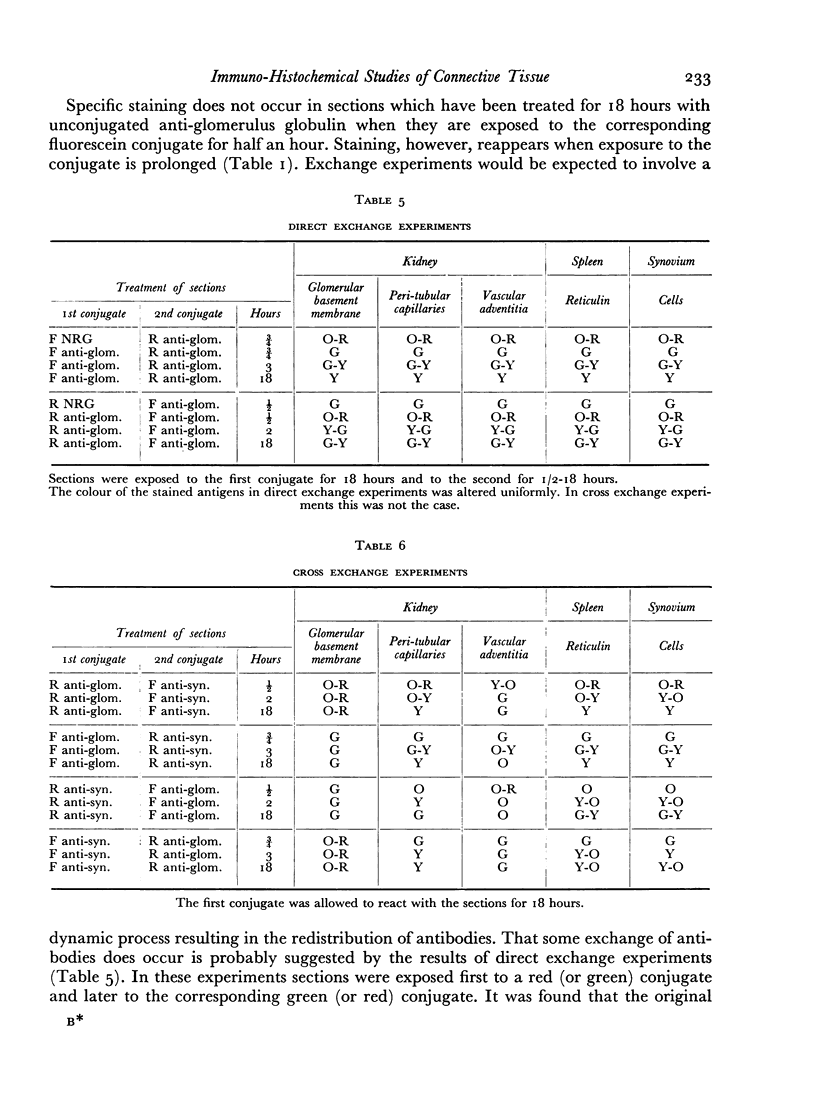

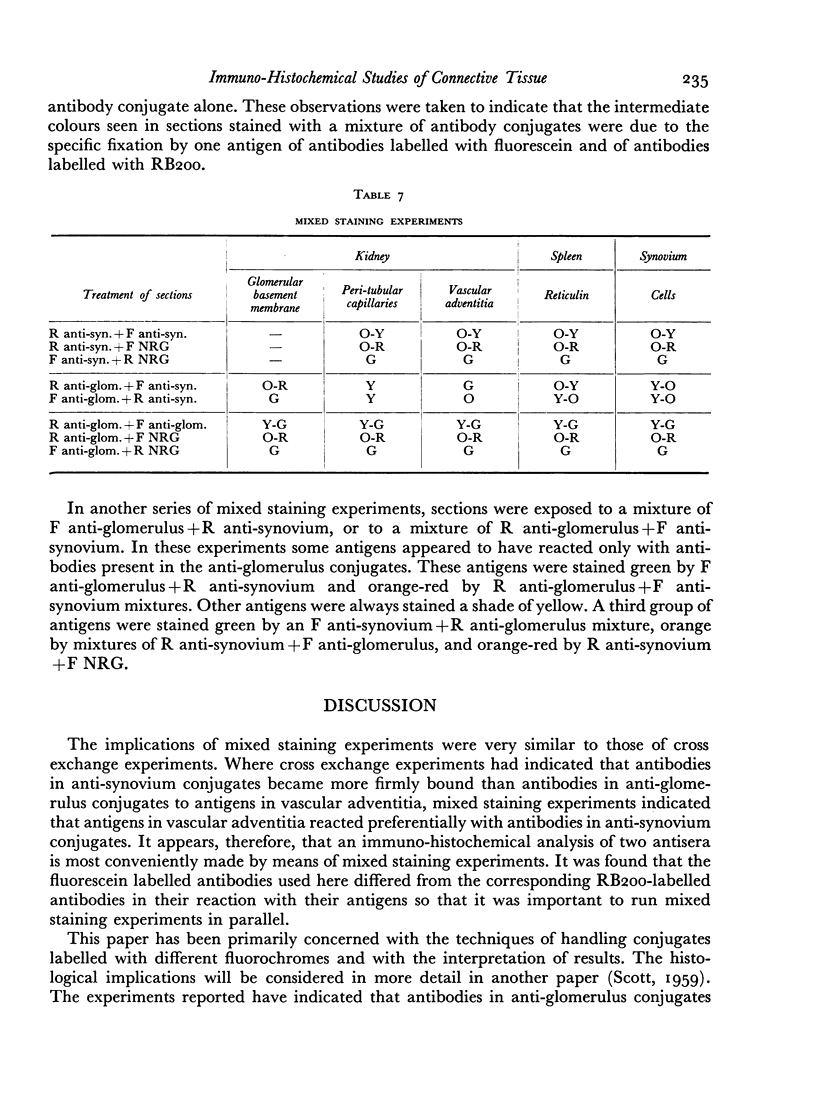

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., LEDUC E. H., CONNOLLY J. M. Studies on antibody production. I. A method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to a study of the hyperimmune rabbit. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):49–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., LEDUC E. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells. VI. The fate of injected foreign proteins in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):173–188. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDETZKI H. M. Labelling of antibodies by 5-dimethylamino-1-naphthalene sulfonyl chloride, its effect on antigen-antibody reactions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 May;98(1):120–122. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-23959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT D. G. An immuno-histological study of connective tissue. Ann Rheum Dis. 1959 Sep;18:207–214. doi: 10.1136/ard.18.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]