Abstract
The technique and results of a two-stage indirect L.E. cell test are described.
An account of the course of the lupus phenomenon as it occurs in this test is given.
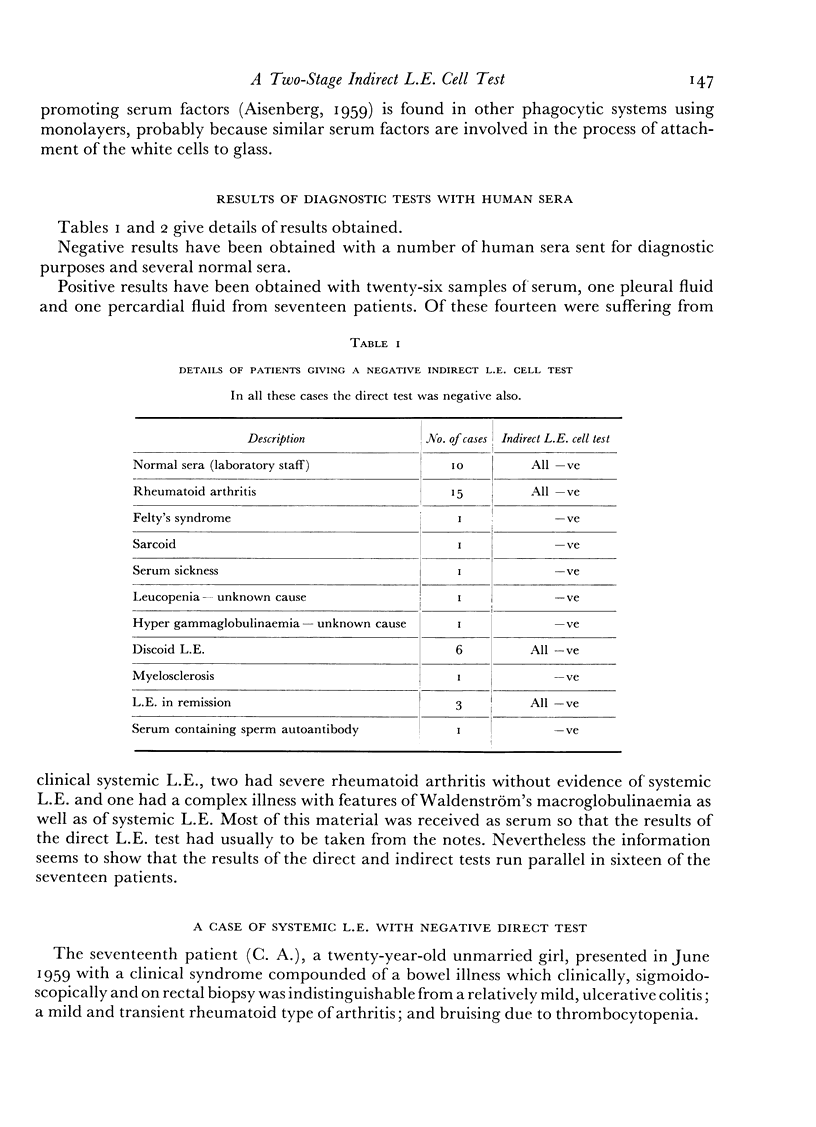
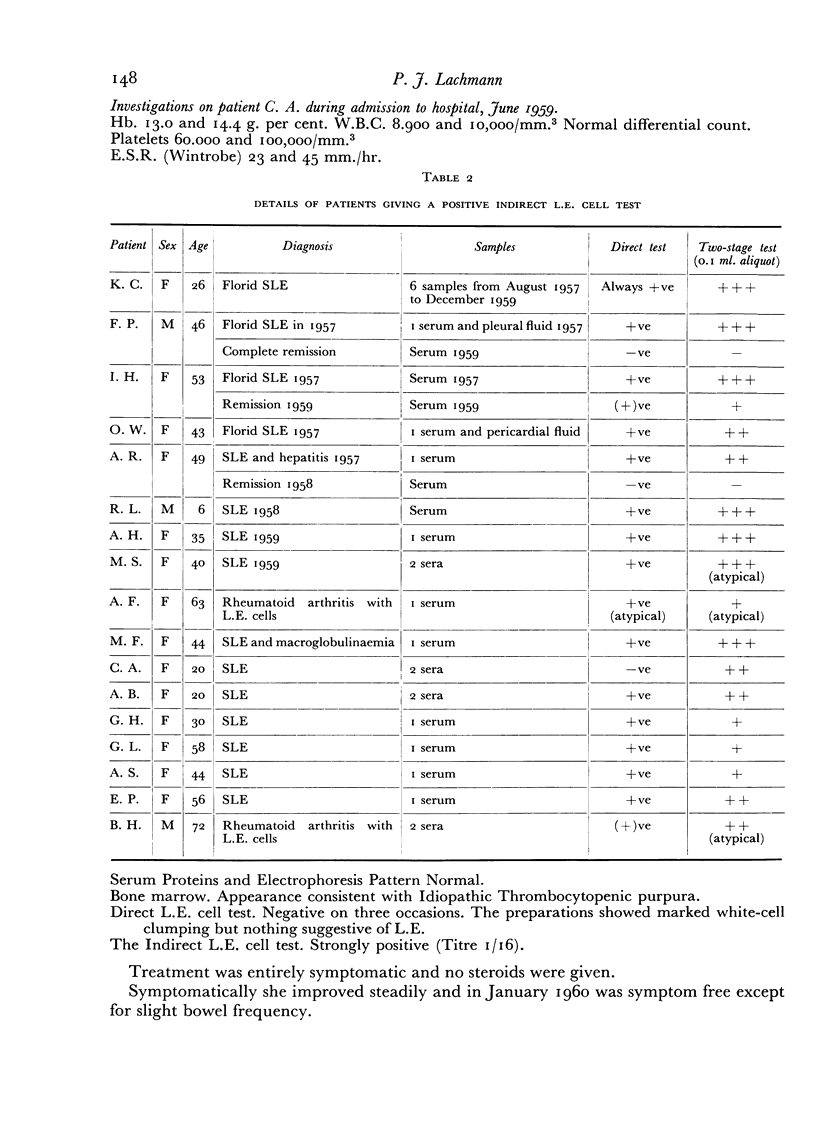
Details are presented of a patient with systemic L.E. whose direct reaction was persistently negative in the presence of a strongly positive indirect reaction.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AISENBERG A. C. Studies on the mechanism of the lupus erythematosus (L.E.) phenomenon. J Clin Invest. 1959 Feb;38(2):325–333. doi: 10.1172/JCI103805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERMAN J. L., HUBER M. Frozen cells as nuclear source in the L.E. cell phenomenon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jan;97(1):221–223. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACHMANN P. J. An attempt to characterize the lupus erythematosus cell antigen. Immunology. 1961 Apr;4:153–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIESCHER P., FAUCONNET M. L'absorption du facteur L. E. par des noyaux cellulaires isolés. Experientia. 1954 Jun 15;10(6):252–253. doi: 10.1007/BF02157392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHAN D. J., SNAPPER I. On the interaction of dead leukocytic nuclei, L. E. factor and living leukocytes in the L. E. cell phenomenon. Blood. 1958 Sep;13(9):883–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIFKIND R. A., GODMAN G. C. Phase contrast and interferometric microscopy of the L. E. cell phenomenon. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):607–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ I., BAUM J., ZIFF M. A new micro-method for the L.E. cell phenomenon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Feb;88(2):300–302. doi: 10.3181/00379727-88-21569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILDY P., RIDLEY M. Separation of human leucocytes from blood. Nature. 1958 Dec 27;182(4652):1801–1803. doi: 10.1038/1821801b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




