Abstract
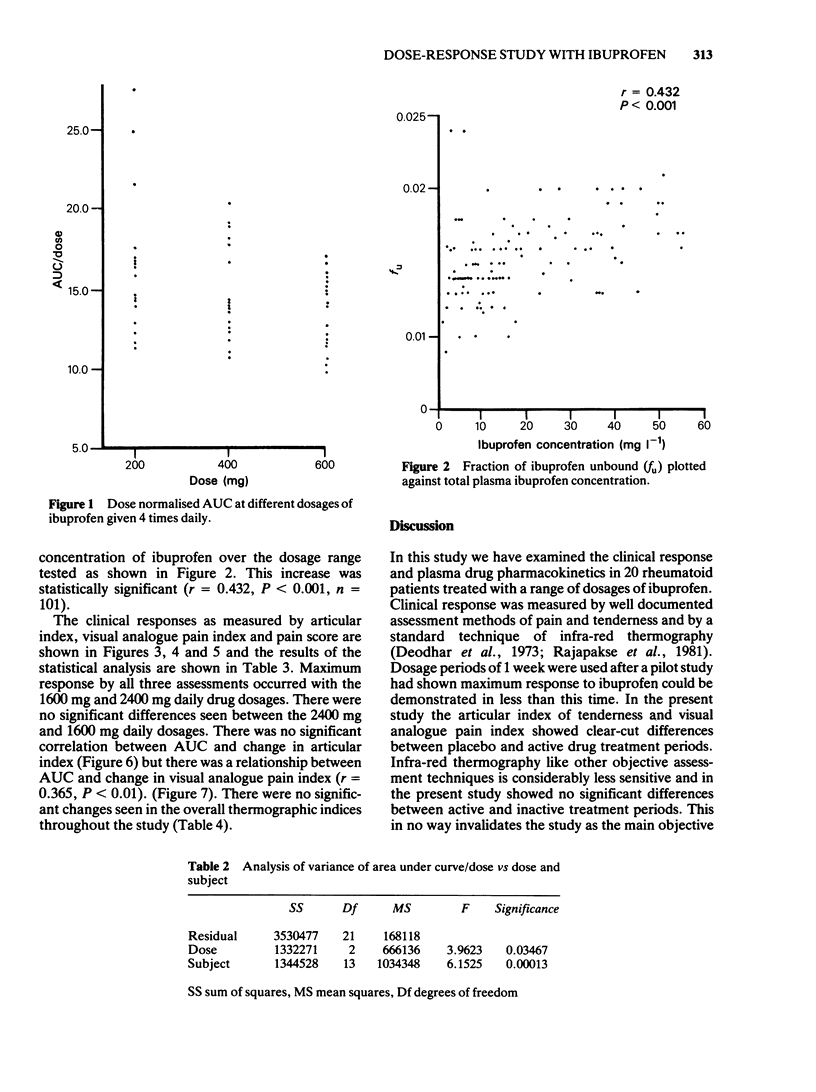
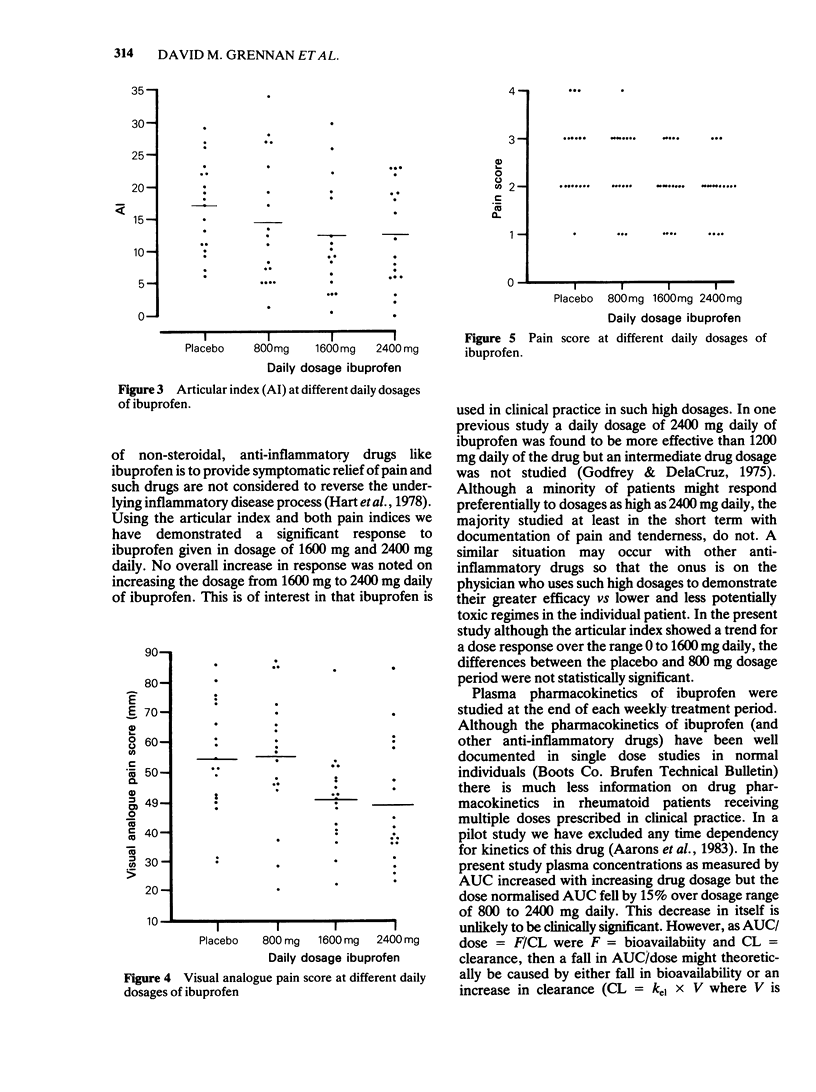
Clinical response and plasma pharmacokinetics were studied in 20 rheumatoid patients receiving three dosages of ibuprofen. There was a significant response to 1600 mg daily of ibuprofen by all three clinical measurements but increasing the daily dosage to 2400 mg produced no overall increase in response. The AUC increased with increasing daily drug dosages from 800 to 2400 mg daily and the dose normalised AUC fell by 15% over the same dosage range. The fraction of ibuprofen not bound to plasma proteins increased with increasing dosage and may contribute to the fall in the dose normalised AUC. There was a considerably inter-individual variation in the AUC. There was no significant correlation between AUC and clinical response as measured by articular index and there was a weakly significant correlation between AUC and clinical response as measured by a visual analogue pain index. Pharmacokinetic variables probably account for only a small part of the inter-individual variation in response of rheumatoid patients treated with increasing dosages of the non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- 1958 REVISION of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1959 Feb;2(1):16–20. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(195902)2:1<16::aid-art1780020104>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aarons L., Grennan D. M., Rajapakse C., Brinkley J., Siddiqui M., Taylor L., Higham C. Anti-inflammatory (ibuprofen) drug therapy in rheumatoid arthritis--rate of response and lack of time dependency of plasma pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;15(3):387–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. J., Ring E. F., Cosh J. A., Bacon P. A. Quantitation of thermography in arthritis using multi-isothermal analysis. I. The thermographic index. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Mar;33(2):113–115. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deodhar S. D., Dick W. C., Hodgkinson R., Buchanan W. W. Measurement of clinical response to anti-inflammatory drug therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1973 Apr;42(166):387–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey R. G., de la Cruz S. Effect of ibuprofen dosage on patient response in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Mar-Apr;18(2):135–137. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf P., Glatt M., Brune K. Acidic nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs accumulating in inflamed tissue. Experientia. 1975 Aug 15;31(8):951–953. doi: 10.1007/BF02358871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gund P., Shen T. Y. A model for the prostaglandin synthetase cyclooxygenation site and its inhibition by antiinflammatory arylacetic acids. J Med Chem. 1977 Sep;20(9):1146–1152. doi: 10.1021/jm00219a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskisson E. C. Measurement of pain. Lancet. 1974 Nov 9;2(7889):1127–1131. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90884-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J., Sellers E. M. Binding of drugs to serum albumin (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 5;294(6):311–316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602052940605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Webb J., Anderson J., Buchanan W. W. Method for assessing therapeutic potential of anti-inflammatory antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1973 Jun 23;2(5868):685–688. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5868.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur J. N., Dawkins P. D., Smith M. J. The displacement of L-tryptophan and dipeptides from bovine albumin in vitro and from human plasma in vivo by antirheumatic drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;23(6):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlam J. B., Brown K. F., Crooks M. J., Room G. F. Transsynovial distribution of ibuprofen in arthritic patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Apr;29(4):487–492. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


