Abstract
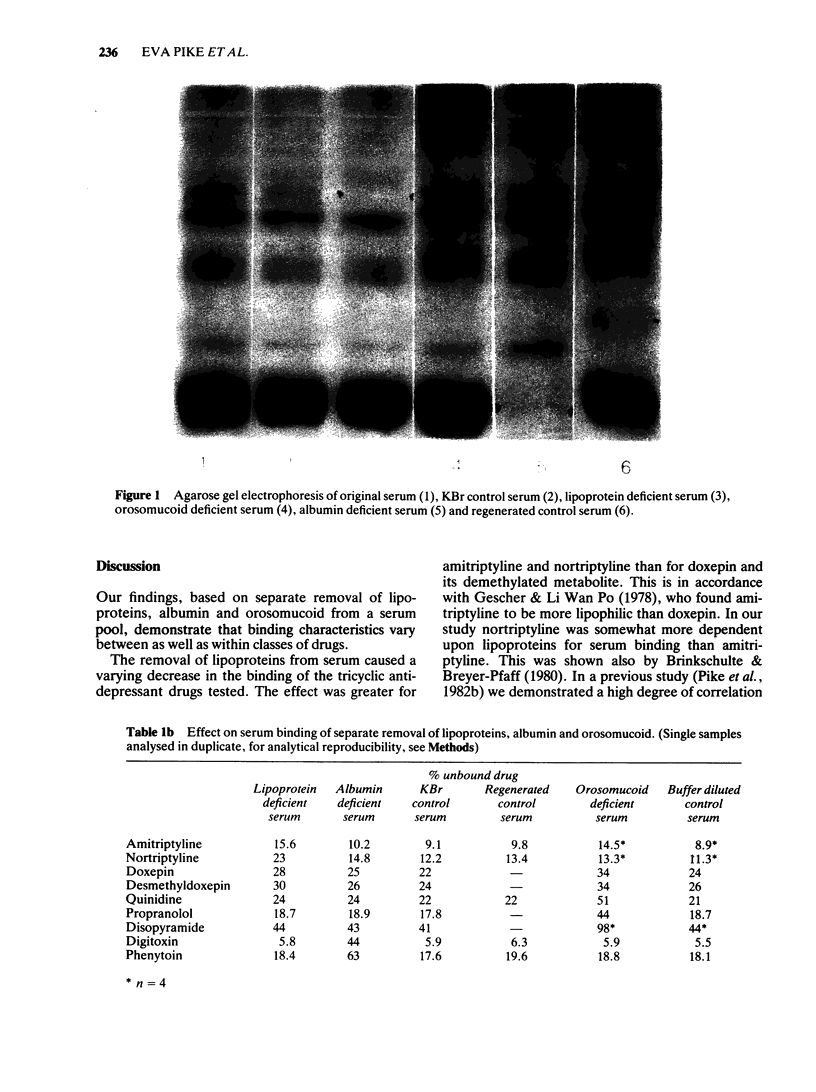
The relative role of lipoproteins, albumin and orosomucoid in the serum binding variation of various drugs was examined by separate removal of these proteins. Lipoproteins were removed from serum by ultracentrifugation, albumin by affinity chromatography and orosomucoid by immunoprecipitation. Removal of the lipoproteins did not affect the serum binding of the acidic (phenytoin) and neutral (digitoxin) drugs tested, nor the basic drugs disopyramide, quinidine or propranolol. A reduction in binding of amitryptyline, nortriptyline, doxepin and desmethyldoxepin was observed. Removal of albumin did, with some exception for nortriptyline, not affect the serum binding of the basic drugs tested. A pronounced reduction in the binding of phenytoin and digitoxin was observed. Removal of orosomucoid did not affect the binding of the acidic and neutral drugs tested. A reduction in the binding of all the basic drugs tested was observed, especially for disopyramide whose binding almost disappeared. Quinidine, propranolol, phenytoin and digitoxin all bound to isolated lipoproteins, but the removal of lipoproteins had no effect on the total serum binding for these drugs. Hence, the use of deficient sera provides valuable information as to the quantitative role of the various proteins in drug binding, whereas studies using purified proteins are often necessary to examine the mechanisms of the drug protein interactions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bredesen J. E., Pike E., Lunde P. K. Plasma binding of disopyramide and mono-N-dealkyldisopyramide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;14(5):673–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb04955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkschulte M., Breyer-Pfaff U. The contribution of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, lipoproteins, and albumin to the plasma binding of perazine, amitriptyline, and nortriptyline in healthy man. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;314(1):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00498432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONN H. L., Jr, LUCHI R. J. Some quantitative aspects of the binding of quinidine and related quinoline compounds by human serum albumin. J Clin Invest. 1961 Mar;40:509–516. doi: 10.1172/JCI104278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Danon A. Binding of reserpine to plasma albumin and lipoproteins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90514-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello P. B., Green F. A., Jung C. Y. Free versus bound salicylate concentration in adults and children with chronic inflammatory joint disease: serum albumin and other potential factors affecting the levels. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jan;25(1):32–37. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gescher A., Li Wan Po A. Correlation of physicochemical properties with absorption and metabolism of some tricyclic drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Jun;30(6):353–358. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:7–19. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHN J. Small-scale membrane filter electrophoresis and immuno-electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1958 Sep;3(5):450–454. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(58)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates R. E., Sokoloski T. D., Comstock T. J. Binding of quinidine to plasma proteins in normal subjects and in patients with hyperlipoproteinemias. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Jan;23(1):30–35. doi: 10.1002/cpt197823130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. L., Richens A. Two dimensional immunoelectrophoresis of human serum proteins for the investigation of protein drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 May;45(1):184P–185P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima J. J., Salzer L. B. Contamination of albumin by alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Sep 15;30(18):2633–2636. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90596-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen O. G., Jacobsen S. The binding of quinidine to protein fractions of normal human sera. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 May 1;24(9):995–998. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen O. G., Leren P., Aakesson I., Jacobsen S. Binding of quinidine in sera with different levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and orosomucoid protein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;27(6):871–876. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90411-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M. Disease-induced changes in the plasma binding of basic drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 May-Jun;5(3):246–262. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005030-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike E., Skuterud B., Kierulf P., Lunde P. K. Significance of lipoproteins in serum binding variations of amitriptyline, nortriptyline, and quinidine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Nov;32(5):599–606. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike E., Skuterud B. Plasma binding variations of amitriptyline and nortriptyline. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Aug;32(2):228–234. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager G., Hansteen V., Aakesson I., Jacobsen S. Effect of heparin on serum binding of propranolol in the acute phase of myocardial infarction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;12(5):613–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager G., Nilsen O. G., Jacobsen S. Variable binding of propranolol in human serum. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 15;28(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. J., Bradwell A. R., Schneider R. E., Bishop H. Propranolol binding to serum orosomucoid. Lancet. 1979 Apr 28;1(8122):930–930. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharples D. Factors affecting the binding of tricyclic tranquillizers and antidepressants to human serum albumin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Feb;28(2):100–105. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Bowen J., Tewksbury D., Johnson D., Pannell R. Isolation of albumin from whole human plasma and fractionation of albumin-depleted plasma. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):301–306. doi: 10.1042/bj1570301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]