Abstract
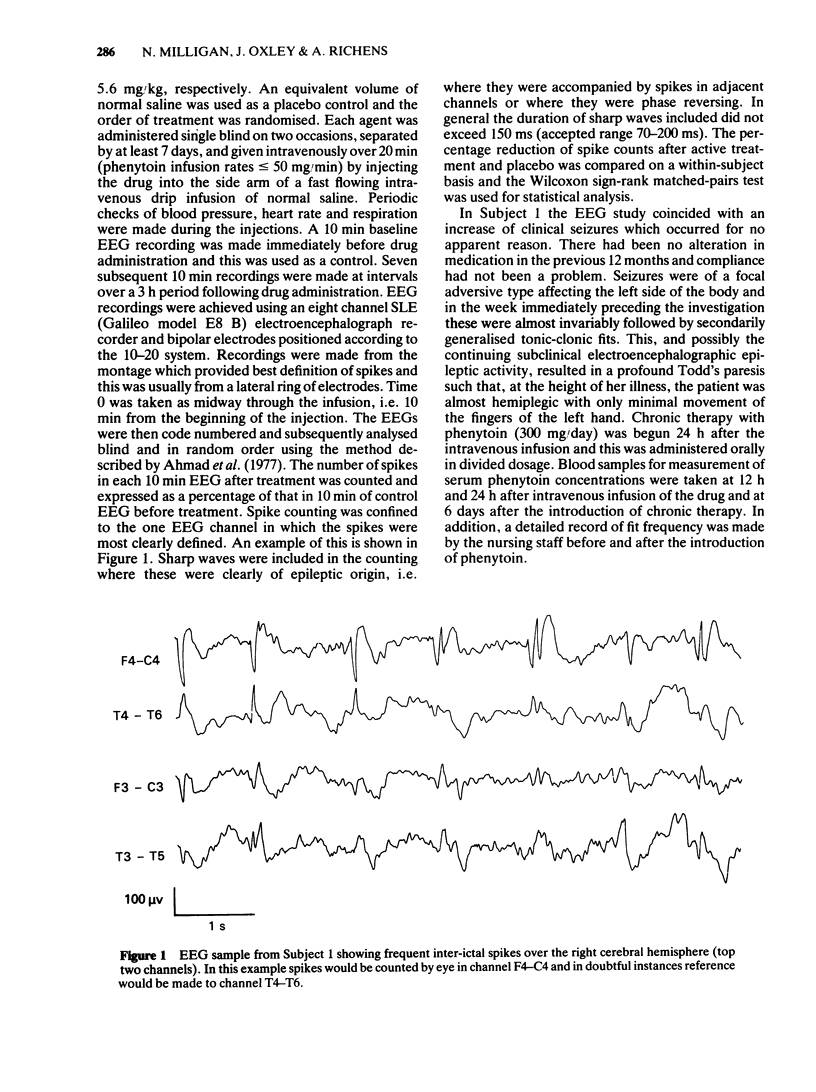
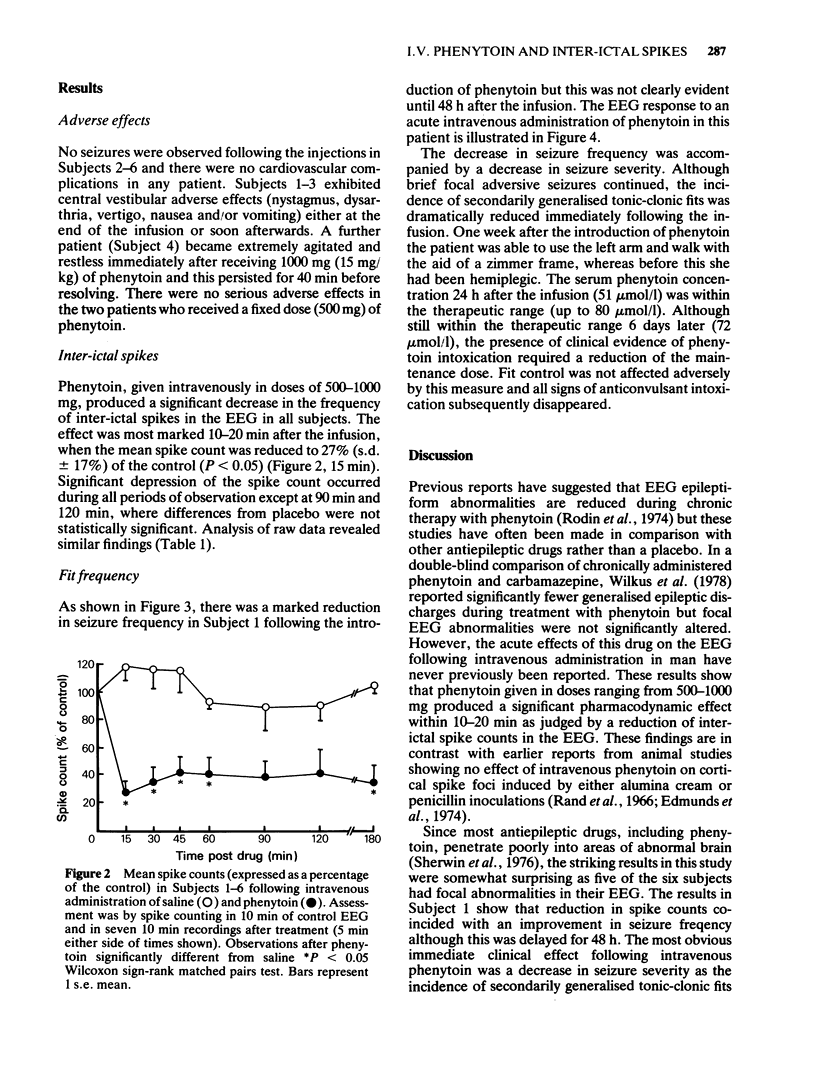
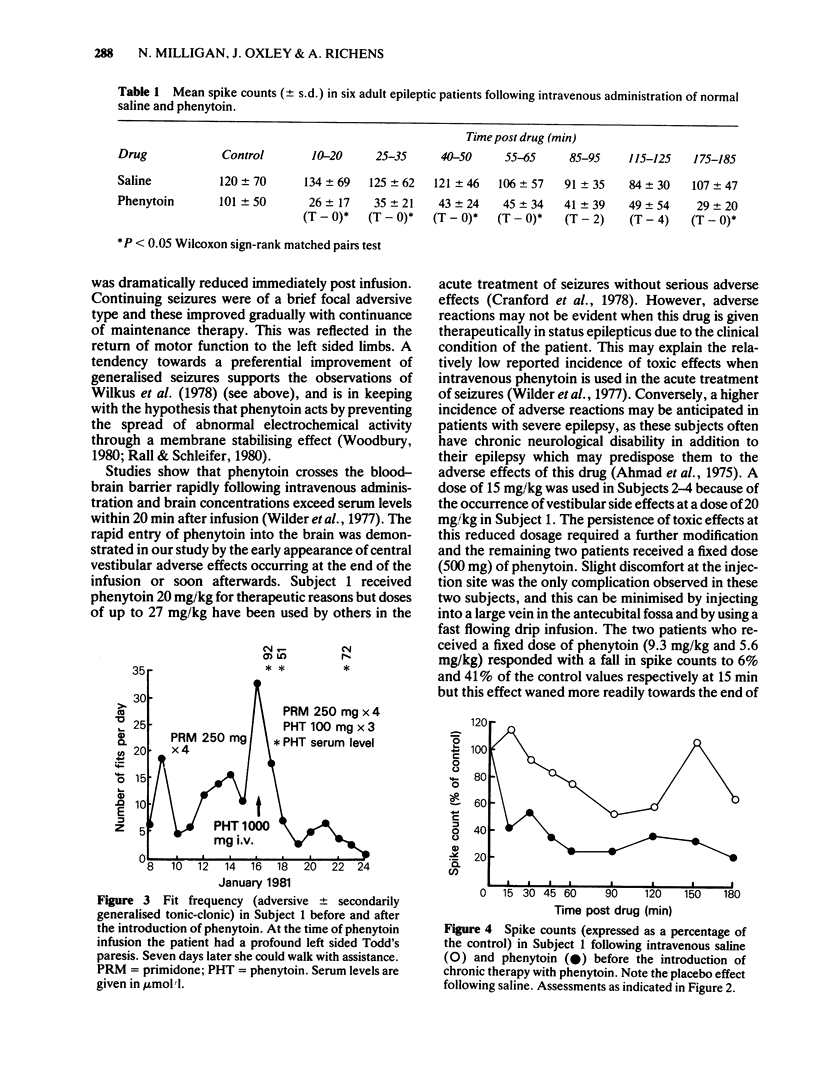
Phenytoin was administered intravenously to six adult epileptic patients in doses ranging from 500--1000 mg (equivalent to 5.6 mg/kg--20 mg/kg body weight). A significant decrease in the frequency of inter-ictal spikes in the EEG was seen and this effect was most marked 10--20 min after the infusion, when the mean spike count was reduced to 27% (s.d. 17%) of the control (P less than 0.05). In one subject the decrease in inter-ictal spikes coincided with a decrease in fit frequency. Adverse reactions affecting the vestibular system occurred in three patients at doses of 15--20 mg/kg. No cardiovascular complications were observed in any subject. The overall results suggest that doses of 7.5--10 mg/kg would be sufficient to significantly reduce the frequency of inter-ictal spikes in the EEG.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S., Laidlaw J., Houghton G. W., Richens A. Involuntary movements caused by phenytoin intoxication in epileptic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Mar;38(3):225–231. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booker H. E., Celesia G. G. Serum concentrations of diazepam in subjects with epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1973 Sep;29(3):191–194. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490270073012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranford R. E., Leppik I. E., Patrick B., Anderson C. B., Kostick B. Intravenous phenytoin: clinical and pharmacokinetic aspects. Neurology. 1978 Sep;28(9 Pt 1):874–880. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.9.874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds H. L., Stark L. G., Hollinger M. A. The effects of diphenylhydantoin, phenobarbital, and diazepam on the penicillin-induced epileptogenic focus in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1974 Nov;45(2):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan N., Dhillon S., Oxley J., Richens A. Absorption of diazepam from the rectum and its effect on interictal spikes in the EEG. Epilepsia. 1982 Jun;23(3):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1982.tb06198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeyer E. Intravenous diazepam and its anticonvulsive action. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1970 Aug;127(2):79–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand B. O., Kelly W. A., Ward A. A., Jr Electrophysiological studies of the action of intravenous diphenylhydantoin (Dilantin). Neurology. 1966 Oct;16(10):1022–1032. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.10.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodin E. A., Rim C. S., Rennick P. M. The effects of carbamazepine on patients with psychomotor epilepsy: results of a double-blind study. Epilepsia. 1974 Dec;15(4):547–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1974.tb04028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder B. J., Ramsay R. E., Willmore L. J., Feussner G. F., Perchalski R. J., Shumate J. B., Jr Efficacy of intravenous phenytoin in the treatment of status epilepticus: kinetics of central nervous system penetration. Ann Neurol. 1977 Jun;1(6):511–518. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkus R. J., Dodrill C. B., Troupin A. S. Carbamazepine and the electroencephalogram of epileptics: a double blind study in comparison to phenytoin. Epilepsia. 1978 Jun;19(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1978.tb04491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


