Abstract
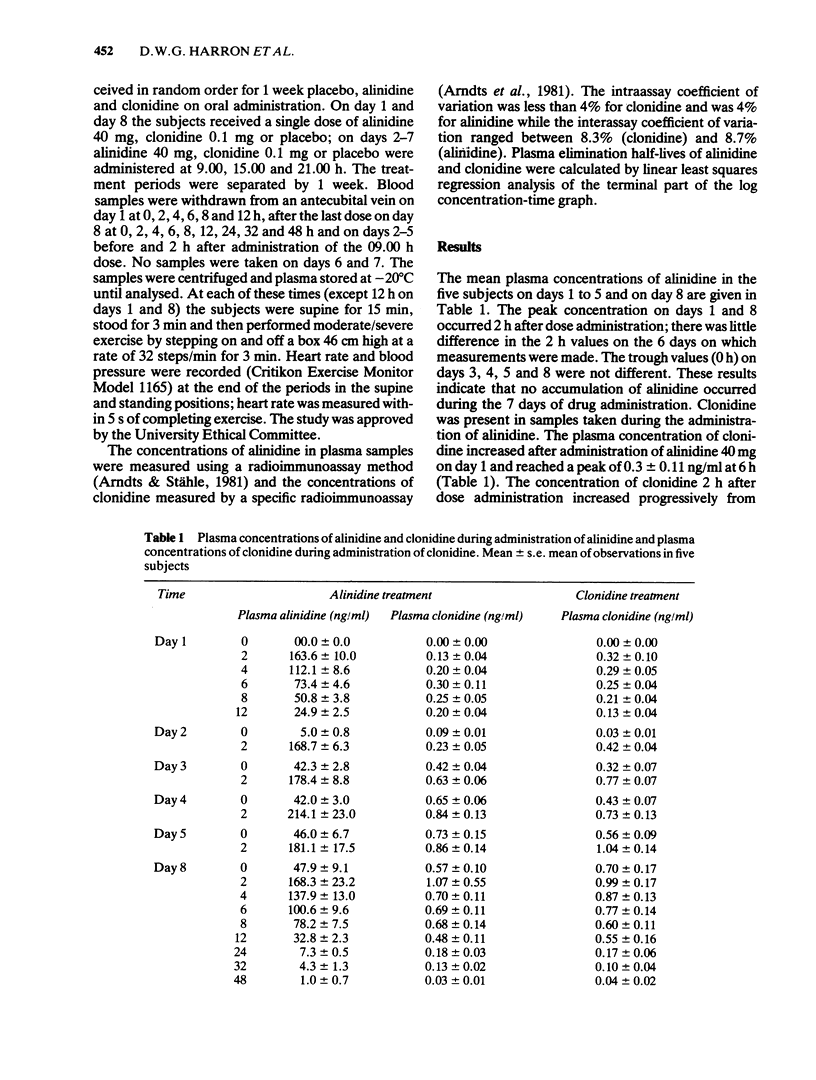
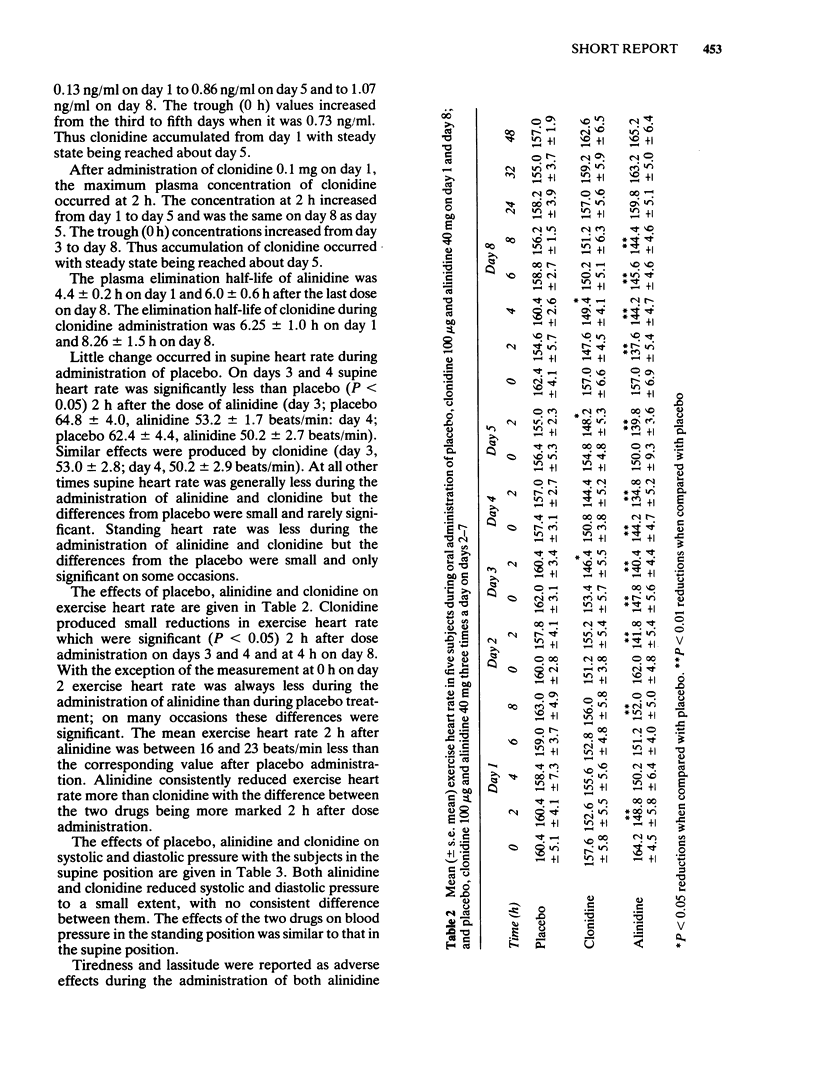
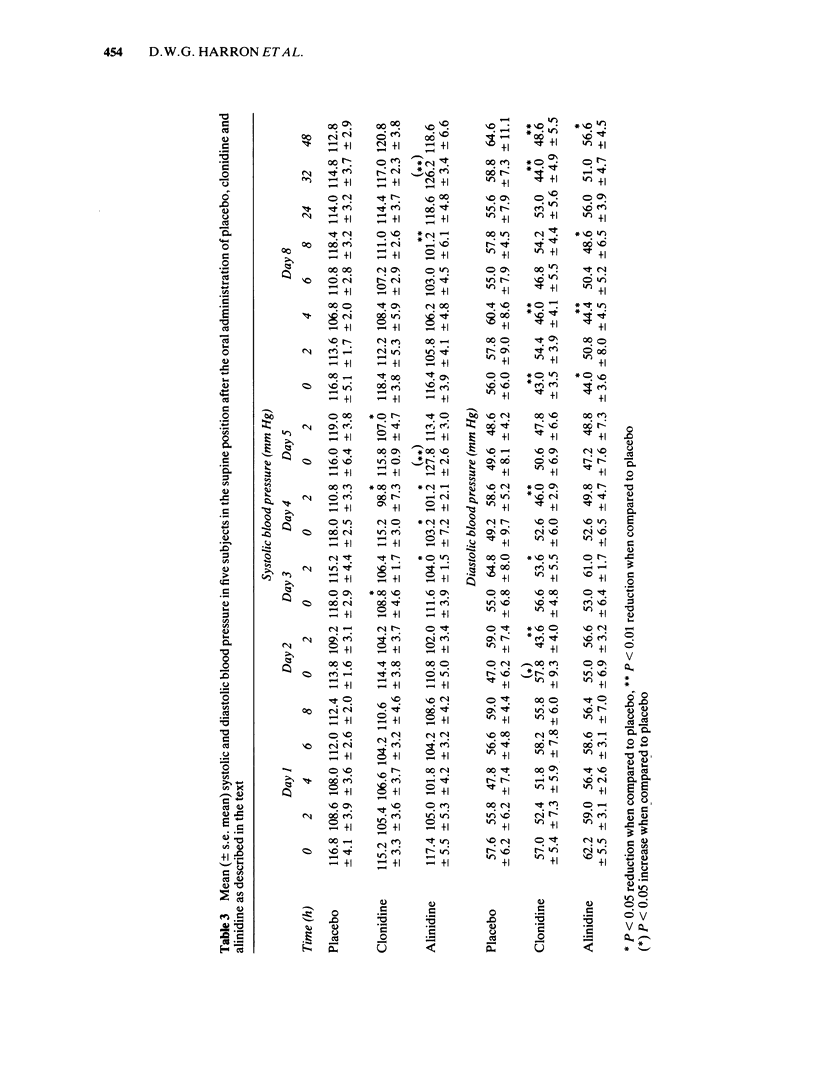
Five healthy volunteers (mean age 20.6 years, mean weight 71 kg) received in random order on day 1 and day 8 a single dose of alinidine 40 mg, clonidine 0.1 mg or placebo and on days 2-7 alinidine 40 mg, clonidine 0.1 mg or placebo given three times a day with 1 week between treatment periods. Blood samples were taken for measurement of concentrations of alinidine and clonidine during alinidine administration and of clonidine during clonidine dosing. Heart rate and blood pressure were recorded in supine and standing positions and heart rate after 3 min exercise. Plasma concentrations of alinidine reached a maximum of 163.6 +/- 10.0 ng/ml 2 h after alinidine administration on day 1 and during chronic administration similar concentrations were achieved. Clonidine plasma concentrations reached 0.3 +/- 0.11 ng/ml 6 h after alinidine 40 mg on day 1, and during chronic administration of alinidine, increased to a steady state on day 5 with trough and 2 h values of 0.73 +/- 0.15 and 0.86 +/- 0.14 ng/ml respectively. After the first dose of clonidine on day 1, the maximum plasma concentration of clonidine was 0.32 +/- 0.1 ng/ml at 4 h, during chronic administration clonidine plasma concentration rose to 1.04 +/- 0.14 ng/ml 2 h after a dose on day 5. Alinidine produced a greater reduction in the exercise tachycardia than clonidine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndts D., Forster H. J. New aspects in the metabolism of alinidine in man. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1981;6(4):313–315. doi: 10.1007/BF03189531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndts D., Stähle H. Development and quality control of a highly sensitive radioimmunoassay for alinidine. J Pharmacol Methods. 1981 Sep;6(2):109–120. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(81)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndts D., Stähle H., Förster H. J. Development of a RIA for clonidine and its comparison with the reference methods. J Pharmacol Methods. 1981 Dec;6(4):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(81)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. S., Wing A. M., Reid J. L., Neill D. M., Tippett P., Dollery C. T. Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships of intervenous and oral clonidine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 May;21(5):593–601. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977215593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollery C. T., Davies D. S., Draffan G. H., Dargie H. J., Dean C. R., Reid J. L., Clare R. A., Murray S. Clinical pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of clonidine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Jan;19(1):11–17. doi: 10.1002/cpt197619111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harron D. W., Arndts D., Shanks R. G. Alinidine pharmacokinetics following acute and chronic dosing. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;13(6):821–827. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harron D. W., Jady K., Riddell J. G., Shanks R. G. Effects of alinidine, a novel bradycardic agent, on heart rate and blood pressure in man. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):213–220. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198203000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Lillie C., Pichler L. Cardiovascular actions of N-allyl-clonidine (ST 567), a substance with specific bradycardic action. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 15;58(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Lillie C., Pichler L. N-Allyl-derivative of clonidine, a substance with specific bradycardic action at a cardiac site. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;306(3):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00507111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L., Wing L. M., Mathias C. J., Frankel H. L., Neill E. The central hypotensive effect of clonidine. Studies in tetraplegic subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Apr;21(4):375–381. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977214375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


