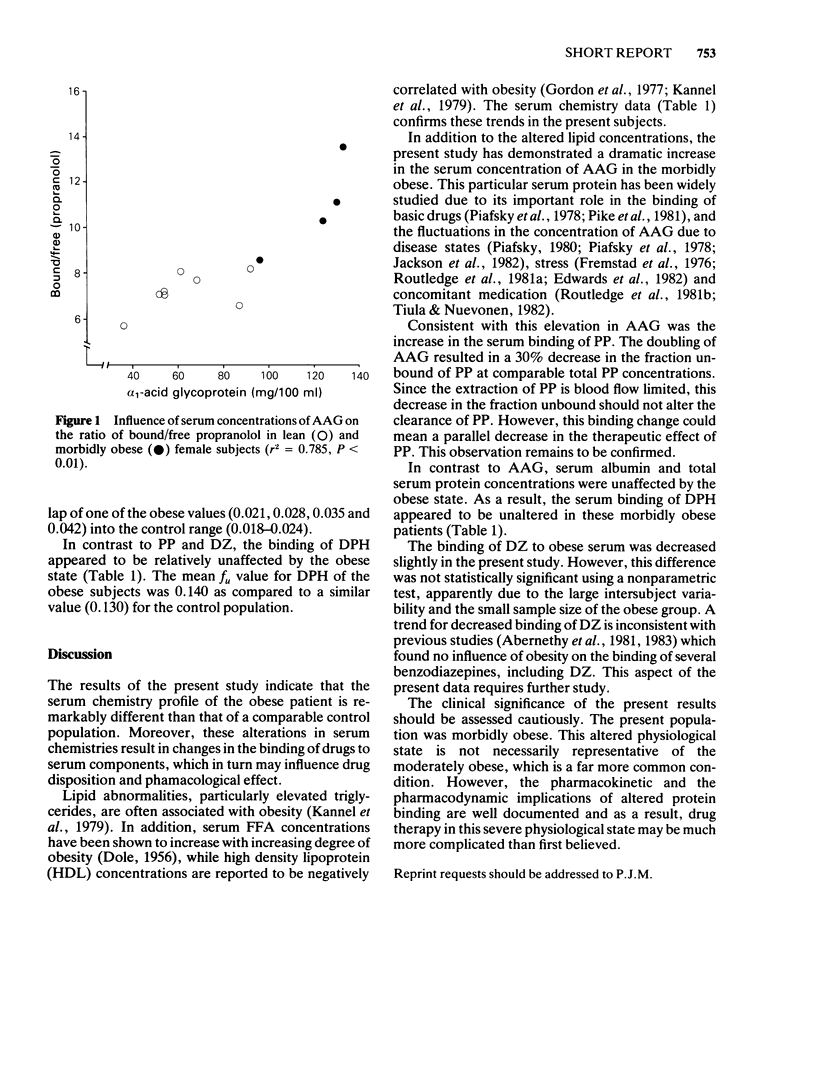
Abstract
Although clinically relevant, drug-protein interactions in the morbidly obese population have not been studied thoroughly. The objective of this study was to evaluate serum chemistry profiles and the degree of serum protein binding of propranolol, diazepam and phenytoin in the serum of four female, morbidly obese (greater than 190% of ideal body weight) and eight control female subjects. Serum triglyceride concentrations were higher and high-density lipoproteins were lower in the obese subjects than in the control group. Serum albumin and total protein concentrations in the obese were not different from controls. Unexpectedly, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein concentrations were doubled in the obese subjects (mean obese value 121 mg/100 ml vs 62.9 mg/100 ml for the control subjects). Obese subjects had a mean fraction unbound (fu) for propranolol of 0.086, which was significantly different from the controls (fu = 0.123). The binding of diazepam was decreased slightly in the obese subjects. The binding of phenytoin was similar in both groups. The altered serum chemistry of obesity may play a significant role in the drug management of the obese patient by altering drug-protein interactions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abernethy D. R., Greenblatt D. J., Divoll M., Harmatz J. S., Shader R. I. Alterations in drug distribution and clearance due to obesity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jun;217(3):681–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abernethy D. R., Greenblatt D. J. Pharmacokinetics of drugs in obesity. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Mar-Apr;7(2):108–124. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. J., Lalka D., Cerra F., Slaughter R. L. Alpha1-acid glycoprotein concentration and protein binding in trauma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Jan;31(1):62–67. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. H., Nies A. S., Shand D. G. The disposition of propranolol. 3. Decreased half-life and volume of distribution as a result of plasma binding in man, monkey, dog and rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jul;186(1):114–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremstad D., Bergerud K., Haffner J. F., Lunde P. K. Increased plasma binding of quinidine after surgery: a preliminary report. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1976;10(6):441–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00563081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. Diabetes, blood lipids, and the role of obesity in coronary heart disease risk for women. The Framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Oct;87(4):393–397. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-4-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. R., Tucker G. T., Woods H. F. Altered plasma drug binding in cancer: role of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and albumin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Sep;32(3):295–302. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Gordon T., Castelli W. P. Obesity, lipids, and glucose intolerance. The Framingham Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jun;32(6):1238–1245. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.6.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell S., Tibbling G. Colorimetric micro-determination of free fatty acids in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Apr;16(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M., Borgá O., Odar-Cederlöf I., Johansson C., Sjöqvist F. Increased plasma protein binding of propranolol and chlorpromazine mediated by disease-induced elevations of plasma alpha1 acid glycoprotein. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1435–1439. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M. Disease-induced changes in the plasma binding of basic drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 May-Jun;5(3):246–262. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005030-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike E., Skuterud B., Kierulf P., Fremstad D., Abdel Sayed S. M., Lunde P. K. Binding and displacement of basic, acidic and neutral drugs in normal and orosomucoid-deficient plasma. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1981 Sep-Oct;6(5):367–374. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198106050-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Shand D. G., Barchowsky A., Wagner G., Stargel W. W. Relationship between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and lidocaine disposition in myocardial infarction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Aug;30(2):154–157. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Stargel W. W., Finn A. L., Barchowsky A., Shand D. G. Lignocaine disposition in blood in epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;12(5):663–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiula E., Neuvonen P. J. Antiepileptic drugs and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 28;307(18):1148–1148. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210283071813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Commentary: a physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):377–390. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yacobi A., Levy G. Comparative pharmacokinetics of coumarin anticoagulants. XIV: relationship between protein binding, distribution, and elimination kinetics of warfarin in rats. J Pharm Sci. 1975 Oct;64(10):1660–1664. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600641015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


