Abstract
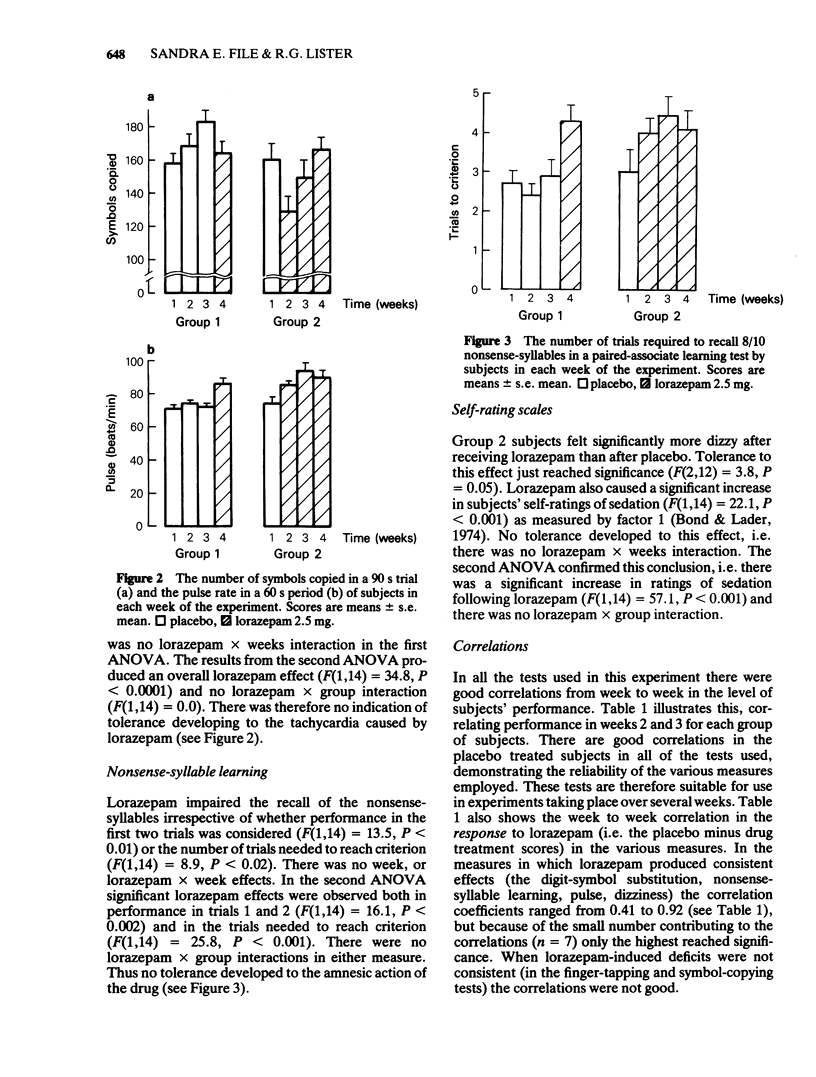
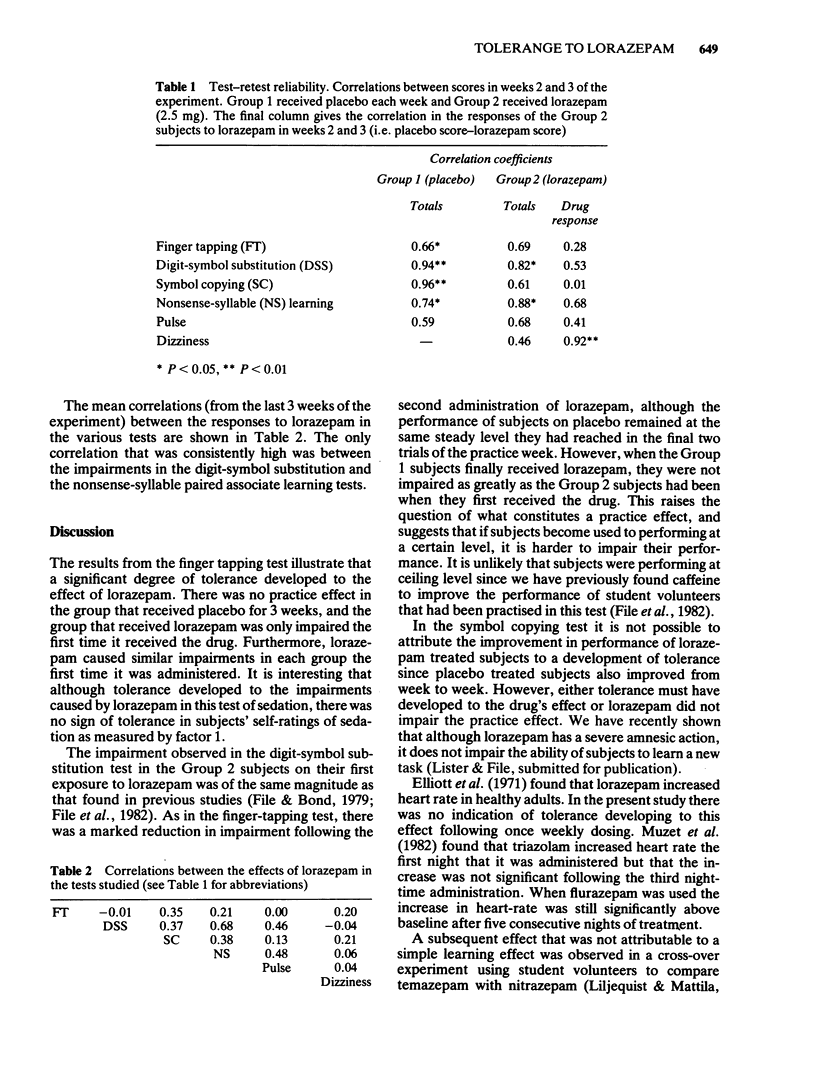
The effect of once weekly administration of lorazepam (2.5 mg) to benzodiazepine-naive student volunteers was assessed in a number of performance tests and on self-ratings. Tolerance developed to the effects of lorazepam on finger-tapping and on self-ratings of dizziness. No tolerance was observed to the drug-induced impairment in a nonsense-syllable paired associate learning test or to the effects on self-ratings of sedation or on heart rate. It is suggested that the reduced impairment in the digit-symbol substitution test observed in weeks 2 and 3 of lorazepam treatment was due to a 'masked' practice effect rather than to tolerance. Test-retest correlation coefficients were calculated for all the tests used. The effect of lorazepam in each test was also correlated with its effect in the other tests. There were significant correlations in performance on placebo in the finger-tapping (r = 0.66), digit-symbol substitution (r = 0.94), symbol copying (r = 0.96) and nonsense-syllable learning (r = 0.74) tests. It is suggested that benzodiazepine experience should be given to drug-naive subjects before they are used in cross-over experiments that involve this class of compound, since the major change in impairment occurred between the first and second exposure to lorazepam.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ameer B., Greenblatt D. J. Lorazepam: a review of its clinical pharmacological properties and therapeutic uses. Drugs. 1981 Mar;21(3):162–200. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198121030-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aranko K., Mattila M. J., Seppälä T. Development of tolerance and cross-tolerance to the psychomotor actions of lorazepam and diazepam in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 May;15(5):545–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond A., Lader M. Correlations among measures of response to benzodiazepines in man. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983 Feb;18(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(83)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane L. A., Nicholson A. N., Stone B. M. Variability of response to hypnotics: sleep studies in man. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983 Feb;18(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(83)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. W., Nomof N., Navarro G., Ruelius H. W., Knowles J. A., Comer W. H. Central nervous system and cardiovascular effects of lorazepam in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 May-Jun;12(3):468–481. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971123468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- File S. E., Bond A. J. Impaired performance and sedation after a single dose of lorazepam. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979;66(3):309–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00428325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- File S. E., Bond A. J., Lister R. G. Interaction between effects of caffeine and lorazepam in performance tests and self-ratings. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1982 Apr;2(2):102–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindmarch I. Psychomotor function and psychoactive drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;10(3):189–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinknecht R. A., Donaldson D. A review of the effects of diazepam on cognitive and psychomotor performance. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1975 Dec;161(6):399–414. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197512000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljequist R., Mattila M. J. Acute effects of temazepam and nitrazepam on psychomotor skills and memory. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1979 May;44(5):364–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1979.tb02346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila M. J., Palva E., Savolainen K. Caffeine antagonizes diazepam effects in man. Med Biol. 1982 Apr;60(2):121–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzet A., Johnson L. C., Spinweber C. L. Benzodiazepine hypnotics increase heart rate during sleep. Sleep. 1982;5(3):256–261. doi: 10.1093/sleep/5.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenborn J. R. Effects of benzodiazepines on psychomotor performance. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979;7 (Suppl 1):61S–67S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb04667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


