Abstract
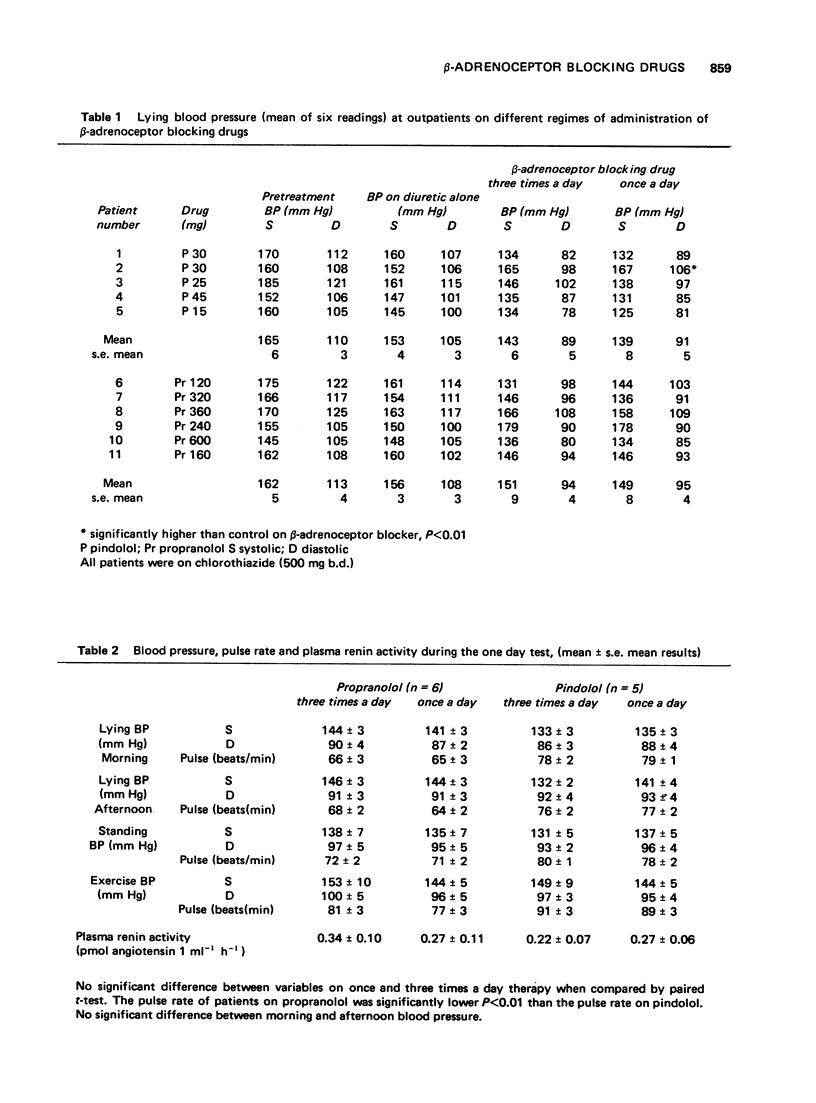
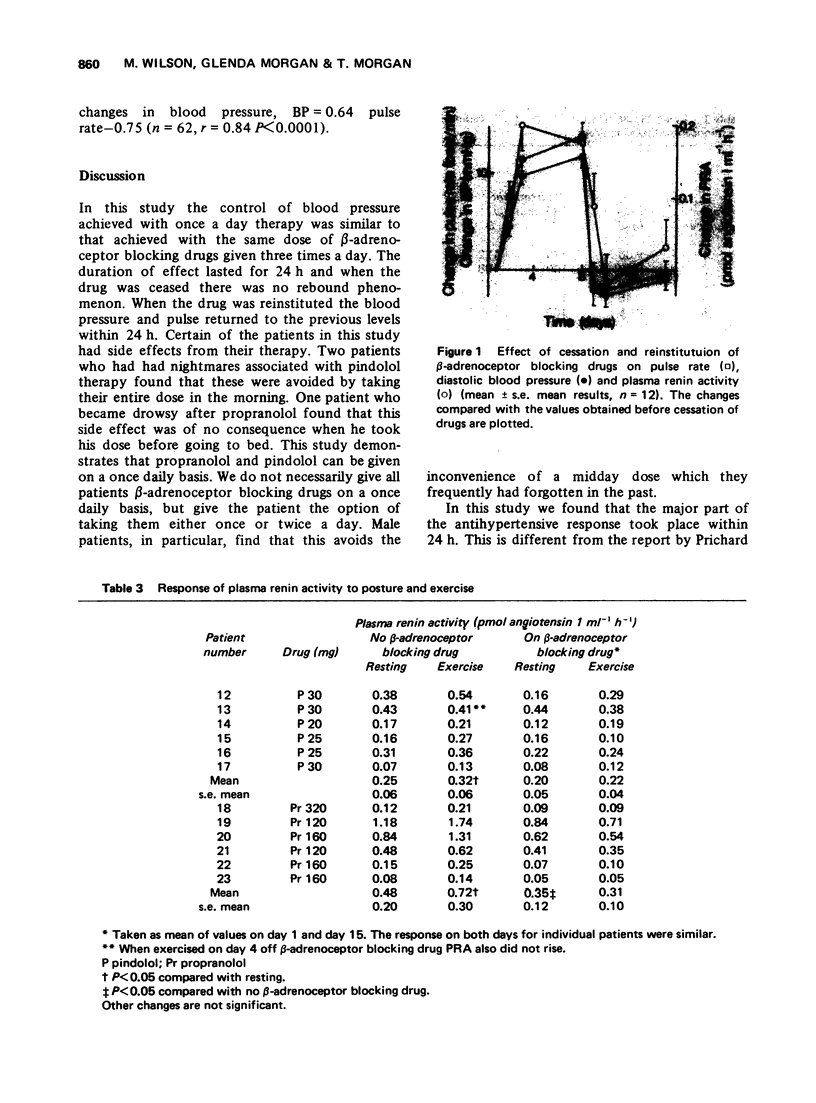
The control of blood pressure achieved was similar whether pindolol or propranolol was given once or three times daily. When the drugs were ceased the antihypertensive effect lasted for longer than 24 h. There was no rebound hypertension. The full effect of the drug on blood pressure was seen within 24 h of its recommencement. Changes in blood pressure, pulse rate, and plasma renin activity occurred but these were not considered to be causally related. The response of plasma renin activity to posture was ablated when the patients were receiving beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Baer L., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Brunner H. R. Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion. A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive diseases. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 14;287(24):1209–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212142872401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. N. Hypertension--1974. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Jun;133(6):911–913. doi: 10.1001/archinte.133.6.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L., Hunyor S. N., Julius S., Hoobler S. W. Blood pressure crisis following withdrawal of clonidine (Catapres, Catapresan), with special reference to arterial and urinary catecholamine levels, and suggestions for acute management. Am Heart J. 1973 May;85(5):605–610. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(73)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T. O., Roberts R., Carney S. L., Louis W. J., Doyle A. E. Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking drugs, hypertension and plasma renin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;2(2):159–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb01571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard B. N., Gillam P. M. Treatment of hypertension with propranolol. Br Med J. 1969 Jan 4;1(5635):7–16. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5635.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


