Abstract
1 Nine healthy volunteers participated in a comparative study of the effects of nomifensine, nomifensine plus alcohol, and placebo plus alcohol, on aspects of psychomotor performance.
2 The study was carried out according to a Latin square design and each treatment was separated from the preceding treatment by 7 days.
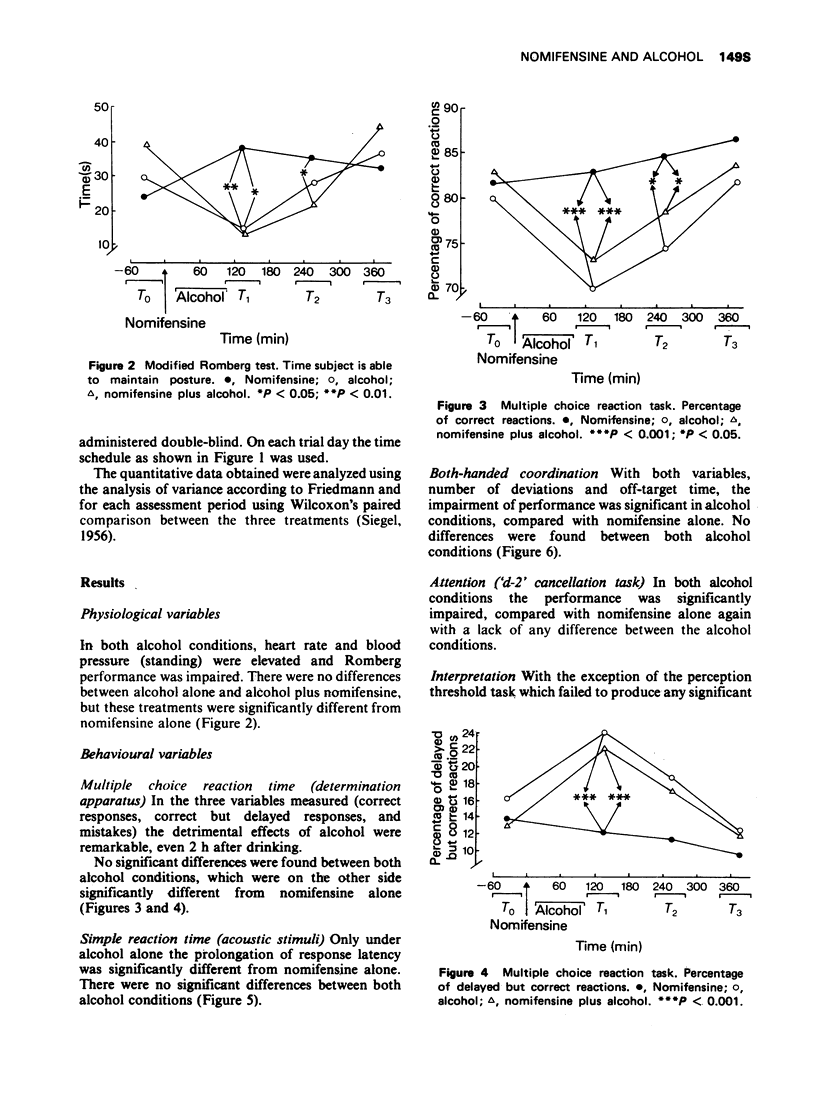
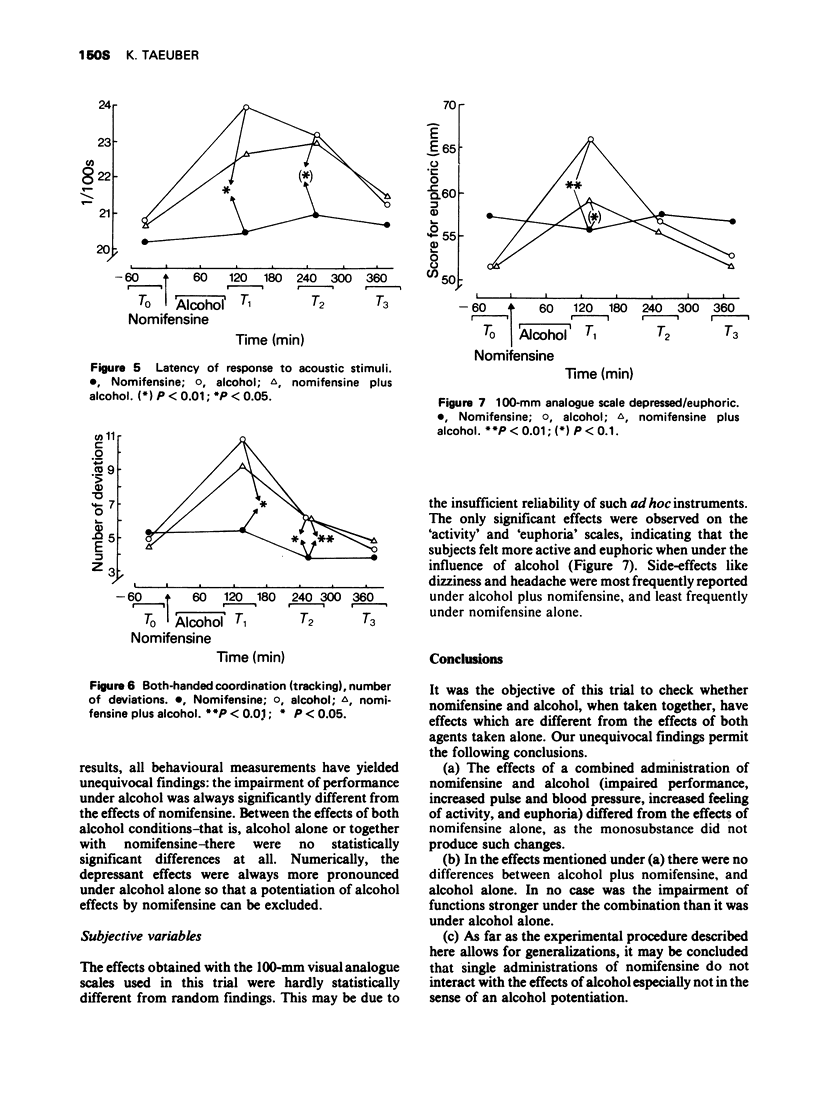
3 Placebo plus alcohol impaired performance, increased pulse rate and blood pressure, and increased feelings of activity and euphoria.
4 Nomifensine plus alcohol produced the same subjective and objective changes as placebo plus alcohol, but in no instance were changes any greater.
5 Nomifensine alone produced none of these changes.
6 It was concluded that single doses of nomifensine did not potentiate the effect of alcohol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hindmarch I. Laboratory investigation of effect of acute doses of nomifensine on a simulated aspect of night-time car driving performance. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1977;4(Suppl 2):175S–178S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1977.tb05748.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenborn J. R., Flaherty C. F., Jr, McGough W. E., Bossange K. A., Nash R. J. A comparison of the effect of imipramine, nomifensine, and placebo on the psychomotor performance of normal males. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Dec 21;51(1):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00426327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


