Abstract
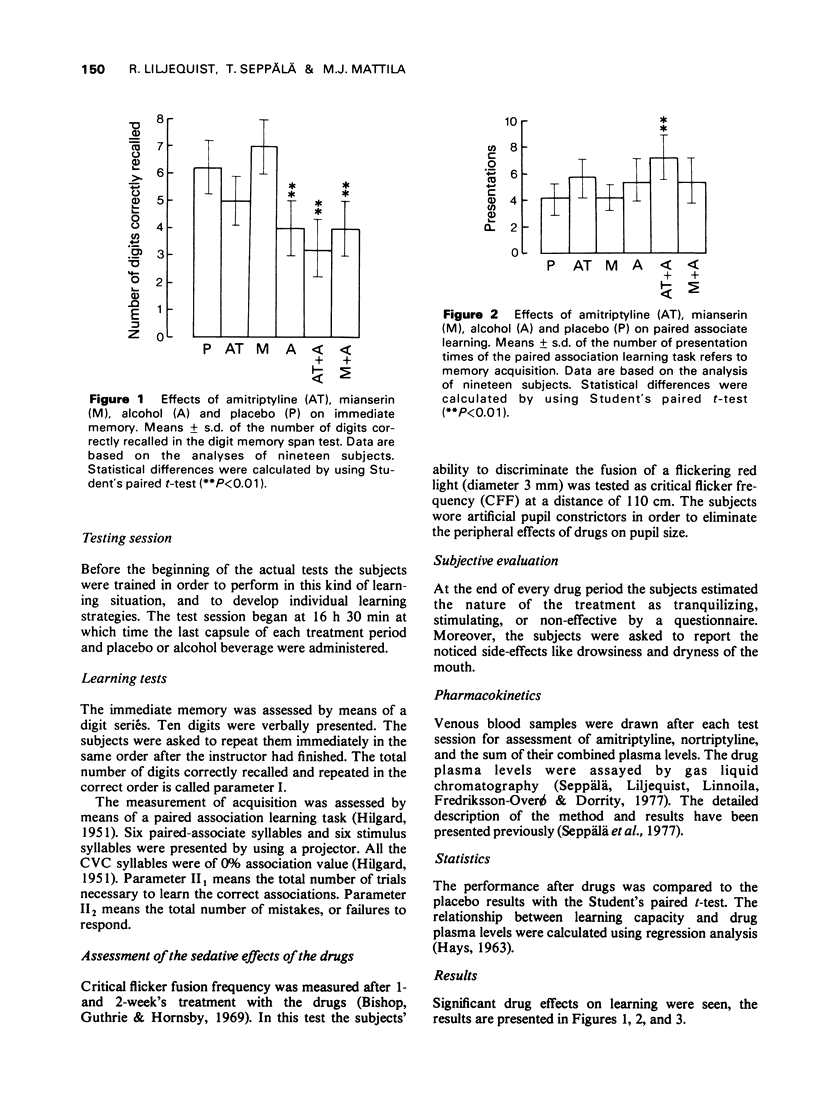
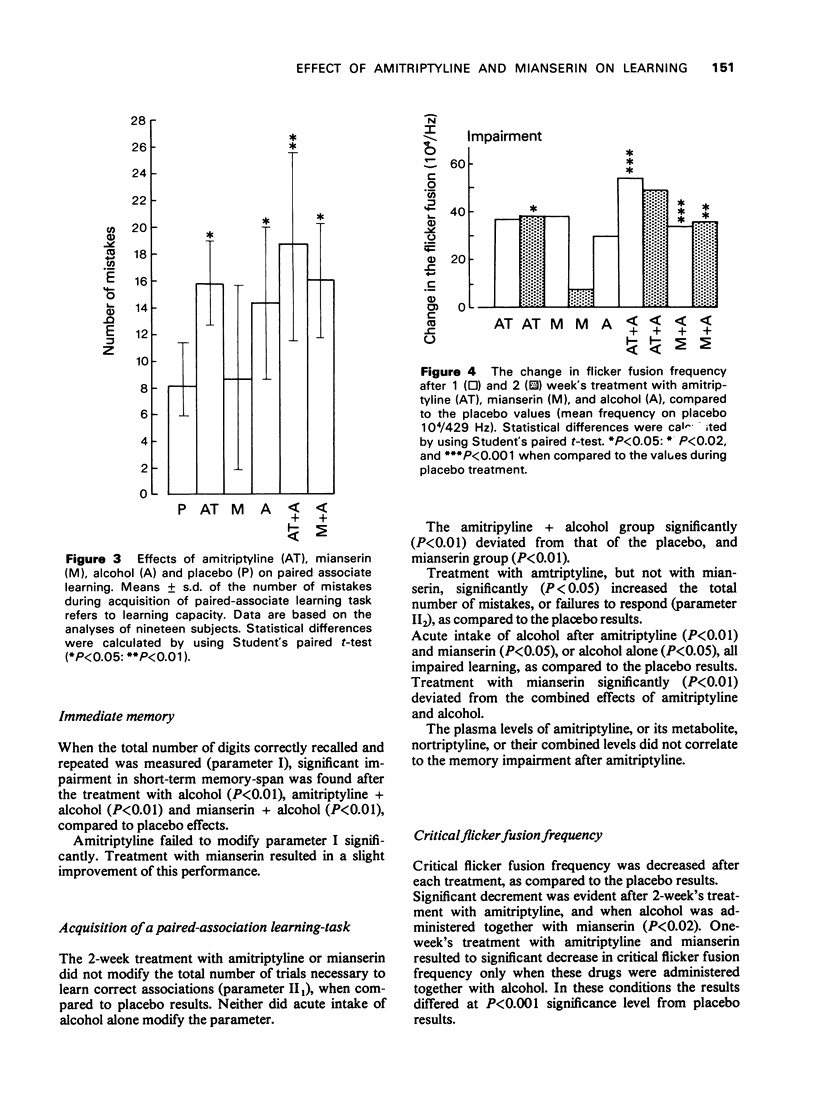
1 The double-blind study on twenty healthy students was an attempt at assessing the effects of 2-week's treatment with amitriptyline (25 mg three times a day) and mianserin (10 mg three times a day), each alone or separatively inbibed with alcohol (0.5 g/kg) on the immediate memory and on the acquisition of a paired-association learning-task. 2 Amitriptyline impaired both the short-term memory-span and acquisition, and alcohol potentiated these effects. The action of mianserin did not deviate significantly from that of the placebo, and it also failed to interact with alcohol. 3 It is concluded that the decrement in learning capacity, that occurs after the 2-week's treatment with therapeutic doses of amitriptyline, reflects changes in both the intrinsic and the regulatory mechanisms of learning.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURESOVA O., BURES J., BOHDANECKY Z., WEISS T. EFFECT OF ATROPINE ON LEARNING, EXTINCTION, RETENTION AND RETRIEVAL IN RATS. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Mar 11;5:255–263. doi: 10.1007/BF02341258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohdanecký Z., Jarvik M. E. Impairment of one-trial passive avoidance learning in mice by scopolamine, scopolamine methylbromide, and physostigmine. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1967 May;6(3):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(67)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson A., Lindqvist M. Effect of ethanol on the hydroxylation of tyrosine and tryptophan in rat brain in vivo. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Jun;25(6):437–440. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb09129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppen A., Gupta R., Montgomery S., Ghose K., Bailey J., Burns B., de Ridder J. J. Mianserin hydrochloride: a novel antidepressant. Br J Psychiatry. 1976 Oct;129:342–345. doi: 10.1192/bjp.129.4.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. The effect of ethanol on the activity of central catecholamine neurones in rat brain. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Dec;18(12):821–823. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghose K., Coppen A., Turner P. Autonomic actions and interactions of mianserin hydrochloride (Org. GB 94) and amitriptyline in patients with depressive illness. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Sep 17;49(2):201–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00427291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafoe W. F., Leonard B. E. The effect of a new tetracyclic anti-depressant compound, Org GB 94, on the turnover of dopamine, noradrenalin and serotonin in the rat brain. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1973 Dec;206(2):389–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannengiesser M. H., Hunt P., Raynaud J. P. An in vitro model for the study of psychotropic drugs and as a criterion of antidepressant activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Jan 1;22(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90256-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljequist R., Linnoila M., Mattila M. J. Effect of two weeks treatment with chlorimipramine and nortriptyline, alone or in combination with alcohol on learning and memory. Psychopharmacologia. 1974;39(2):181–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00440847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljequist R., Linnoila M., Mattila M. J., Saario I., Seppälä T. Effect of two weeks' treatment with thioridazine, chlorpromazine, sulpiride and bromazepam, alone or in combination with alcohol, on learning and memory in man. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Oct 31;44(2):205–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00421011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Angelini F., Bertollini A. Comparative study of the effects of mianserin, a tetracyclic antidepressant, and of imipramine on uptake and release of neurotransmitters in synaptosomes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;28(6):483–488. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb02770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä T., Linnoila M., Elonen E., Mattila M. J., Mäki M. Effect of tricyclic antidepressants and alcohol in psychomotor skills related to driving. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 May;17(5):515–522. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975175515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä T. Psychomotor skills during acute and two-week treatment with mianserin (ORG GB 94) and amitriptyline, and their combined effects with alcohol. Ann Clin Res. 1977 Apr;9(2):66–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Coignet J. L., de Vos C. J., Grijsen H., Bonta I. L. Mianserin hydrochloride: peripheral and central effects in relation to antagonism against 5-hydroxytryptamine and tryptamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Nov-Dec;16(3):336–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITEHOUSE J. M. EFFECTS OF ATROPINE ON DISCRIMINATION LEARNING IN THE RAT. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1964 Feb;57:13–15. doi: 10.1037/h0043889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


