Abstract
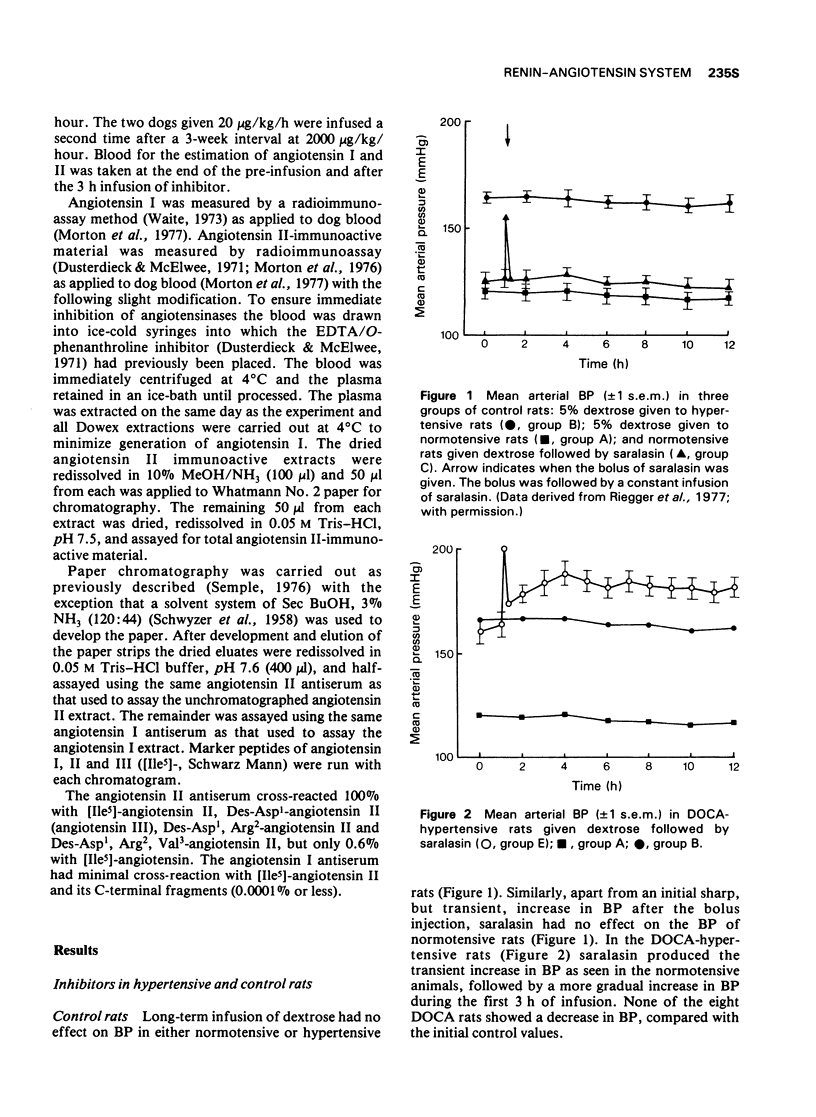
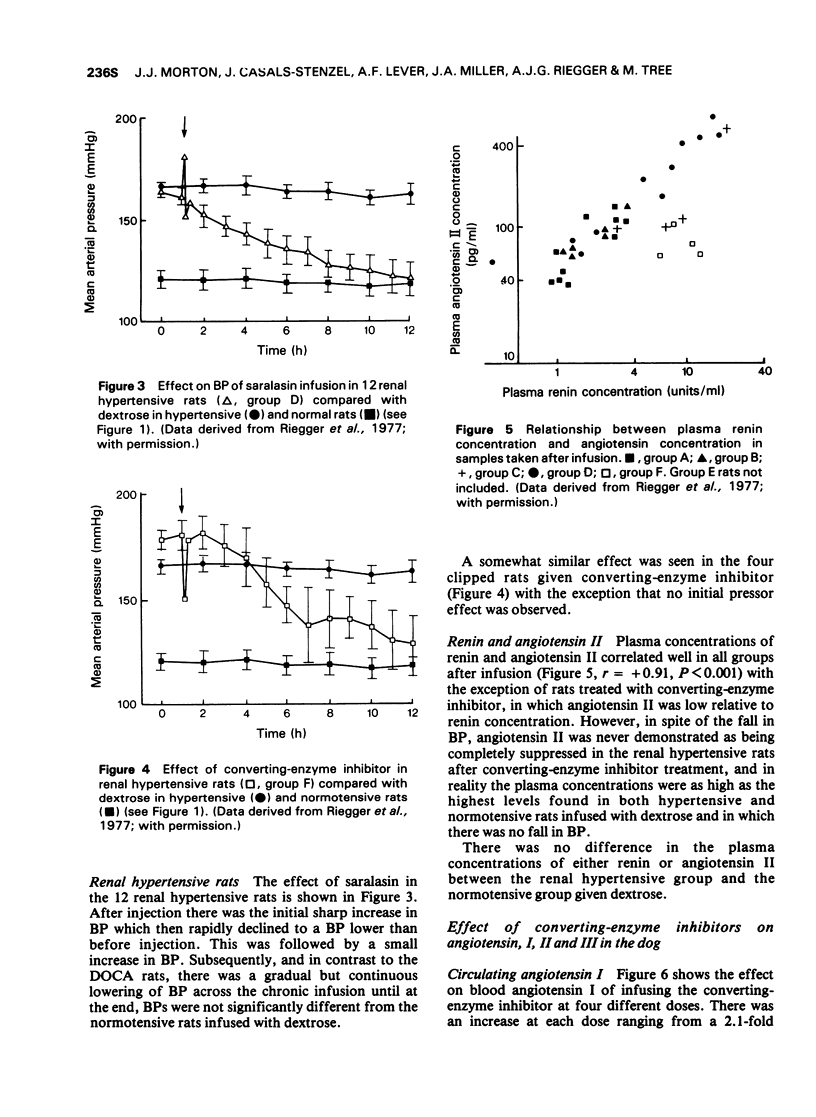
1 Prolonged infusion (11 h) of both saralasin and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (SQ20881) gradually lowered BP in two-kidney hypertensive rats to levels similar to that in normotensive rats infused with dextrose.
2 Saralasin did not lower BP in DOCA-salt-hypertensive rats.
3 These observations support the notion that in chronic renal hypertension, angiotensin II may maintain hypertension by a slowly developing action.
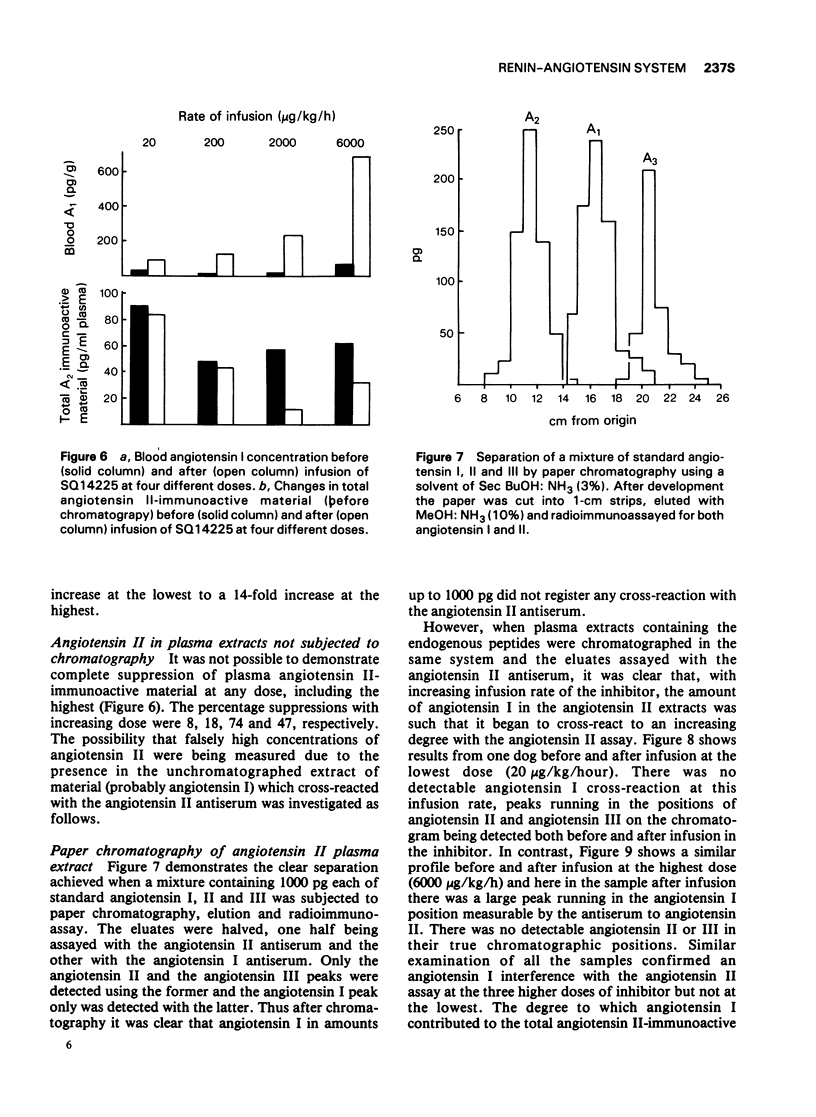
4 Plasma angiotensin II in rats infused with SQ20881 was suppressed relative to renin, but was not eliminated.
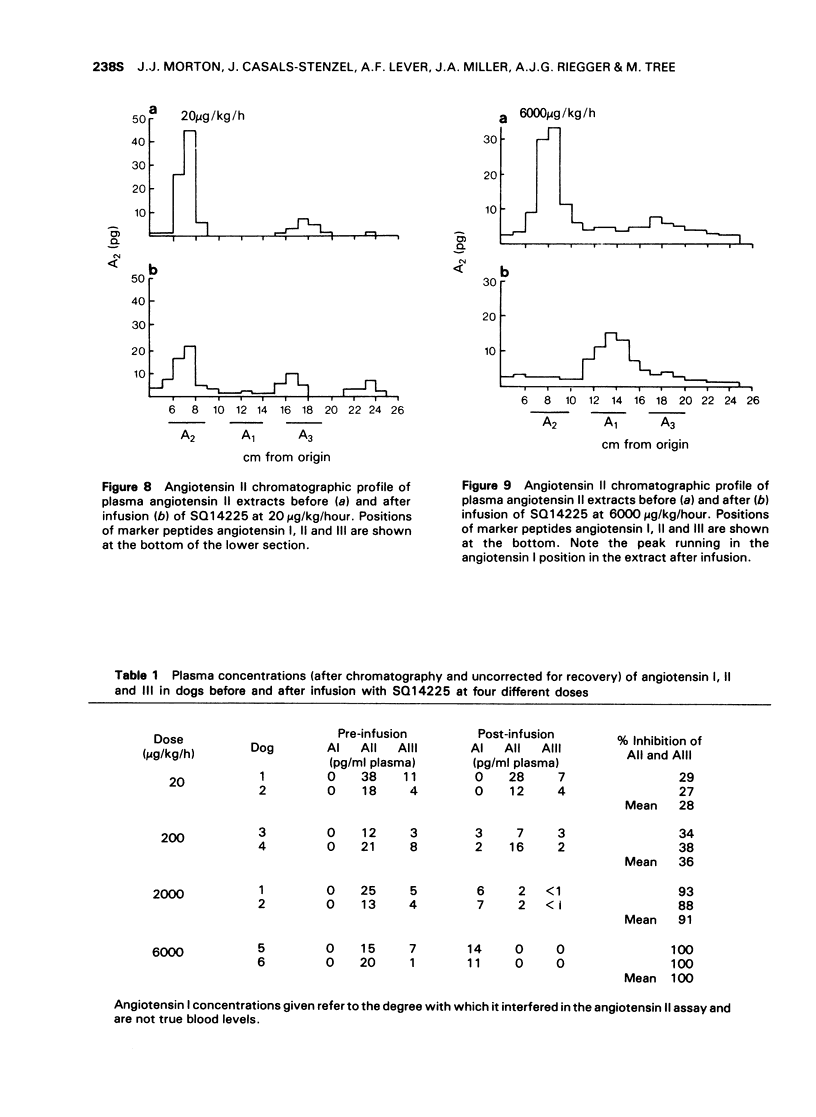
5 Chromatography of angiotensin II extracts from dogs infused with converting enzyme inhibitor (SQ14,225) showed that the very high levels of angiotensin I achieved after treatment with SQ14,225 can lead to falsely high estimated angiotensin II levels as a result of angiotensin I cross-reacting with the angiotensin II assay.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchi G., Baldoli E., Lucca R., Barbin P. Pathogenesis of arterial hypertension after the constriction of the renal artery leaving the opposite kidney intact both in the anaesthetized and in the conscious dog. Clin Sci. 1972 Jun;42(6):651–664. doi: 10.1042/cs0420651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. J., Brown W. C., Fraser R., Lever A. F., Morton J. J., Robertson J. I., Rosei E. A., Trust P. M. The effects of saralasin, an angiotensin II antagonist, on blood pressure and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in normal and hypertensive subjects. Aust N Z J Med. 1976 Aug;6(3 Suppl):48–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1976.tb03335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. J., Davies D. L., Morton J. J., Robertson J. I., Cuesta V., Lever A. F., Padfield P. L., Trust P. Mechanism of renal hypertension. Lancet. 1976 Jun 5;1(7971):1219–1221. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. R., Kirshman J. D., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H. Hypertension of renal origin: evidence for two different mechanisms. Science. 1971 Dec 24;174(4016):1344–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caravaggi A. M., Bianchi G., Brown J. J., Lever A. F., Morton J. J., Powell-Jackson J. D., Robertson J. I., Semple P. F. Blood pressure and plasma angiotensin II concentration after renal artery constriction and angiotensin infusion in the dog. (5-Isoleucine)angiotensin II and its breakdown fragments in dog blood. Circ Res. 1976 Apr;38(4):315–321. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.4.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. G., Guyton A. C. The pressor role of angiotensin in salt deprivation and renal hypertension in rats. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1975 Jun;2:45s–48s. doi: 10.1042/cs048045s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley A. W., DeClue J. W. Quantification of baroreceptor influence on arterial pressure changes seen in primary angiotension-induced hypertension in dogs. Circ Res. 1976 Dec;39(6):779–787. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.6.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKINSON C. J., LAWRENCE J. R. A slowly developing pressor response to small concentrations of angiotensin. Its bearing on the pathogenesis of chronic renal hypertension. Lancet. 1963 Jun 22;1(7295):1354–1356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91929-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düsterdieck G., McElwee G. Estimation of angiotensin II concentration in human plasma by radioimmunoassay. Some applications to physiological and clinical states. Eur J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;2(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1971.tb00565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel S. L., Schaeffer T. R., Gold B. I., Rubin B. Inhibition of pressor effects of angiotensin I and augmentation of depressor effects of bradykinin by synthetic peptides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):240–244. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyer M. A. Renal control of interstitial space compliance: a physiological mechanism which may play a part in the etiology of hypertension. Clin Nephrol. 1975 Oct;4(4):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras H., Brunner H. B., Vaughan E. D., Laragh J. H. Angiotensin-sodium interaction in blood pressure maintenance of renal hypertensive and normotensive rats. Science. 1973 Jun 29;180(4093):1369–1371. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4093.1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton A. C., Young D. B., DeClue J. W., Trippodo N., Hall J. E. Fluid balance, renal function, and blood pressure. Clin Nephrol. 1975 Oct;4(4):122–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Guyton A. C., Trippodo N. C., Lohmeier T. E., McCaa R. E., Cowley A. W., Jr Intrarenal control of electrolyte excretion by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jun;232(6):F538–F544. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.6.F538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. D., Malvin R. L. Stimulation of renal sodium reabsorption by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):F298–F306. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.4.F298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald G. J., Boyd G. W., Peart W. S. Effect of the angiotensin II blocker 1-Sar-8-Ala-angiotensin II on renal artery clip hypertension in the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Nov;37(5):640–646. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.5.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki Z., Ferrario C. M., Bumpus F. M., Bravo E. L., Khosla M. C. The course of arterial pressure and the effect of Sar1-Thr8-angiotensin II in a new model of two-kidney hypertension in conscious dogs. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Feb;52(2):163–170. doi: 10.1042/cs0520163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubbin J. W., DeMoura R. S., Page I. H., Olmsted F. Arterial hypertension elicited by subpressor amounts of angiotensin. Science. 1965 Sep 17;149(3690):1394–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3690.1394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. D., Jr, Samuels A. I., Haber E., Barger A. C. Inhibition of angiotensin conversion and prevention of renal hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1975 Feb;228(2):448–453. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.2.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. J., Semple P. F., Ledingham I. M., Stuart B., Tehrani M. A., Garcia A. R., McGarrity G. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (SQ 20881) on the plasma concentration of angiotensin I, angiotensin II, and arginine vasopressin in the dog during hemorrhagic shock. Circ Res. 1977 Sep;41(3):301–308. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhring J., Möhring B., Näumann H-J, Philippi A., Homsy E., Orth H., Dauda G., Kazda S. Salt and water balance and renin activity in renal hypertension of rats. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1847–1855. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pals D. T., Masucci F. D., Denning G. S., Jr, Sipos F., Fessler D. C. Role of the pressor action of angiotensin II in experimental hypertension. Circ Res. 1971 Dec;29(6):673–681. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.6.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Jackson F. D., Macgregor J. Radioimmunoassay of angiotensin II in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1976 Jan;68(1):175–176. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0680175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegger A. J., Lever A. F., Millar J. A., Morton J. J., Slack B. Correction of renal hypertension in the rat by prolonged infusion of angiotensin inhibitors. Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1317–1319. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobian L., Coffee K., McCrea P. Contrasting exchangeable sodium in rats with different types of Goldblatt hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1969 Aug;217(2):458–460. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M. A. Measurement of concentrations of angiotensin I in human blood by radioimmunoassay. Clin Sci. 1973 Jul;45(1):51–64. doi: 10.1042/cs0450051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


