Abstract
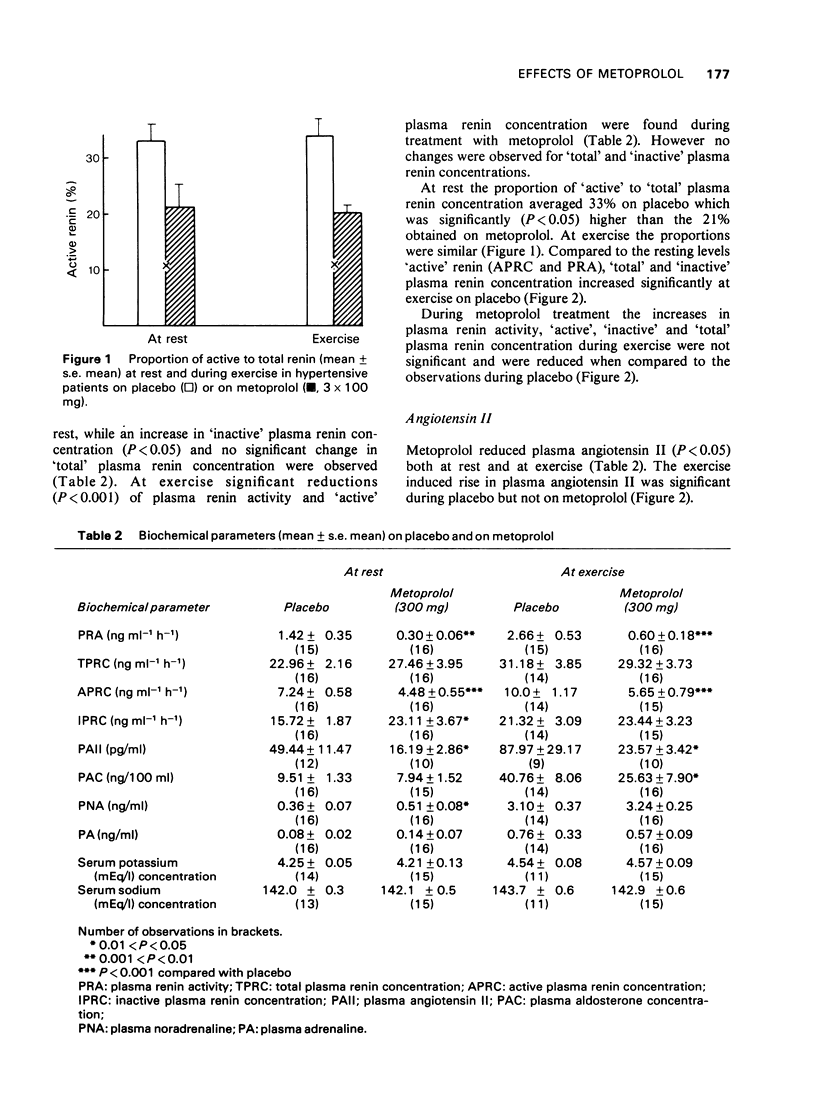
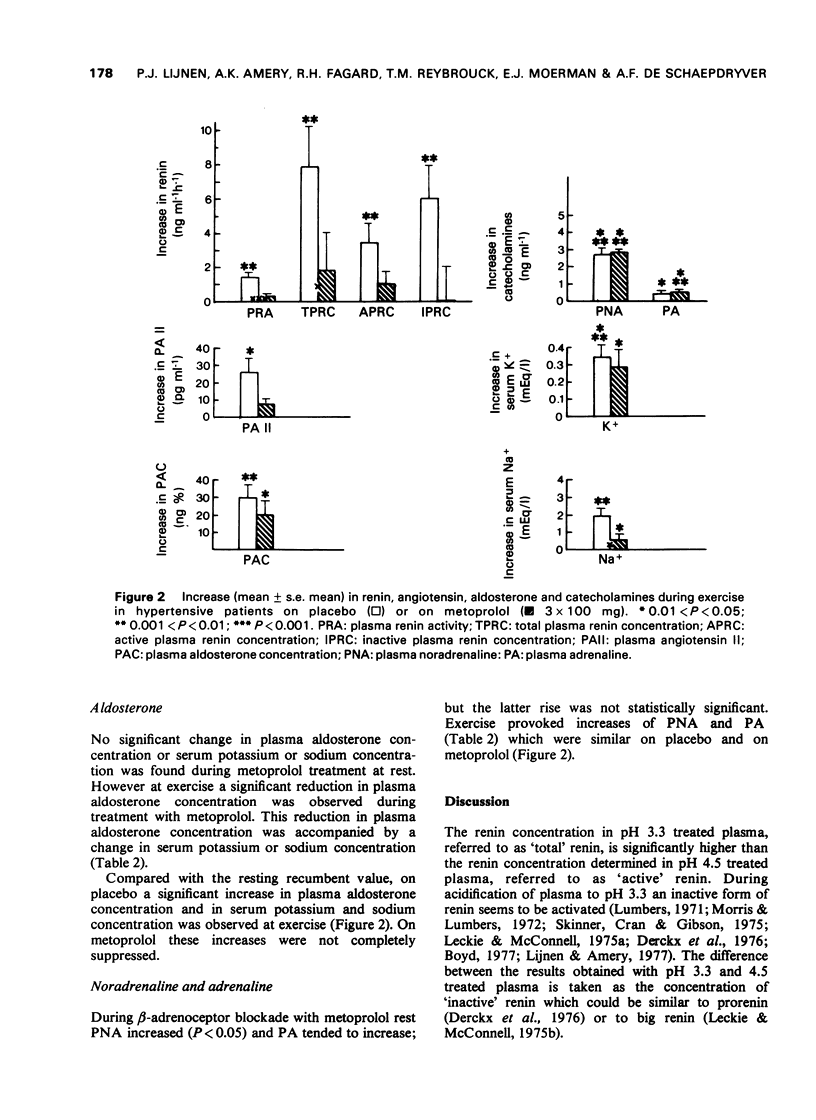
1 beta-adrenoceptor blockade with metoprolol provoked, both at rest and during exercise, a decrease of 'active' renin and angiotensin II together with an increase of 'inactive' renin and unchanged 'total' renin. The significant exercise-provoked increases in angiotensin II, plasma renin activity and 'active', 'inactive' and 'total' renin when on placebo, were reduced by metoprolol. 2 No significant change in serum sodium and potassium and in plasma aldosterone was found during beta-adrenoceptor blockade at rest. During exercise plasma aldosterone dropped significantly without any change in serum sodium or potassium. 3 Plasma noradrenaline increased significantly at rest on metoprolol. The increase in plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline during exercise was similar on placebo and on metoprolol.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberg H. Plasma renin activity after the use of a new beta-adrenergic blocking agent (I.C.I. 66,032). Int J Clin Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;9(2):98–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amery A., Billiet L., Fagard R. Letter: Beta receptors and renin release. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 31;290(5):284–284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401312900516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amery A., Lijnen P., Fagard R., Reybrouck T. Atenolol and plasma renin concentration in hypertensive patients. Postgrad Med J. 1977;53 (Suppl 3):116–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H., Moon C. Plasma renin and "prorenin" in essential hypertension during sodium depletion, beta-blockade, and reduced arterial pressure. Lancet. 1977 Oct 15;2(8042):785–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90723-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attman P. O., Aurell M., Johnsson G. Effects of metoprolol and propranolol on furosemide-stimulated renin release in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Apr 4;8(3-4):201–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00567115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenhäger W. H., Krauss X. H., Schalekamp M. A., Kolsters G., Kroon B. J. Antihypertensive effects of propranolol. Observations on predictability. Folia Med Neerl. 1971;14(2):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonelli J., Waldhäusl W., Magometschnigg D., Schwarzmeier J., Korn A., Hitzenberger G. Effect of exercise and of prolonged oral administration of propranolol on haemodynamic variables, plasma renin concentration, plasma aldosterone and c-AMP. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;7(5):337–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Baer L., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Brunner H. R. Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion. A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive diseases. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 14;287(24):1209–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212142872401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodakowska J., Nazar K., Wocial B., Jarecki M., Skórka B. Plasma catecholamines and renin activity in response to exercise in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Nov;49(5):511–514. doi: 10.1042/cs0490511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. P., Luetscher J. A. Biochemical properties of big renin extracted from human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jun;40(6):1085–1093. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-6-1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. P., Luetscher J. A., Gonzales C. M. Occurrence of big renin in human plasma, amniotic fluid and kidney extracts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jun;40(6):1078–1084. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-6-1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkx F. H., von Gool J. M., Wenting G. J., Verhoeven R. P., Man in 't Veld A. J., Schalekamp M. A. Inactive renin in human plasma. Lancet. 1976 Sep 4;1(7984):496–499. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90791-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub M. S., Speckart P. F., Zia P. K., Horton R. The effect of prostaglandin A1 on renin and aldosterone in man. Circ Res. 1976 Oct;39(4):574–579. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.4.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klumpp F., Braun B., Klaus D., Lemke R., Zehner J. Die Behandlung der essentiellen Hypertonie mit Propranolol. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1976 Oct 8;101(41):1482–1488. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1104295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotchen T. A., Hartley L. H., Rice T. W., Mougey E. H., Jones L. G., Mason J. W. Renin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine responses to graded exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Aug;31(2):178–184. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckie B. J., McConnell A. A renin inhibitor from rabbit kidney: conversion of a large inactive renin to a smaller active enzyme. Circ Res. 1975 Apr;36(4):513–519. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen P. F., Amery A. K., Fagard R. H. Comparison between a biological and a radioimmunological assay of plasma renin concentration. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 1;61(1):32–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80164-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen P. J., Amery A. K., Fagard R. H. Direct radioimmunoassay of plasma angiotensin II [proceedings]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1977 Dec;85(5):996–997. doi: 10.3109/13813457709053326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen P. J., Amery A. K., Fagard R. H., Reybrouck T. M. Relative significance of plasma renin activity and concentration in physiologic and pathophysiologic conditions. Angiology. 1978 May;29(5):354–366. doi: 10.1177/000331977802900502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen P., Amery A., Fagard R., Corvol P. Direct radioimmunoassay of plasma aldosterone in normal subjects. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Mar 15;84(3):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90246-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., McAllister R. G. The effect of chronic adrenergic receptor blockade on plasma renin activity in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Feb;34(2):386–394. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-2-386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman E. J., Bogaert M. G., de Schaepdryver A. F. Estimation of plasma catecholamines in man. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Oct 1;72(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Lumbers E. R. The activation of renin in human amniotic fluid by proteolytic enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 7;289(2):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWELL L. B., BLACKMON J. R., BRUCE R. A. INDOCYANINE GREEN CLEARANCE AND ESTIMATED HEPATIC BLOOD FLOW DURING MILD TO MAXIMAL EXERCISE IN UPRIGHT MAN. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1677–1690. doi: 10.1172/JCI105043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reybrouck T., Amery A., Billiet L. Hemodynamic response to graded exercise after chronic beta-adrenergic blockade. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Feb;42(2):133–138. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassard J., Pozet N., Vincent M., Zech P. Y. Letter: Atenolol and renin release. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):787–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Moon C., Laragh J. H., Alderman M. Plasma prorenin: cryoactivation and relationship to renin substrate in normal subjects. Am J Med. 1976 Nov;61(5):731–738. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L., Cran E. J., Gibson R., Taylor R., Walters W. A., Catt K. J. Angiotensins I and II, active and inactive renin, renin substrate, renin activity, and angiotensinase in human liquor amnii and plasma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Mar 1;121(5):626–630. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verniory A., Staroukine M., Delwiche F., Telerman M. Effect of sotalol on haemodynamics and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in hypertensive patients. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Jul;51(1):9–17. doi: 10.1042/cs0510009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Yoon M. S., Freedman A. D. Adrenergic receptor mediation of renin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


