Abstract
1 Measurements of antipyrine clearance in saliva have been made in 128 London factory and office workers. 2 Mean antipyrine clearance in 56 Asian immigrants was 40% slower than in 72 White subjects. 3 Although dietary differences existed between the two groups, analysis of their effect independently of race was impossible since all but one of the vegetarians were Asian and the non-vegetarians were nearly all White. 4 In the White subjects, use of the oral contraceptive reduced clearance by 38% in women, while cigarette smoking increase clearance by 38% in men.
Full text
PDF
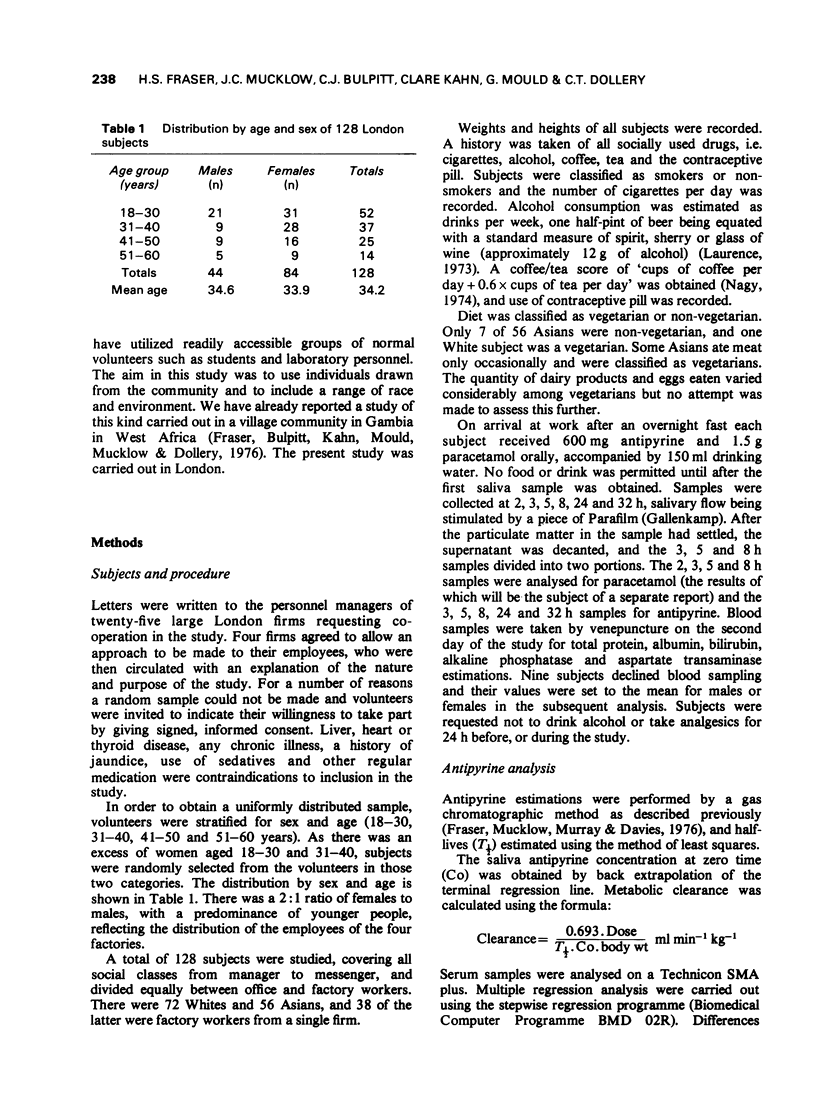
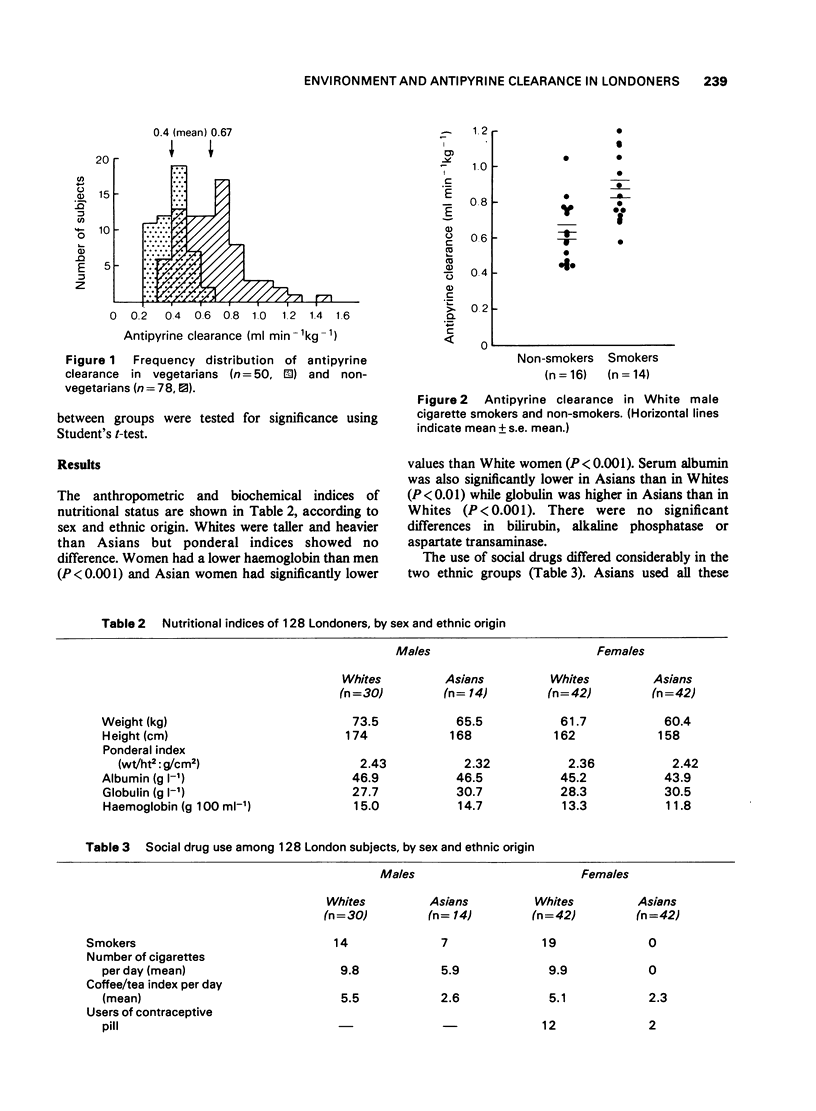
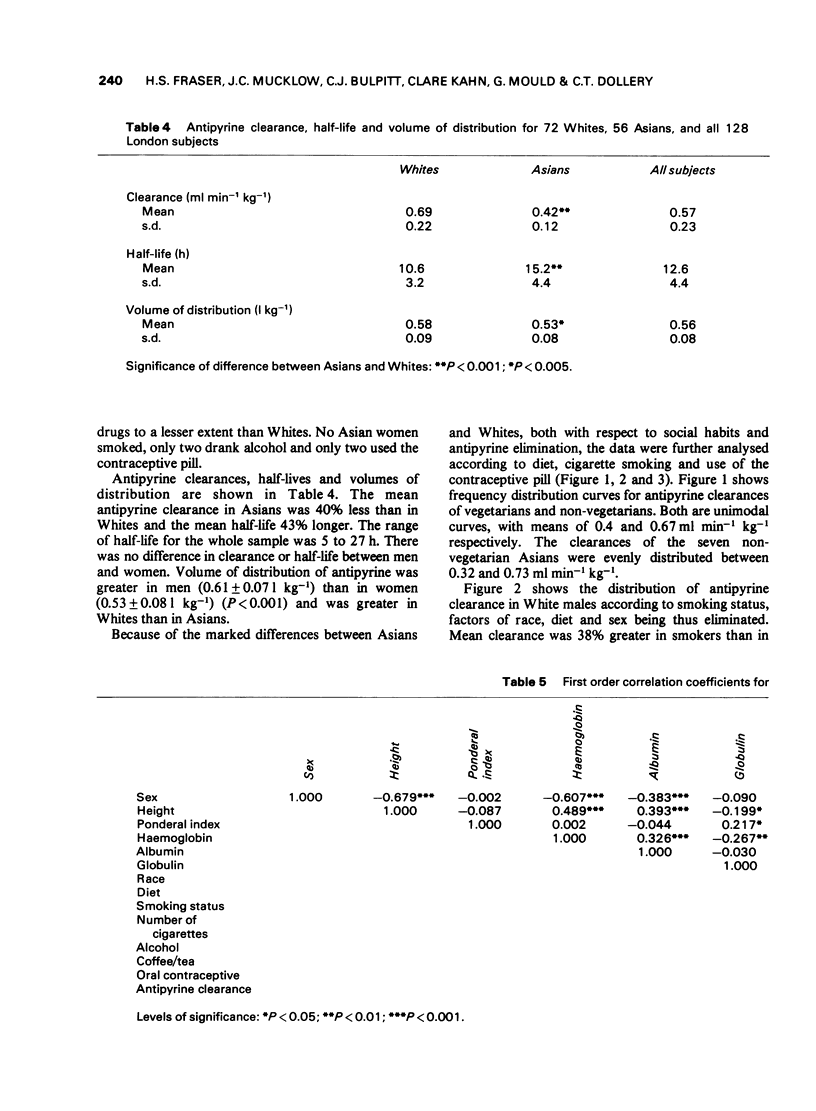
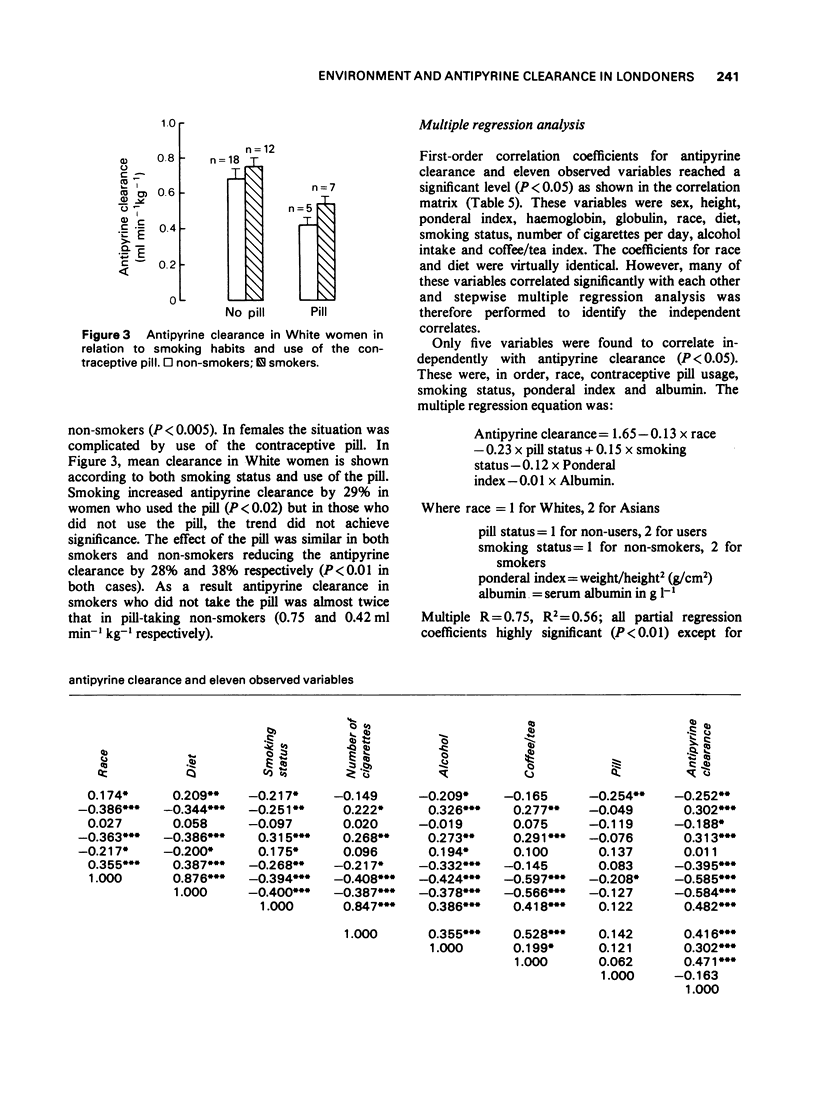


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexanderson B., Evans D. A., Sjöqvist F. Steady-state plasma levels of nortriptyline in twins: influence of genetic factors and drug therapy. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 27;4(5686):764–768. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5686.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvares A. P., Anderson K. E., Conney A. H., Kappas A. Interactions between nutritional factors and drug biotransformations in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2501–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN L. K., HANSEN J. M., KRISTENSEN M. SULPHAPHENAZOLE-INDUCED HYPOGLYCAEMIC ATTACKS IN TOLBUTAMIDE-TREATED DIABETICS. Lancet. 1963 Dec 21;2(7321):1298–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90847-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen L. K., Skovsted L. Inhibition of drug metabolism by chloramphenicol. Lancet. 1969 Dec 27;2(7635):1397–1399. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90937-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser H. S., Bulpitt C. J., Kahn C., Mould G., Mucklow J. C., Dollery C. T. Factors affecting antipyrine metabolism in West African villagers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Sep;20(3):369–376. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976203369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser H. S., Mucklow J. C., Murray S., Davies D. S. Assessment of antipyrine kinetics by measurement in saliva. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;3(2):321–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer W., Sjöqvist F. Plasma levels of monomethylated tricyclic antidepressants during treatment with imipramine-like compounds. Life Sci. 1967 Sep 1;6(17):1895–1903. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P., Farrell G. C., Cooksley W. G., Powell L. W. Enhanced drug metabolism in cigarette smokers. Br Med J. 1976 Jul 17;2(6028):147–149. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6028.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne H., Nagasawa H., McHugh R., MacDonald F., Wyse E. Decreased theophylline half-life in cigarette smokers. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 15;17(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolmodin B., Azarnoff D. L., Sjöqvist F. Effect of environmental factors on drug metabolism: decreased plasma half-life of antipyrine in workers exposed to chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Sep-Oct;10(5):638–642. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969105638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutt H., Winters W., McDowell F. H. Depression of prahydroxylation of diphenylhydantoin by antituberculosis chemotherapy. Neurology. 1966 Jun;16(6):594–602. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.6.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOESER E. W., Jr Studies on the metabolism of diphenylhydantoin (Dilantin). Neurology. 1961 May;11:424–429. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.5.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K., Stevenson I. H., Crooks J. Impairment of human drug metabolism by oral contraceptive steroids. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Jul-Aug;13(4):552–557. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972134552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K., Stevenson I. H., Wood M. Proceedings: Drug metabolizing ability in operating theatre personnel. Br J Anaesth. 1973 Aug;45(8):924–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S. Genetic and environmental factors affecting drug response in man. Fed Proc. 1972 Jul-Aug;31(4):1253–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Page J. G. Genetic control of drug levels in man: antipyrine. Science. 1968 Jul 5;161(3836):72–73. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3836.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Page J. G. Genetic control of drug levels in man: phenylbutazone. Science. 1968 Mar 29;159(3822):1479–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3822.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestal R. E., Norris A. H., Tobin J. D., Cohen B. H., Shock N. W., Andres R. Antipyrine metabolism in man: influence of age, alcohol, caffeine, and smoking. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):425–432. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


