Abstract
1 A rapid, accurate and convenient technique for determination of acetylator phenotype of patients or subjects has not been available for routine clinical application. 2 An improved method for rapid and convenient determination of acetylator phenotype is described. 3 The plasma concentrations of dapsone (DDS) and monoacetyldapsone (MAD) were measured 3 h after a single oral 100 mg dose of dapsone using a specific and sensitive high performance liquid chromatographic assay. 4 The plasma concentration ratio of monoacetyldapsone to dapsone can accurately assess acetylator phenotype in patients or subjects. 5 The clinical applications for this method are discussed.
Full text
PDF

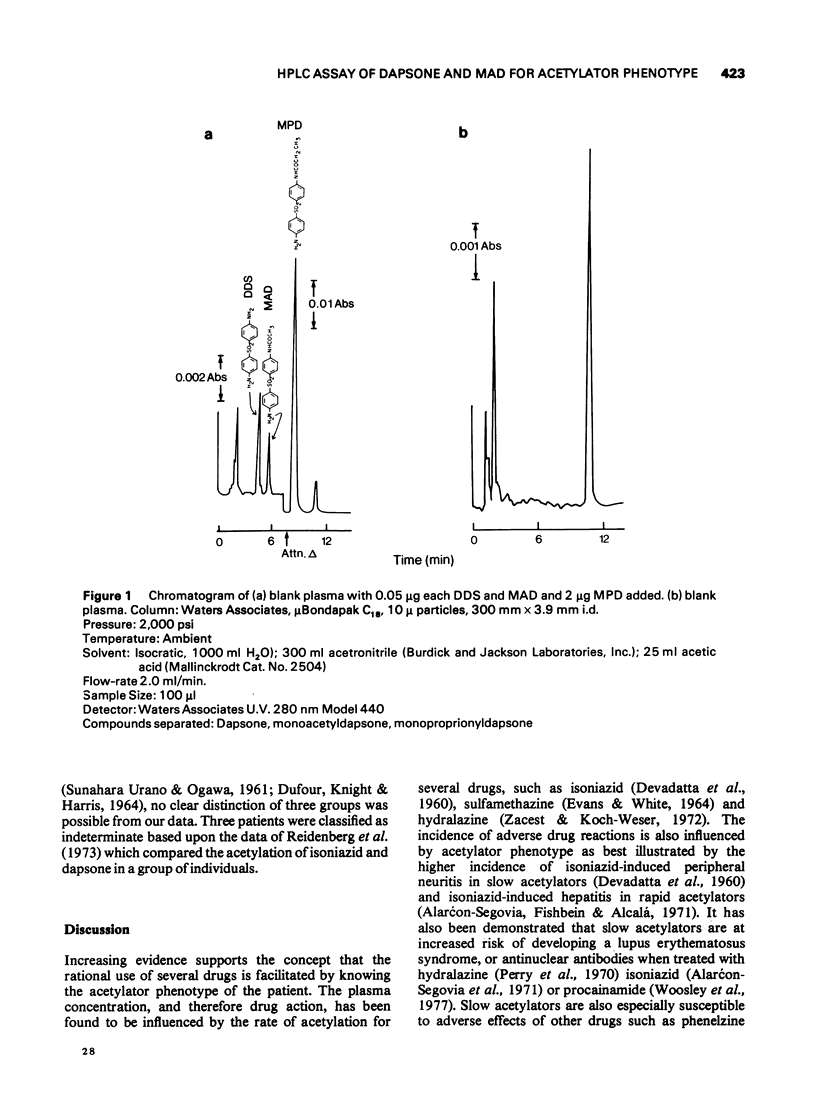
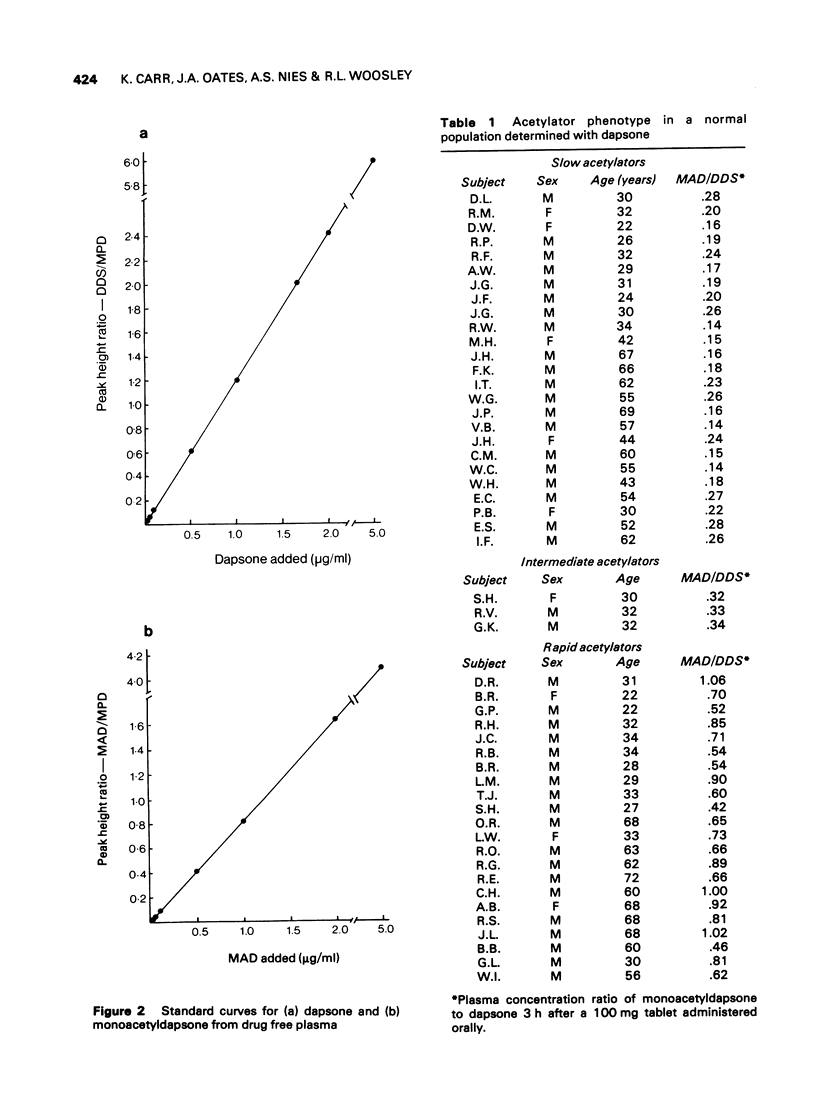
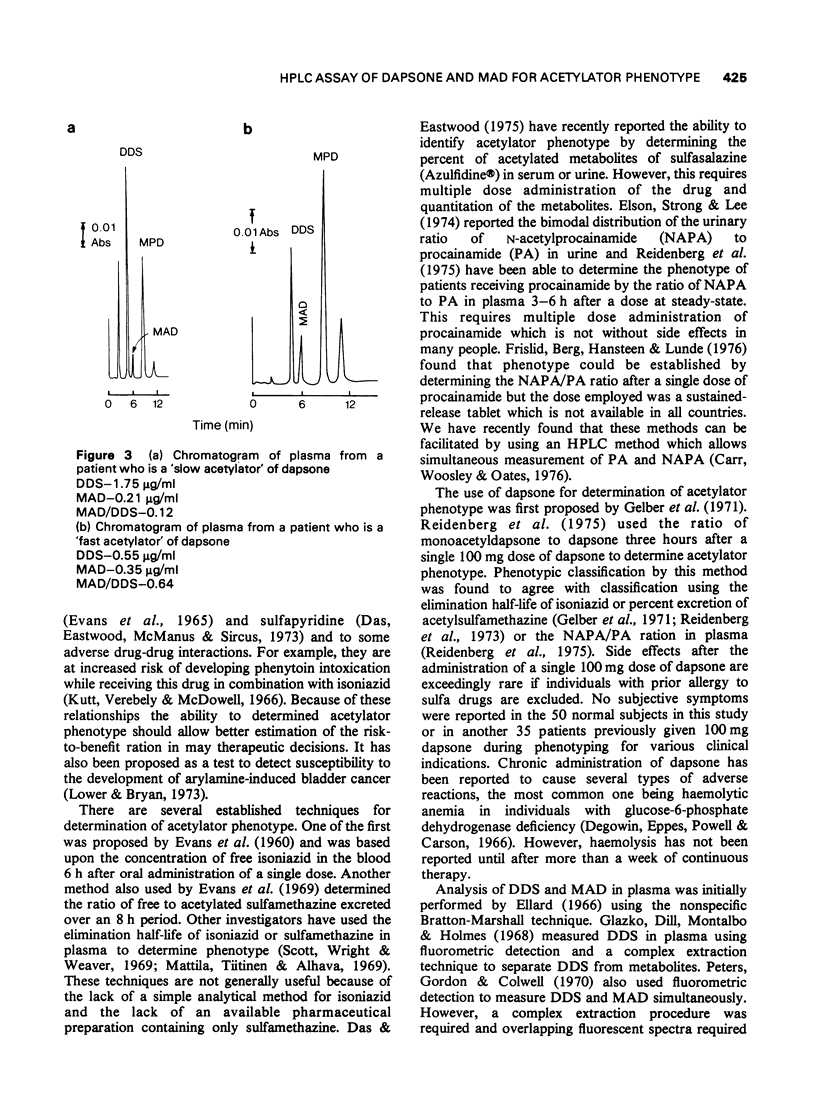


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Fishbein E., Alcalá H. Isoniazid acetylation rate and development of antinuclear antibodies upon isoniazid treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Nov-Dec;14(6):748–752. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr K., Woosley R. L., Oates J. A. Simultaneous quantification of procainamide and N-acetylprocainamide with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1976 Dec 22;129:363–368. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)87796-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVADATTA S., GANGADHARAM P. R., ANDREWS R. H., FOX W., RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., SELKON J. B., VELU S. Peripheral neuritis due to isoniazid. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;23:587–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFOUR A. P., KNIGHT R. A., HARRIS H. W. GENETICS OF ISONIAZID METABOLISM IN CAUCASIAN, NEGRO, AND JAPANESE POPULATIONS. Science. 1964 Jul 24;145(3630):391–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das K. M., Eastwood M. A. Acetylation polymorphism of sulfapyridine in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Nov;18(5 Pt 1):514–520. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975185part1514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das K. M., Eastwood M. A., McManus J. P., Sircus W. Adverse reactions during salicylazosulfapyridine therapy and the relation with drug metabolism and acetylator phenotype. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 6;289(10):491–495. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309062891001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degowin R. L., Eppes R. B., Powell R. D., Carson P. E. The haemolytic effects of diaphenylsulfone (DDS) in normal subjects and in those with glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase deficiency. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(2):165–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., DAVISON K., PRATT R. T. THE INFLUENCE OF ACETYLATOR PHENOTYPE ON THE EFFECTS OF TREATING DEPRESSION WITH PHENELZINE. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1965 Jul-Aug;6:430–435. doi: 10.1002/cpt196564430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., MANLEY K. A., McKUSICK V. A. Genetic control of isoniazid metabolism in man. Br Med J. 1960 Aug 13;2(5197):485–491. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5197.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., WHITE T. A. HUMAN ACETYLATION POLYMORPHISM. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Mar;63:394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellard G. A. Absorption, metabolism and excretion of di(rho-aminophenyl) sulphone (dapsone) and di(rho-aminophenyl) sulphoxide in man. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Jan;26(1):212–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson J., Strong J. M., Lee W. K., Atkinson A. J., Jr Antiarrhythmic potency of N-acetylprocainamide. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Feb;17(2):134–140. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975172134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A. An improved and simplified method of detecting the acetylator phenotype. J Med Genet. 1969 Dec;6(4):405–407. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.4.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRYMOYER J. W., JACOX R. F. INVESTIGATION OF THE GENETIC CONTROL OF SULFADIAZINE AND ISONIAZID METABOLISM IN THE RABBIT. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Dec;62:891–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frislid K., Berg M., Hansteen V., Lunde P. K. Comparison of the acetylation of procainamide and sulfadimidine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Mar 22;09(5-6):433–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00606561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelber R., Peters J. H., Gordon G. R., Glazko A. J., Levy L. The polymorphic acetylation of dapsone in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 Mar-Apr;12(2):225–238. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971122part1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazko A. J., Dill W. A., Montalbo R. G., Holmes E. L. A new analytical procedure for dapsone. Application to blood-level and urinary-excretion studies in normal men. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 May;17(3):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutt H., Winters W., McDowell F. H. Depression of prahydroxylation of diphenylhydantoin by antituberculosis chemotherapy. Neurology. 1966 Jun;16(6):594–602. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.6.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lower G. M., Jr, Bryan G. T. Enzymatic N-acetylation of carcinogenic aromatic amines by liver cytosol of species displaying different organ susceptibilities. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Jul 1;22(13):1581–1588. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila M. J., Tiitinen H., Alhava E. Acetylation pattern of different sulphonamides in rapid and slow isoniazid inactivators. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. F., Jr, Gordon G. R., Peters J. H. A chromatographic-fluorometric procedure for the determination of nanogram quantities of antileprotic sulfones. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Jr, Tan E. M., Carmody S., Sakamoto A. Relationship of acetyl transferase activity to antinuclear antibodies and toxic symptoms in hypertensive patients treated with hydralazine. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):114–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Gordon G. R., Colwell W. T., Jr The fluorometric measurement of 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl sulfone and its acetylated derivatives in plasma and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Aug;76(2):338–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Drayer D. E., Levy M., Warner H. Polymorphic acetylation procainamide in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Jun;17(6):722–730. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975176722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Drayer D., DeMarco A. L., Bello C. T. Hydralazine elimination in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Nov-Dec;14(6):970–977. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973146970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNAHARA S., URANOM, OGAWAM Genetical and geographic studies on isoniazid inactivation. Science. 1961 Nov 10;134(3489):1530–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3489.1530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. M., Wright R. C., Weaver D. D. The discrimination of phenotypes for rate of disappearance of isonicotinoyl hydrazide from serum. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1173–1176. doi: 10.1172/JCI106081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacest R., Koch-Weser J. Relation of hydralazine plasma concentration to dosage and hypotensive action. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 May-Jun;13(3):420–425. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972133420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


