Abstract
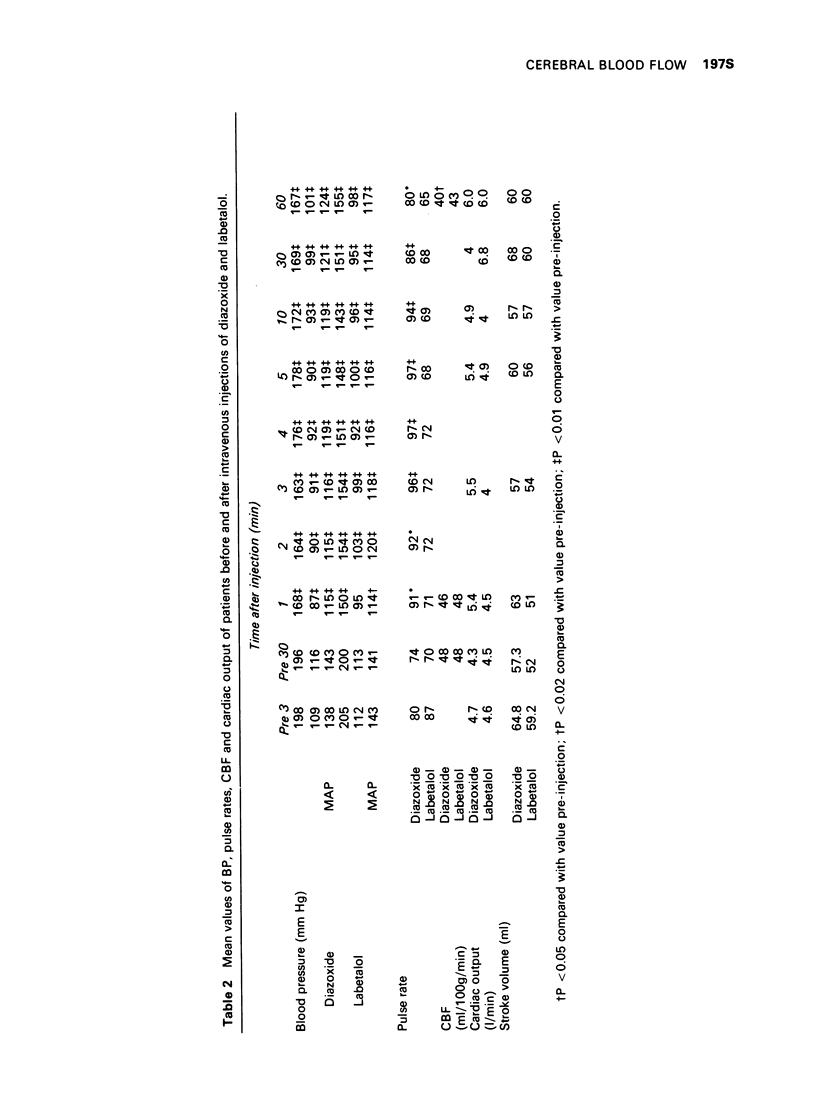
1 Diazoxide 300 mg and labetalol 150 mg were each injected intravenously on separate occasions into five patients with essentail hypertension. The reduction in BP caused by labetalol was slightly greater than that produced by diazoxide. 2 In contrast the reduction in cerebral blood flow (CBF) by labetalol was not statistically significant, whereas diazoxide gave a greater and statistically significant reduction in CBF. 3 These observations suggest that labetalol may have an advantage over diazoxide for the rapid reduction in BP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gabriel S., Atterhög J. H., Orö L., Ekelund L. G. Measurement of cardiac output by impedance cardiography in patients with myocardial infarction. Comparative evaluation of impedance and dye dilution methods. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Jan;36(1):29–34. doi: 10.1080/00365517609068015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg H. I., Codario R. A., Banka R. S., Reivich M. Patterns of cerebral dysautoregulation in severe hypertension to blood pressure reduction with diazoxide. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1977;64:64–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handt A., Farber M. O., Szwed J. J. Intradialytic measurement of cardiac output by thermodilution and impedance cardiography. Clin Nephrol. 1977 Feb;7(2):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich W. L., Cronin R., Miller P. D., Anderson R. J. Hypotensive sequelae of diazoxide and hydralazine therapy. JAMA. 1977 Jan 17;237(3):264–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar G. K., Dastoor F. C., Robayo J. R., Razzaque M. A. Side effects of diazoxide. JAMA. 1976 Jan 19;235(3):275–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. M., Havard C. W. Intravenous labetalol in hypertensive patients given by fast and slow injection. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 May;5(5):401–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. M., Havard C. W. Intravenous labetalol in hypertensive patients treated with beta-adrenoreceptor-blocking drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):795–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard B. N., Thompson F. O., Boakes A. J., Joekes A. M. Some haemodynamic effects of compound AH 5158 compared with propranolol, propranolol plus hydrallazine, and diazoxide: the use of AH 5158 in the treatment of hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1975 Jun;2:97s–100s. doi: 10.1042/cs048097s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers E. M., Koch-Weser J. Protein binding and vascular activity of diazoxide. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 20;281(21):1141–1145. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911202812102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandgaard S., Olesen J., Skinhoj E., Lassen N. A. Autoregulation of brain circulation in severe arterial hypertension. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 3;1(5852):507–510. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5852.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust P. M., Rosei E. A., Brown J. J., Fraser R., Lever A. F., Morton J. J., Robertson J. I. Effect of blood pressure angiotensin II and aldosterone concentrations during treatment of severe hypertension with intravenous labetalol: comparison with propranolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):799–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyper D. J., Lennox G. A., Rowan J. O. Two minute slope inhalation technique for cerebral blood flow measurement in man. 2. Clinical appraisal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;39(2):147–151. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyper D. J., Rowan J. O. The construction and use of nomograms for cerebral blood flow calculation using a 133Xe inhalation technique. Phys Med Biol. 1976 May;21(3):406–413. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/21/3/006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


