Abstract
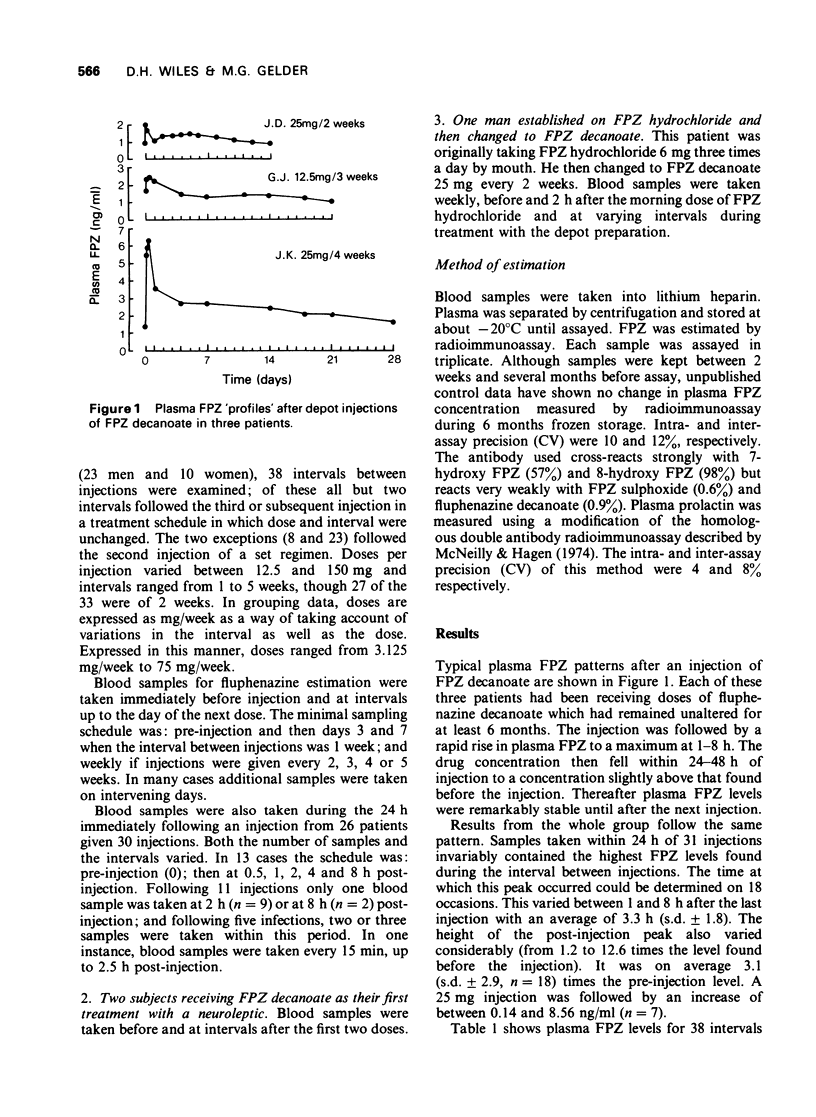
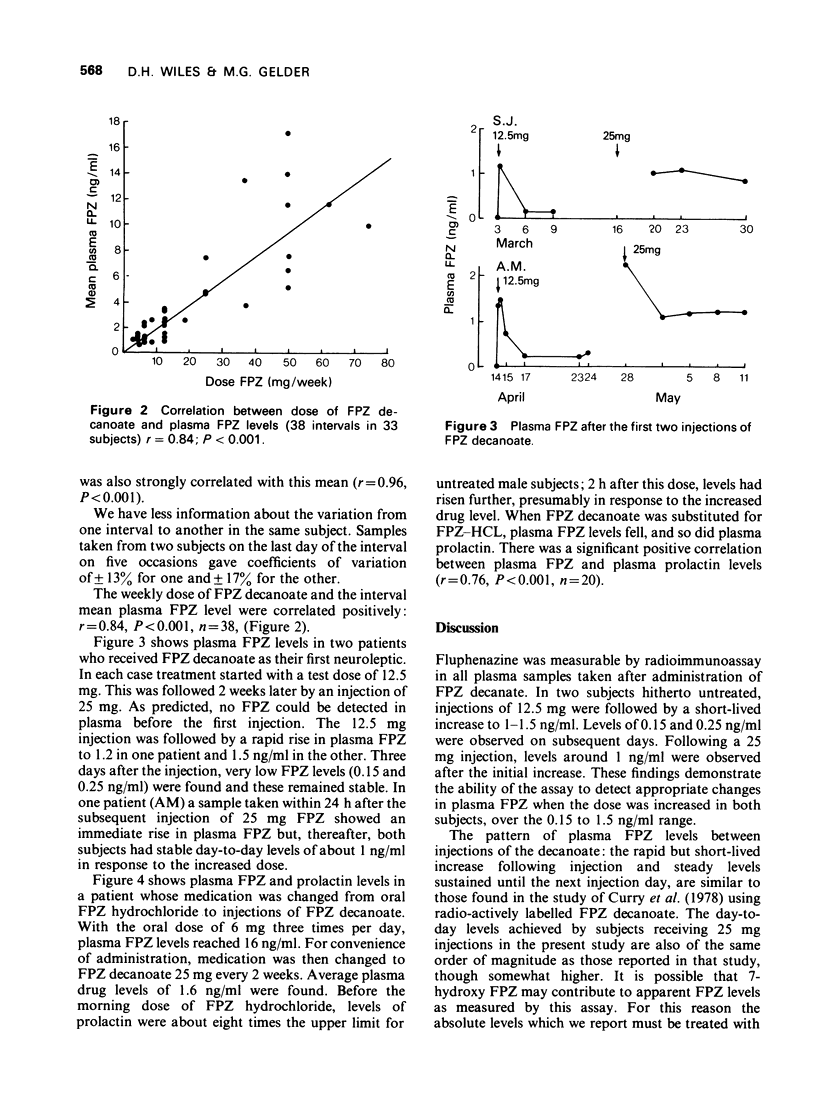
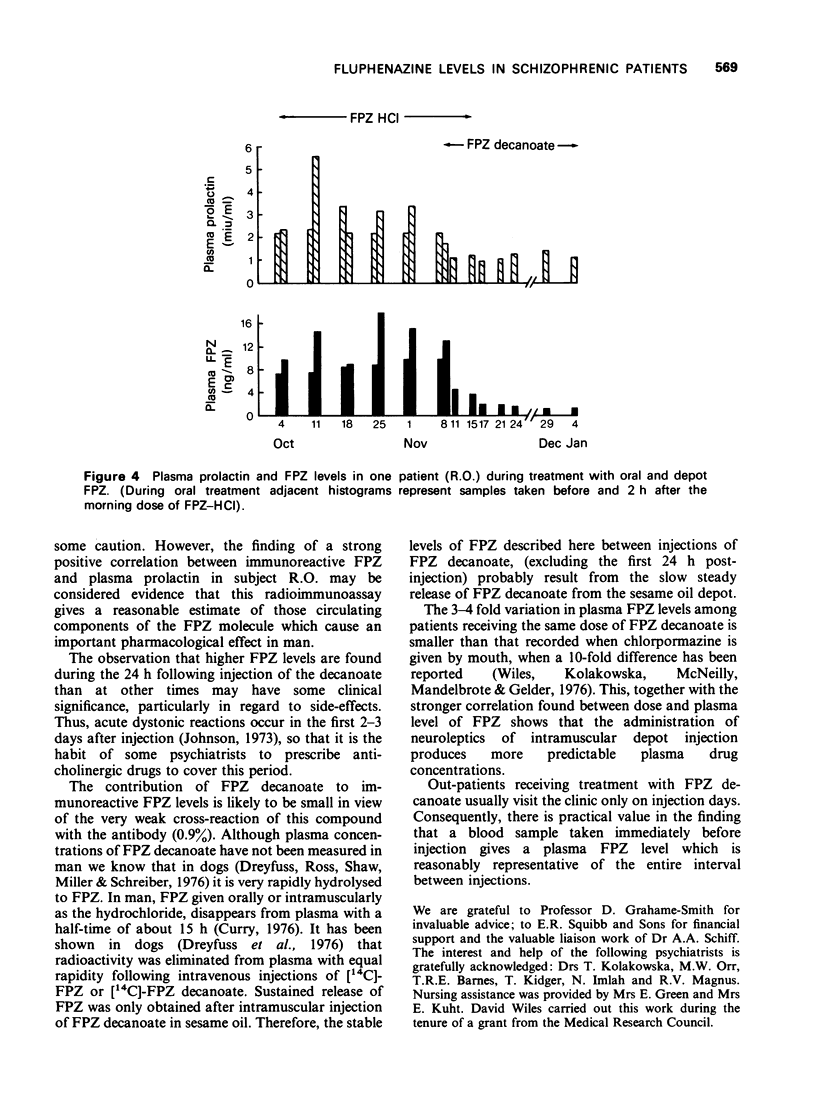
1 Using a radioimmunoassay, plasma fluphenazine (FPZ) concentrations were examined in 33 schizophrenic patients during 38 intervals between injections of FPZ decanoate. Doses ranged from 12.5 to 150 mg and intervals from 1 to 5 weeks. At least three blood samples were taken between injections from each subject; also in 26 subjects additional samples were taken during the first 24 h post-injection. 2 FPZ was measurable in all plasma samples. 3 Each injection was followed by a rapid rise in plasma FPZ concentration to a maximum at 1-8 h. The height of this peak varied considerably. Within the next 12-36 h plasma FPZ fell to a level slightly above that found before injection and then remained stable until the next injection, thus confirming the steady release of FPZ from the depot over this period. 4 For the group, dose and mean plasma FPZ levels correlated strongly. 5 Despite this, there was a four-fold variation in plasma FPZ concentration among subjects receiving the same dose. 6 The FPZ level on the last day of an interval between injections was a satisfactory estimate of the mean FPZ level for the interval. 7 In one subject examined in this way, a positive correlation was found (r = 0.76) between plasma FPZ (by radioimmunoassay) and plasma prolactin levels.
Full text
PDF
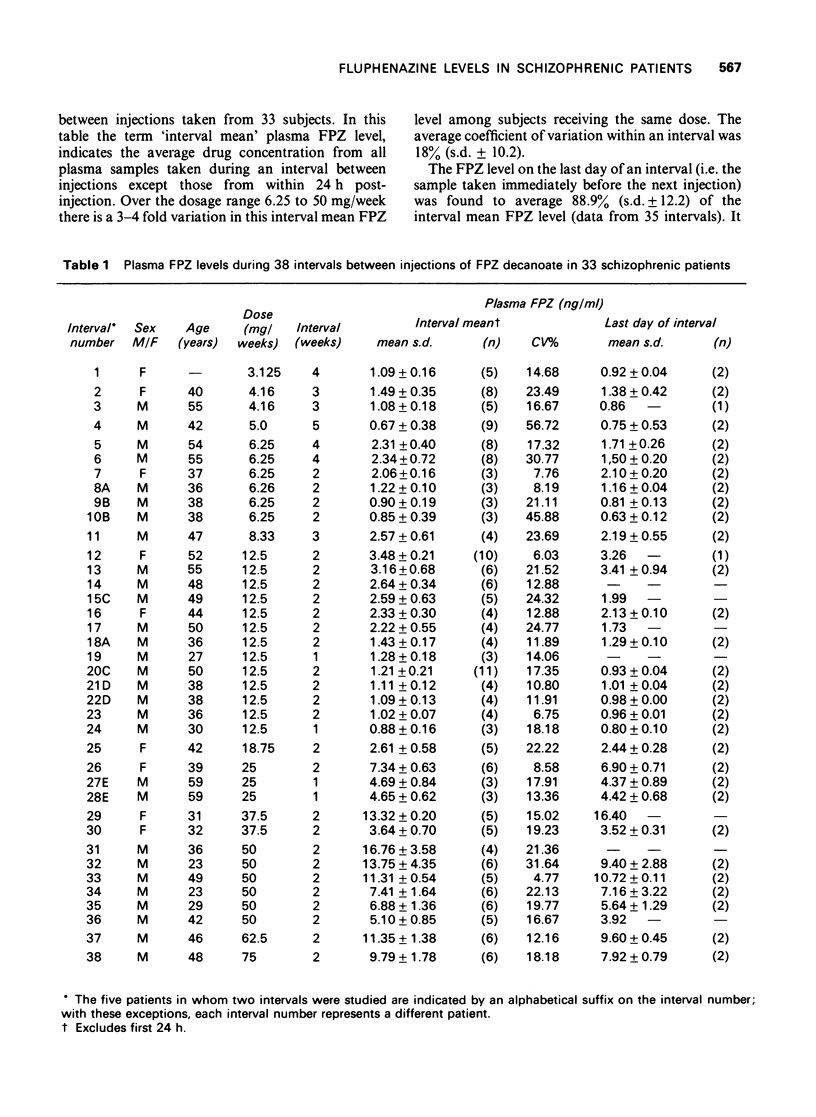

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curry S. H., Whelpton R., de Schepper P. J., Vranckx S., Schiff A. A. Plasma-fluphenazine concentrations after injection of long-acting esters. Lancet. 1978 Jun 3;1(8075):1217–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss J., Ross J. J., Jr, Shaw J. M., Miller I., Schreiber E. C. Release and elimination of 14C-fluphenazine enanthate and decanoate esters administered in sesame oil to dogs. J Pharm Sci. 1976 Apr;65(4):502–507. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600650407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S. R., Gaind R., Rohde P. D., Stevens B. C., Wing J. K. Outpatient maintenance of chronic schizophrenic patients with long-acting fluphenazine: double-blind placebo trial. Report to the Medical Research Council Committee on Clinical Trials in Psychiatry. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 17;1(5854):633–637. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5854.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A. Practical considerations in the use of depot neuroleptics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Br J Hosp Med. 1977 Jun;17(6):546–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A. The side-effects of fluphenazine decanoate. Br J Psychiatry. 1973 Nov;123(576):519–522. doi: 10.1192/bjp.123.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilly A. S., Hagen C. Prolactin, TSH, LH and FSH responses to a combined LHRH-TRH test at different stages of the menstrual cycle. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1974 Oct;3(4):427–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1974.tb02813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles D. H., Franklin M. Radioimmunoassay for fluphenazine in human plasma. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Mar;5(3):265–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles D. H., Kolakowska T., McNeilly A. S., Mandelbrote B. M., Gelder M. G. Clinical significance of plasma chlorpromazine levels. I. Plasma levels of the drug, some of its metabolites and prolactin during acute treatment. Psychol Med. 1976 Aug;6(3):407–415. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700015841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


