Abstract
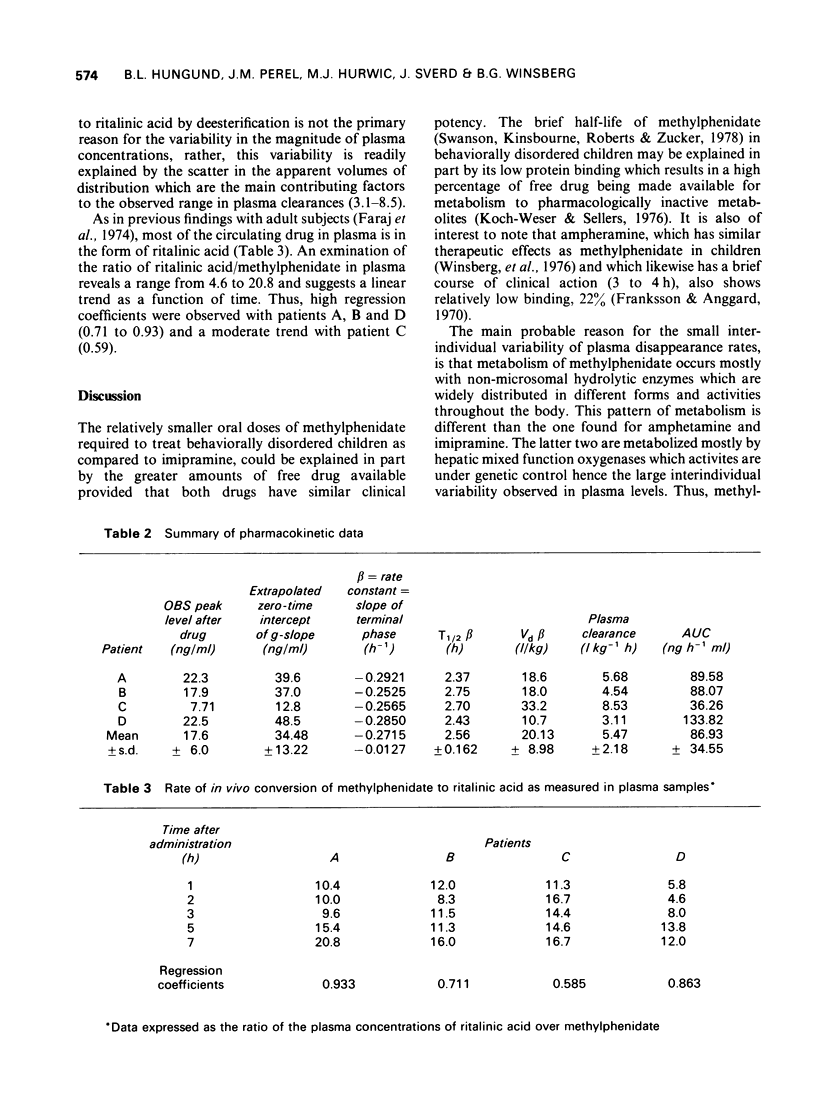
1 Pharmacokinetic study has been carried out following oral administration of 10-20 mg of methylphenidate hydrochloride to four behaviorally disorders children. 2 It is indicated that the drug is metabolized to ritalinic acid with an apparent plasma half life of 2.5 h. 3 The variability in magnitude of plasma concentration seems to be due not to its metabolism to ritalinic acid but due to the variability in the apparent volume of distribution. 4 The brief half life of methylphenidate which parallels the short duration of action of methylphenidate in behaviorally disordered children may be explained in part by its low protein binding which results in high percentage of free drug being made available for metabolism to pharmacologically inactive metabolites.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braithwaite R. A., Goulding R., Theano G., Bailey J., Coppen A. Plasma concentration of amitriptyline and clinical response. Lancet. 1972 Jun 17;1(7764):1297–1300. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Ebert M. H., Hunt R. D. Plasma d-amphetamine absorption and elimination in hyperactive children. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1978 Jul;14(3):33–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covino B. G. Comparative clinical pharmacology of local anesthetic agents. Anesthesiology. 1971 Aug;35(2):158–167. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197108000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorchik B. H., Vessell E. S. Significance of error associated with use of the one-compartment formula to calculate clearance of thirty-eight drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Jun;23(6):617–623. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978236617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franksson G., Anggård E. The plasma protein binding of amphetamine, catecholamines and related compounds. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1970;28(3):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1970.tb00546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal J., Hodshon B. J., Pintauro C., Flamm B. L., Cho A. K. Pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate in the rat using single-ion monitoring GLC-mass spectrometry. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Jun;66(6):866–869. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassman A. H., Perel J. M., Shostak M., Kantor S. J., Fleiss J. L. Clinical implications of imipramine plasma levels for depressive illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Feb;34(2):197–204. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770140087010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram L. F., Reisby N., Ibsen I., Nagy A., Dencker S. J., Bech P., Petersen G. O., Christiansen J. Plasma levels and antidepressive effect of imipramine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Mar;19(3):318–324. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976193318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungund B. L., Hanna M., Winsberg B. G. A sensitive gas chromatographic method for the determination of methylphenidate (Ritalin) and its major metabolite alpha-phenyl-2-piperidine acetic acid (ritalinic acid) in human plasma using nitrogen-phosphorous detector. Commun Psychopharmacol. 1978;2(3):203–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J., Sellers E. M. Binding of drugs to serum albumin (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 5;294(6):311–316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602052940605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krager J. M., Safer D. J. Type and prevalence of medication used in the treatment of hyperactive children. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 21;291(21):1118–1120. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411212912108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Sørensen P., Asberg M., Eggert-Hansen C. Plasma-nortriptyline levels in endogenous depression. Lancet. 1973 Jan 20;1(7795):113–115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIER R., GROSS F., TRIPOD J. Ritalin, eine neuartige synthetische Verbindung mit spezifischer zentralerregender Wirkungskomponente. Klin Wochenschr. 1954 May 15;32(19-20):445–450. doi: 10.1007/BF01466968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milberg R. M., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Sprague R. L., Sleator E. K. A reproducible gas chromatographic mass spectrometric assay for low levels of methylphenidate and ritalinic acid in blood and urine. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1975 Feb;2(1):2–8. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200020103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEREL J. M., SNELL M. M., CHEN W., DAYTON P. G. A STUDY OF STRUCTURE--ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIPS IN REGARD TO SPECIES DIFFERENCE IN THE PHENYLBUTAZONE SERIES. Biochem Pharmacol. 1964 Sep;13:1305–1317. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(64)90231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport J. L., Quinn P. O., Bradbard G., Riddle K. D., Brooks E. Imipramine and methylphenidate treatments of hyperactive boys. A double-blind comparison. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1974 Jun;30(6):789–793. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1974.01760120049008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal J. L., Cunningham R. F., Dayton P. G., Israili Z. H. (14C)Methylphenidate hydrochloride. Studies on disposition in rat brain. Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 Mar-Apr;4(2):140–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kinsbourne M., Roberts W., Zucker K. Time-response analysis of the effect of stimulant medication on the learning ability of children referred for hyperactivity. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):21–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R., Hammond K. B., Rodgerson D. O. Gas-liquid chromatographic procedure for measurement of methylphenidate hydrochloride and its metabolite, ritalinic acid, in urine. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):440–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsberg B. G., Perel J. M., Hurwic M. J., Klutch A. Imipramine protein binding and pharmacokinetics in children. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1974;9(0):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsberg B. G., Yepes L. E., Bialer I. Pharmacologic management of children with hyperactive/aggressive/inattentive behavior disorders. Suggestions for the pediatrician. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1976 May;15(5):471–477. doi: 10.1177/000992287601500512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


