Abstract
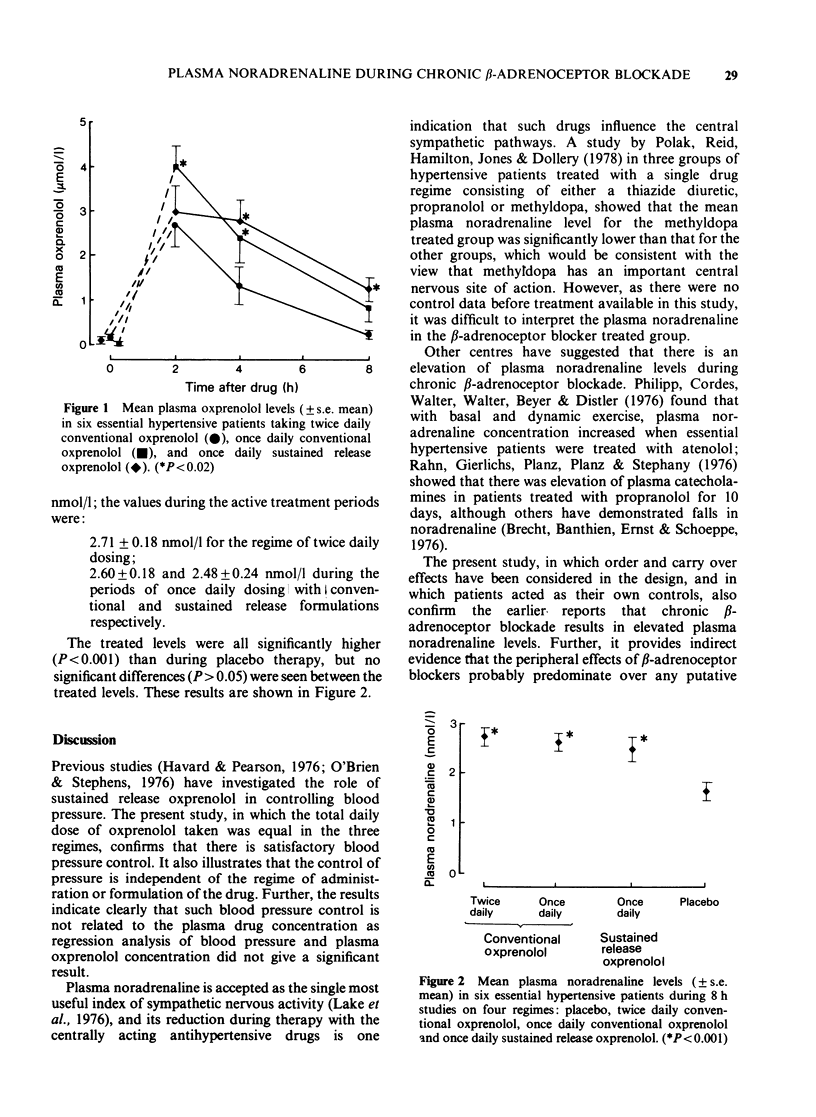
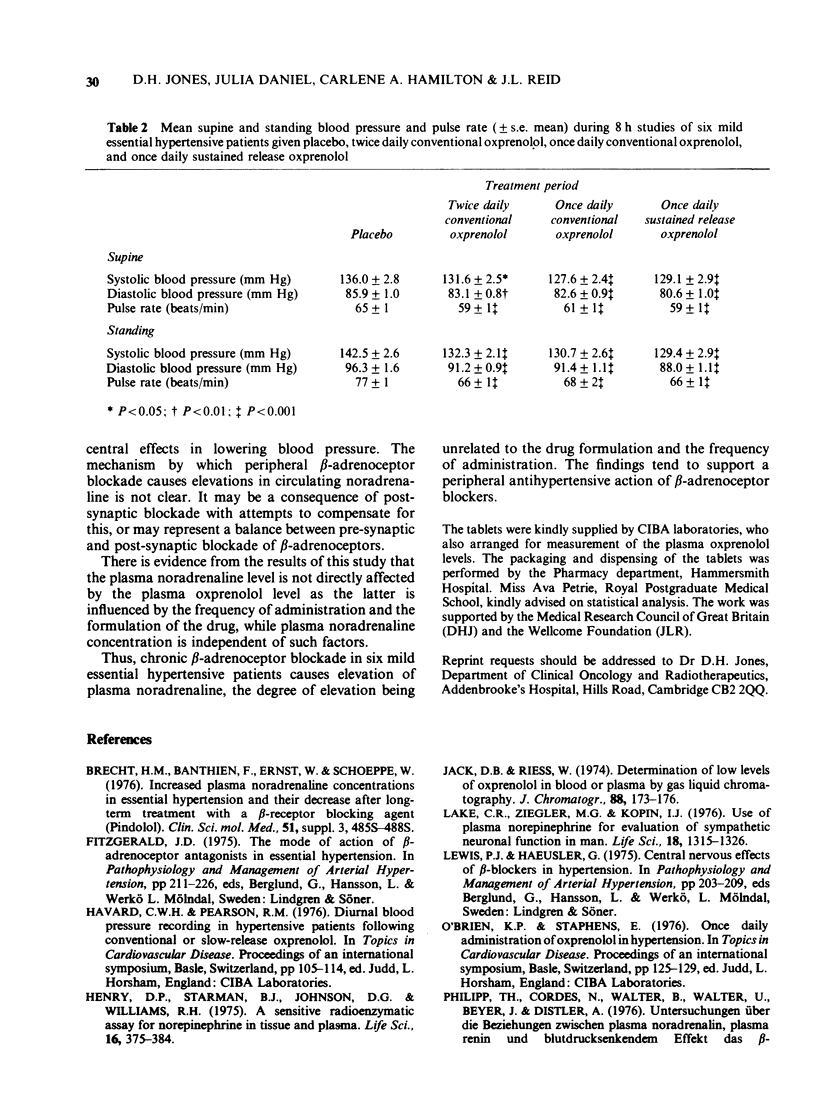
1. Chronic beta-adrenoceptor blockade with oxprenolol causes elevation of plasma noradrenaline levels, as compared with placebo, despite a significant fall in blood pressure and pulse rate. 2. The plasma noradrenaline concentration is not influenced by the frequency of administration or the formulation of the drug. 3. Plasma noradrenaline levels are not correlated with the plasma concentration of the drug. 4. The changes in plasma noradrenaline concentrations support a peripheral rather than central mechanism of action of beta-adrenoceptor blockers in man.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brecht H. M., Banthien F., Ernst W., Schoeppe W. Increased plasma noradrenaline concentrations in essential hypertension and their decrease after long-term treatment with a beta-receptor-blocking agent (prindolol). Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:485S–488S. doi: 10.1042/cs051485s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D. P., Starman B. J., Johnson D. G., Williams R. H. A sensitive radioenzymatic assay for norepinephrine in tissues and plasma. Life Sci. 1975 Feb 1;16(3):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake C. R., Ziegler M. G., Kopin I. J. Use of plasma norepinephrine for evaluation of sympathetic neuronal function in man. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 1;18(11):1315–1325. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL C. E., SLATER I. H. Blocking of inhibitory adrenergic receptors by a dichloro analog of isoproterenol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Apr;122(4):480–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak G., Reid J. L., Hamilton C. A., Jones D. H., Dollery C. T. Sympathetic nervous function and renin activity in hypertensives on long term drug treatment with propranolol, methyldopa or bendrofluazide. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1978;1(1):1–9. doi: 10.3109/10641967809068591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard B. N., Gillam P. M. Treatment of hypertension with propranolol. Br Med J. 1969 Jan 4;1(5635):7–16. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5635.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. M., Reid J. L., Hamilton C. A., Sever P., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Effects of clonidine on biochemical indices of sympathetic function and plasma renin activity in normotensive man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Jul;53(1):45–53. doi: 10.1042/cs0530045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


