Abstract
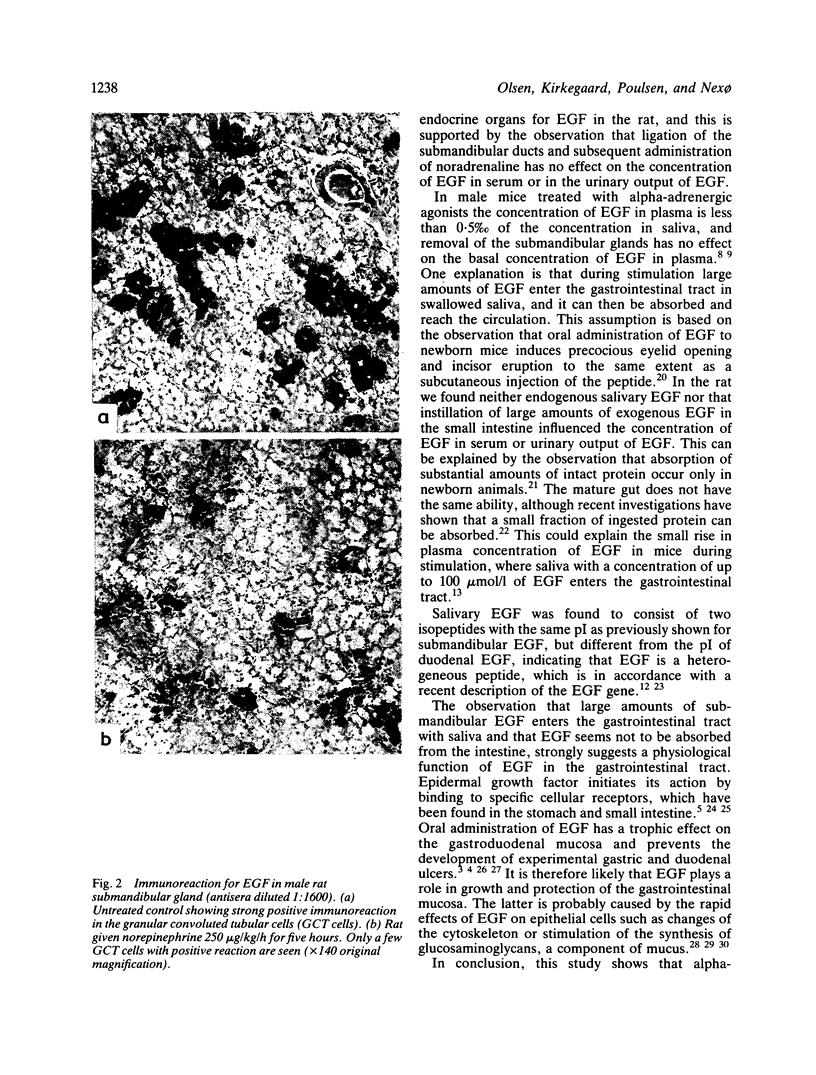
The present study was undertaken to investigate the effect of alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists on secretion of epidermal growth factor (EGF) from the rat submandibular glands and to test the possibility of intestinal absorption of EGF. Alpha-adrenergic agonists increased the concentration of salivary EGF by approximately a hundred times, while the serum concentration of EGF was unchanged. The contents of EGF in the submandibular glands decreased upon administration of the alpha-adrenergic agonist noradrenaline, and this was confirmed on immunohistochemical investigation of the glands. Beta-adrenergic agonists had no effect on secretion of EGF from the submandibular glands. Intestinal absorption of EGF could not be confirmed, as stimulation by noradrenaline with free passage of saliva to the gastrointestinal tract and intrajejunal infusion of EGF had no influence on the concentration of EGF in serum. This study shows that alpha-adrenergic agonists stimulate exocrine secretion of submandibular EGF and that EGF in physiological amounts are not absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alm P. Adrenergic and cholinergic nerves of bovine, guinea pig and hamster salivary glands. A light and electron microscopic study. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Apr 17;138(3):407–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00307102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barka T. Biologically active polypeptides in submandibular glands. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Aug;28(8):836–859. doi: 10.1177/28.8.7003006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barka T., Gresik E. W., vad der Noen H. Stimulation of secretion of epidermal growth factor and amylase of cyclocytidine. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jan 17;186(2):269–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00225536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byyny R. L., Orth D. N., Cohen S., Doyne E. S. Epidermal growth factor: effects of androgens and adrenergic agents. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):776–782. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Gudor R. C., Sun T. T., Chen A. B., Mosesson M. W. Control of a cell surface major glycoprotein by epidermal growth factor. Science. 1977 Aug 19;197(4305):776–778. doi: 10.1126/science.302030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M. Epidermal growth factor: mechanisms of action. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;78:233–256. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembiński A., Gregory H., Konturek S. J., Polański M. Trophic action of epidermal growth factor on the pancreas and gastroduodenal mucosa in rats. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:35–42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue-Lafitte M. E., Kobari L., Gespach C., Chamblier M. C., Rosselin G. Characterization and repartition of epidermal growth factor-urogastrone receptors in gastric glands isolated from young and adult guinea pigs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 10;798(2):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Garrido J., Vial J. D. Epidermal growth factor inhibits cytoskeleton-related changes in the surface of parietal cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):108–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresik E. W., van der Noen H., Barka T. Epidermal growth factor-like material in rat submandibular gland. Am J Anat. 1979 Sep;156(1):83–89. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001560108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard P., Olsen P. S., Poulsen S. S., Nexø E. Epidermal growth factor inhibits cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcers. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1277–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Brzozowski T., Piastucki I., Dembinski A., Radecki T., Dembinska-Kiec A., Zmuda A., Gregory H. Role of mucosal prostaglandins and DNA synthesis in gastric cytoprotection by luminal epidermal growth factor. Gut. 1981 Nov;22(11):927–932. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.11.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembach K. J. Enhanced synthesis and extracellular accumulation of hyaluronic acid during stimulation of quiescent human fibroblasts by mouse epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Oct;89(2):277–288. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews D. M., Adibi S. A. Peptide absorption. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jul;71(1):151–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Pantazis N. J., Papastavros M. Epidermal growth factor and nerve growth factor in mouse saliva: a comparative study. Dev Biol. 1979 Aug;71(2):356–370. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Saide J. D., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Nerve growth factor in mouse serum and saliva: role of the submandibular gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2330–2333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Watson A. Y., Metz J., Forssmann W. G. The mouse submandibular gland: an exocrine organ for growth factors. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Aug;28(8):890–902. doi: 10.1177/28.8.6969274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen P. S., Nexø E. Quantitation of epidermal growth factor in the rat. Identification and partial characterization of duodenal EGF. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Sep;18(6):771–776. doi: 10.3109/00365528309182093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Pedersen E. B. Increase in plasma renin in aggressive mice originates from kidneys, submaxillary and other salivary glands, and bites. Hypertension. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):180–184. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. L., Reade P. C. The relationship between the secretion of amylase and epidermal growth factor in the mouse submandibular salivary gland. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Oct;20(10):693–694. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. L. The in vitro secretion of epidermal growth factor by mouse submandibular salivary gland. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;296(3):301–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00498698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald R. Intestinal transport of antibodies in the newborn rat. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):189–211. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheving L. A., Yeh Y. C., Tsai T. H., Scheving L. E. Circadian phase-dependent stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, caecum, colon, and rectum of the adult male mouse. Endocrinology. 1980 May;106(5):1498–1503. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-5-1498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheving L. A., Yeh Y. C., Tsai T. H., Scheving L. E. Circadian phase-dependent stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the tongue, esophagus, and stomach of the adult male mouse. Endocrinology. 1979 Dec;105(6):1475–1480. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-6-1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steidler N. E., Reade P. C. An immunohistochemical study of secretagogue-induced secretion of epidermal growth factor in the submandibular salivary glands of mice. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1980 Jun;58(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/icb.1980.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Partlow L. M. alpha-Adrenergic regulation of secretion of mouse saliva rich in nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]