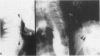
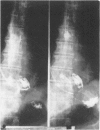
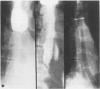
Abstract
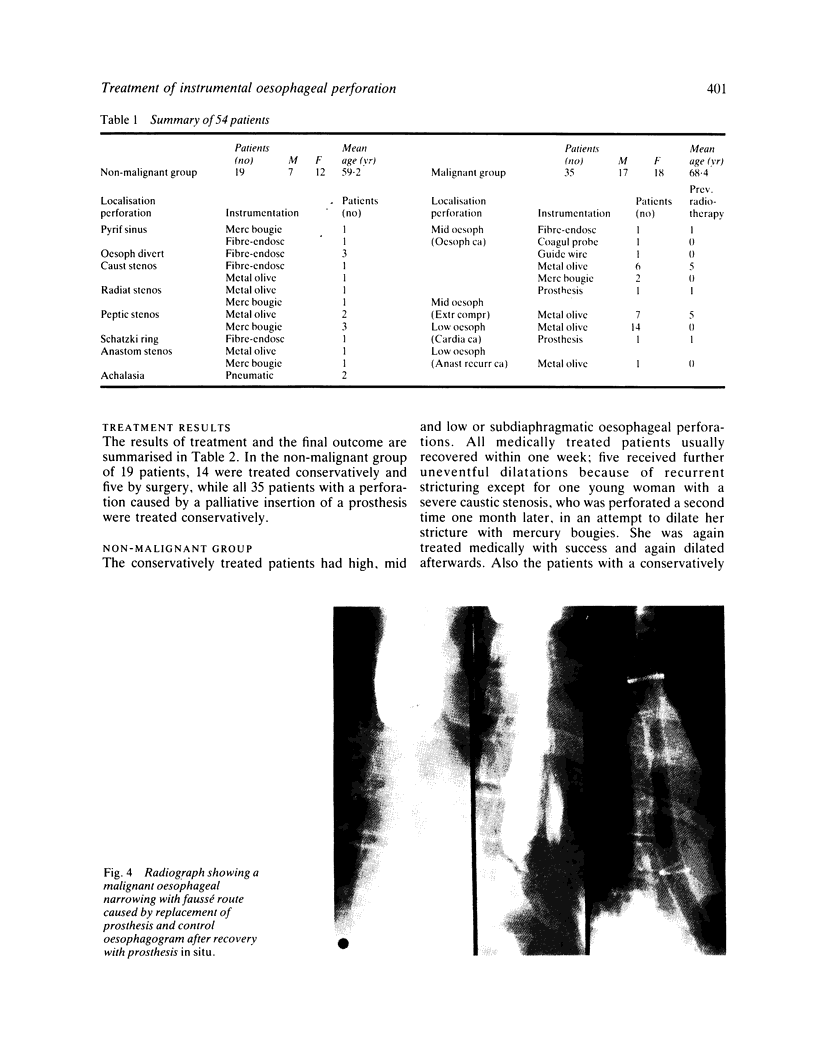
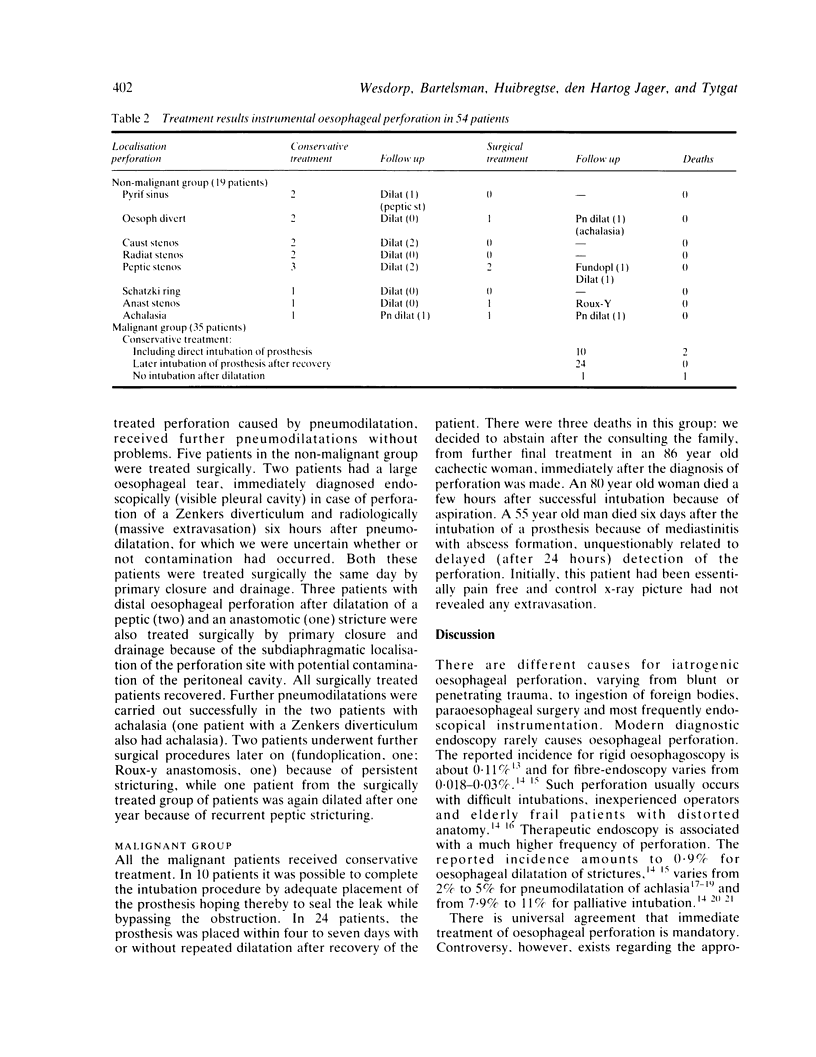
Results of a conservative approach in the treatment of instrumental oesophageal perforation were evaluated in 54 patients. The perforations occurred either during introduction of/or manipulation with fibre-endoscopes (six), during dilatation procedures with metal olives (five), mercury bougies (six) or during pneumodilatation (two) in 19 patients without malignancy and during an intubation procedure of a plastic prosthesis in 35 patients with an inoperable malignant oesophageal narrowing. In the majority of patients (94.4%) the diagnosis of oesophageal perforation was made within two hours. Conservative treatment consisted of nothing by mouth, antibiotics and naso-oesophageal suction. Of the 19 patients without malignancy, 14 were treated conservatively and five by surgery (primary closure and drainage) with no deaths. All patients with an oesophageal perforation caused by palliative intubation received conservative treatment with three deaths (8.6%). Non-surgical treatment of instrumental oesophageal perforation is feasable and acceptable, provided the perforation is detected early, before major contamination has occurred and is indicated in case of perforation in patients with malignancy.
Full text
PDF

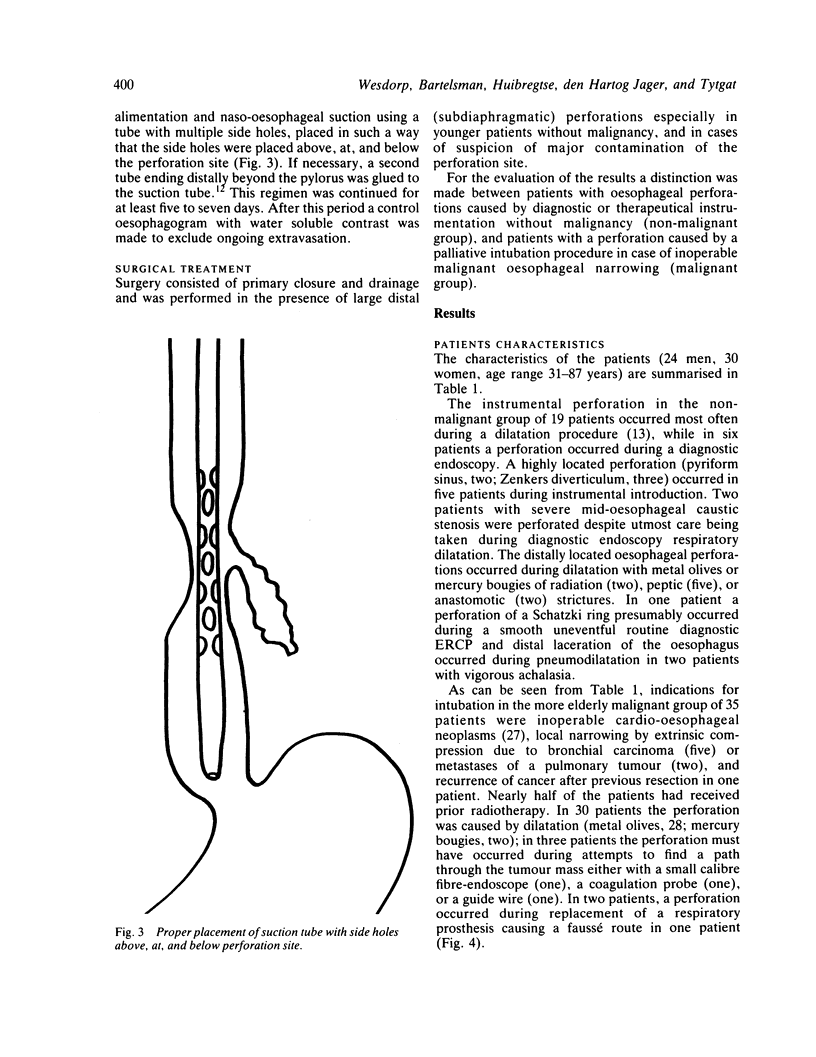


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks J. G., Bancewicz J. Perforation of the oesophagus: experience in a general hospital. Br J Surg. 1981 Aug;68(8):580–584. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. R., Hendrix T. R. Treatment of achalasia with pneumatic dilatation. Mod Treat. 1970 Nov;7(6):1217–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry B. E., Ochsner J. L. Perforation of the esophagus. A 30 year review. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973 Jan;65(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J., Cockel R. Oesophageal perforation at fibreoptic gastroscopy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Aug 29;283(6291):583–583. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6291.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. C., Choudhry K. U., Beattie E. J., Jr Perforation of the esophagus. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 Nov;135(5):729–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. A., Thompson W. R. Esophageal perforations: a 15 year experience. Am J Surg. 1982 Apr;143(4):495–503. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inberg M. V., Manner R., Puhakka H. Management of instrumental and spontaneous (atraumatic) perforations of the oesophagus. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1971;5(1):61–66. doi: 10.3109/14017437109131953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen C. W., Jr Perforation of the intrathoracic oesophagus. A report of nineteen cases. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;10(2):189–192. doi: 10.3109/14017437609167791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemerin E. E. Results of Treatment of Perforation of the Esophagus. Ann Surg. 1948 Nov;128(5):971–975. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194811000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly J. O., McCaffery T. D., Jr Esophageal stricture dilatation. A new method adapted to the fiberoptic esophagoscope. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Dec;16(12):1137–1140. doi: 10.1007/BF02235173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons W. S., Seremetis M. G., deGuzman V. C., Peabody J. W., Jr Ruptures and perforations of the esophagus: the case for conservative supportive management. Ann Thorac Surg. 1978 Apr;25(4):346–350. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)63554-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A. L., Dronfield M. W., Ferguson R., Atkinson M. Palliative intubation of oesophagogastric neoplasms at fibreoptic endoscopy. Gut. 1982 Dec;23(12):1060–1067. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.12.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandrasagra F. A., English T. A., Milstein B. B. The management and prognosis of oesophageal perforation. Br J Surg. 1978 Sep;65(9):629–632. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800650912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers J. L., Lane C. E., Foster J. H., Daniel R. A. Esophageal perforation: an increasing challenge. Ann Thorac Surg. 1975 Mar;19(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvis S. E., Nebel O., Rogers G., Sugawa C., Mandelstam P. Endoscopic complications. Results of the 1974 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Survey. JAMA. 1976 Mar 1;235(9):928–930. doi: 10.1001/jama.235.9.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggiani E., Belsey R. Oesophageal trauma: incidence, diagnosis, and management. Thorax. 1977 Jun;32(3):241–249. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.3.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantrappen G., Hellemans J. Treatment of achalasia and related motor disorders. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):144–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesdorp I. C., Bartelsman J. F., den Hartog Jager F. C., Huibregtse K., Tytgat G. N. Results of conservative treatment of benign esophageal strictures: a follow-up study in 100 patients. Gastroenterology. 1982 Mar;82(3):487–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichern W. A., Jr Perforation of the esophagus. Am J Surg. 1970 May;119(5):534–536. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(70)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolloch Y., Zer M., Dintsman M., Tiqva P. Iatrogenic perforations of the esophagus. Therapeutic considerations. Arch Surg. 1974 Mar;108(3):357–360. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350270087015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hartog Jager F. C., Bartelsman J. F., Tytgat G. N. Palliative treatment of obstructing esophagogastric malignancy by endoscopic positioning of a plastic prosthesis. Gastroenterology. 1979 Nov;77(5):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]