Abstract
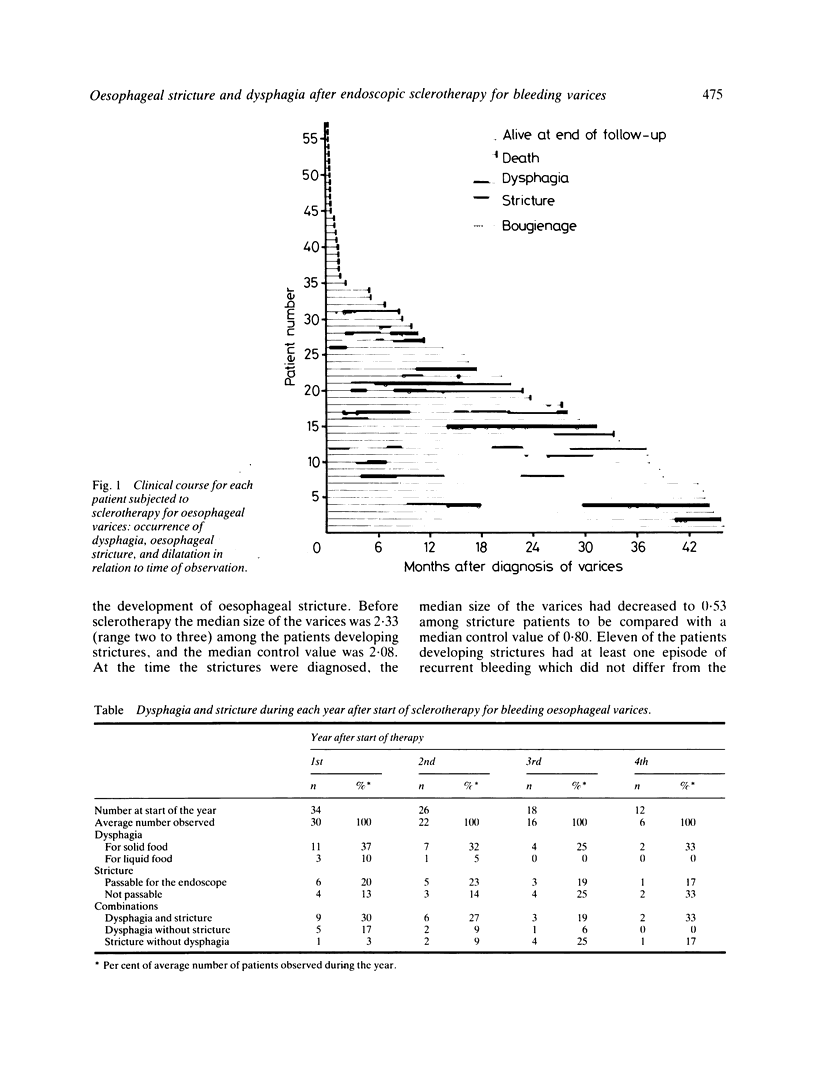
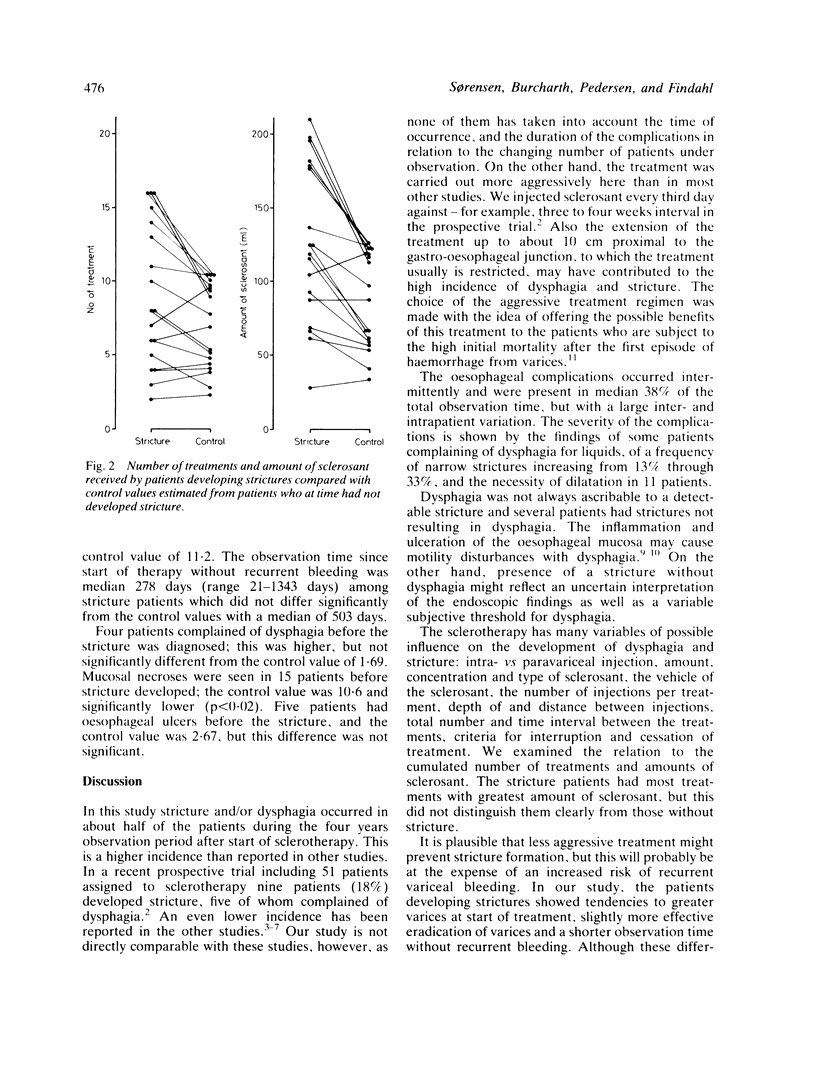
Oesophageal stricture and dysphagia after endoscopic sclerotherapy of oesophageal varices were assessed with regard to occurrence and severity and the relation to the treatment. We followed 34 patients for three to 47 months who had two to 25 treatments with submucosal, paravenous injections of polidocanol (3%). Twenty patients (59%) developed stricture or dysphagia; 14 both dysphagia and endoscopically verified stricture, two dysphagia without stricture, and four stricture without dysphagia. Both phenomena occurred intermittently and often independent of each other, but occupied median 38% of the observation time in these 20 patients. The patients developing strictures had received significantly more treatments and greater amount of sclerosant, and they had significantly more preceding mucosal necroses. The varices were eradicated to about the same degree and the incidence of recurrent haemorrhage was the same as in the patients who had not developed stricture.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsoum M. S., Abdel-Wahab Mooro H., Bolous F. I., Ramzy A. F., Rizk-Allah M. A., Mahmoud F. I. The complications of injection sclerotherapy of bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1982 Feb;69(2):79–81. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800690207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., Macdougall B. R., Westaby D., Mitchell K. J., Silk D. B., Strunin L., Dawson J. L., Williams R. Prospective controlled trial of injection sclerotherapy in patient with cirrhosis and recent variceal haemorrhage. Lancet. 1980 Sep 13;2(8194):552–554. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91990-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Jones D. B., Cleary B. K., Smith P. M. Oesophageal varices treated by sclerotherapy: a histopathological study. Gut. 1982 Jul;23(7):615–620. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.7.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARCEAU A. J., CHALMERS T. C. The natural history of cirrhosis. I. Survival with esophageal varices. N Engl J Med. 1963 Feb 28;268:469–473. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196302282680905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. W., Rodgers H. W. A review of 15 years' experience in the use of sclerotherapy in the control of acute haemorrhage from oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Oct;60(10):797–800. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800601011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougall B. R., Westaby D., Theodossi A., Dawson J. L., Williams R. Increased long-term survival in variceal haemorrhage using injection sclerotherapy. Results of a controlled trial. Lancet. 1982 Jan 16;1(8264):124–127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle S. J., Kirk C. J., Bailey R. J., Johnson A. G., Williams R., Murray-Lyon I. M. Oesophageal function in cirrhotic patients undergoing injection sclerotherapy for oesophageal varices. Digestion. 1978;18(3-4):178–185. doi: 10.1159/000198200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquet K. J., Oberhammer E. Sclerotherapy of bleeding oesophageal varices by means of endoscopy. Endoscopy. 1978 Feb;10(1):7–12. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1098252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbruch T., Wirsching R., Leisner B., Weinzierl M., Pfahler M., Paumgartner G. Esophageal function after sclerotherapy of bleeding varices. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1982 Sep;17(6):745–751. doi: 10.3109/00365528209181088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terblanche J., Northover J. M., Bornman P., Kahn D., Silber W., Barbezat G. O., Sellars S., Campbell J. A., Saunders S. J. A prospective controlled trial of sclerotherapy in the long term management of patients after esophageal variceal bleeding. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Mar;148(3):323–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


