Abstract
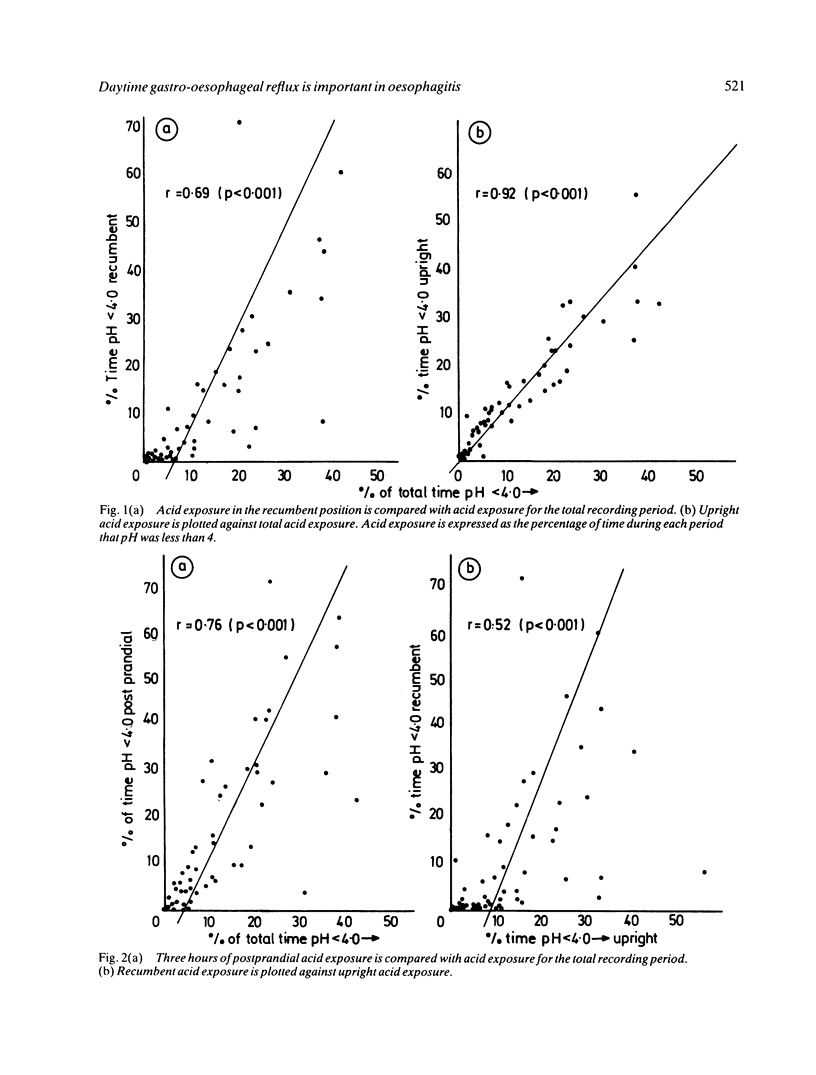
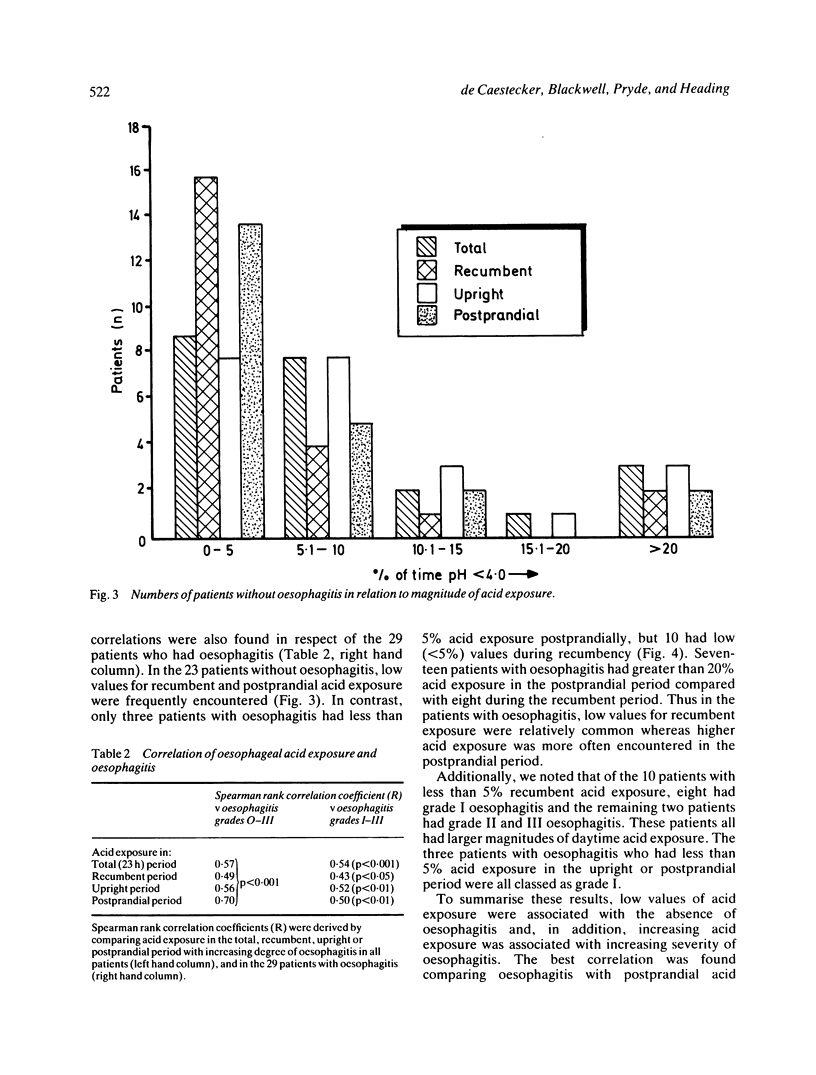
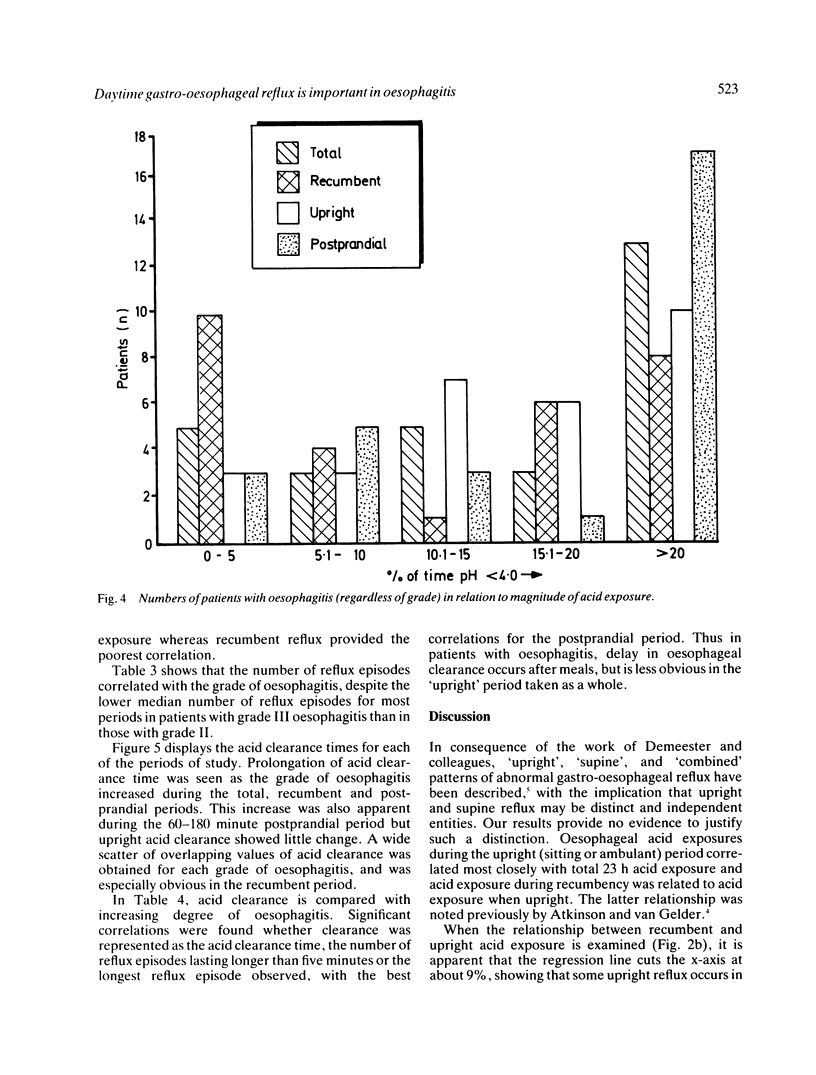
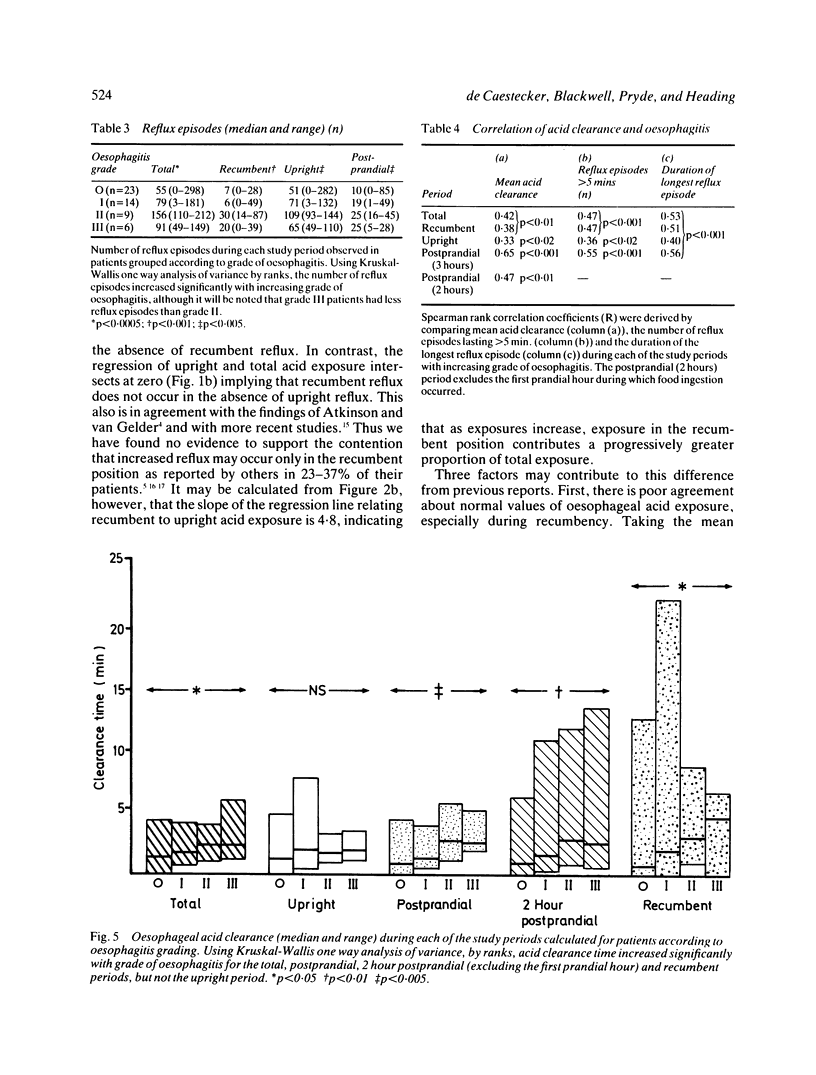
Fifty two patients were studied to investigate the patterns of gastro-oesophageal reflux during ambulatory pH monitoring and the relationship of reflux to presence and severity of oesophagitis. Twenty nine had evidence of oesophagitis which was graded according to severity. Acid exposure (pH less than 4) was calculated in each case for the total study period, the recumbent and upright periods, and the three hour period after the evening meal. Exposure in the upright period correlated closet (r=0.92: p less than 0.001) with that during the total period. Recumbent exposure correlated with both upright and postprandial exposure (p less than 0.001). Acid exposure during all four periods correlated significantly with the severity of oesophagitis, but postprandial acid exposure correlated best and recumbent acid exposure least well. Although acid clearance in the total, recumbent and upright periods correlated with oesophagitis, postprandial clearance showed the closest relationship. Thus the magnitude of daytime reflux, especially postprandial reflux and acid clearance, is more closely related than nocturnal reflux to oesophagitis. The results do not support the contention that night time reflux is inherently more injurious than daytime reflux to the oesophageal mucosa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M., Van Gelder A. Esophageal intraluminal pH recording in the assessment of gastroesophageal reflux and its consequences. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):365–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01072195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babka J. C., Castell D. O. On the genesis of heartburn. The effects of specific foods on the lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 May;18(5):391–397. doi: 10.1007/BF01071988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boesby S. Gastro-oesophageal acid reflux and sphincter pressure in normal human subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(7):731–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth D. J., Kemmerer W. T., Skinner D. B. Acid clearing from the distal esophagus. Arch Surg. 1968 May;96(5):731–734. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330230039006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branicki F. J., Evans D. F., Jones J. A., Ogilvie A. L., Atkinson M., Hardcastle J. D. A frequency-duration index (FDI) for the evaluation of ambulatory recordings of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg. 1984 Jun;71(6):425–430. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branicki F. J., Evans D. F., Ogilvie A. L., Atkinson M., Hardcastle J. D. Ambulatory monitoring of oesophageal pH in reflux oesophagitis using a portable radiotelemetry system. Gut. 1982 Nov;23(11):992–998. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.11.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Wang C. I., Wernly J. A., Pellegrini C. A., Little A. G., Klementschitsch P., Bermudez G., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Technique, indications, and clinical use of 24 hour esophageal pH monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 May;79(5):656–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Joseph G. J., Toscano M. S., Hall A. W., Skinner D. B. Patterns of gastroesophageal reflux in health and disease. Ann Surg. 1976 Oct;184(4):459–470. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197610000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON D. J., SANCHEZ-PALOMERA E., SAKO Y., CLATWORTHY H. W., Jr, TOON R. W., WANGENSTEEN O. H. Studies on experimental esophagitis. Surgery. 1950 Dec;28(6):1022–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink S. M., McCallum R. W. The role of prolonged esophageal pH monitoring in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux. JAMA. 1984 Sep 7;252(9):1160–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlihy K. J., Orlando R. C., Bryson J. C., Bozymski E. M., Carney C. N., Powell D. W. Barrett's esophagus: clinical, endoscopic, histologic, manometric, and electrical potential difference characteristics. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):436–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs R. H., Castell D. O., Eastwood G. L. Studies on the mechanism of esophagitis-induced lower esophageal sphincter hypotension in cats. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jul;71(1):51–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Horton P. F., Pope C. E., 2nd Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Feb;58(2):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R., Haggitt R. C. Esophageal epithelial response to gastroesophageal reflux. A quantitative study. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Jun;23(6):498–509. doi: 10.1007/BF01072693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRILUK L. B., MERENDINO K. A. The comparative sensitivity of the mucosa of the various segments of the alimentary tract in the dog to acid-peptic action. Surgery. 1954 Apr;35(4):547–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye M. D. Postprandial gastro-oesophageal reflux in healthy people. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):709–712. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén G., Tibbling L. Influence of body position, dry and water swallows, smoking, and alcohol on esophageal acid clearing. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(3):283–288. doi: 10.3109/00365527809179821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter I. Measurement of gastro-oesophageal acid reflux: its significance in hiatus hernia. Br J Surg. 1974 Apr;61(4):253–258. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800610402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little A. G., DeMeester T. R., Kirchner P. T., O'Sullivan G. C., Skinner D. B. Pathogenesis of esophagitis in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Surgery. 1980 Jul;88(1):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebel O. T., Castell D. O. Lower esophageal sphincter pressure changes after food ingestion. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):778–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Johnson L. F., Robinson M. G. Effect of sleep on swallowing, esophageal peristalsis, and acid clearance. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):814–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Robinson M. G., Johnson L. F. Acid clearance during sleep in the pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 May;26(5):423–427. doi: 10.1007/BF01313584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. E., Castell D. O. Gastroesophageal reflux. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jul;97(1):93–103. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger P. K., Donahue P. E., Schmid B., Layden T. J. Limitations of 24-hour intraesophageal pH monitoring in the hospital setting. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):797–804. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90575-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Steinkamp U., Weise A., Berges W., Wienbeck M., Rohner H. G., Peter P. Salivary secretion in reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):889–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. Prolonged pH recording in the study of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg. 1969 Dec;56(12):912–914. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800561211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanciu C., Bennett J. R. Oesophageal acid clearing: one factor in the production of reflux oesophagitis. Gut. 1974 Nov;15(11):852–857. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.11.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitale G. C., Cheadle W. G., Sadek S., Michel M. E., Cuschieri A. Computerized 24-hour ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring and esophagogastroduodenoscopy in the reflux patient. A comparative study. Ann Surg. 1984 Dec;200(6):724–728. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198412000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M., Bogoch E. R., Bowes K. L. The normal human esophageal mucosa: a histological reappraisal. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):40–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


