Abstract
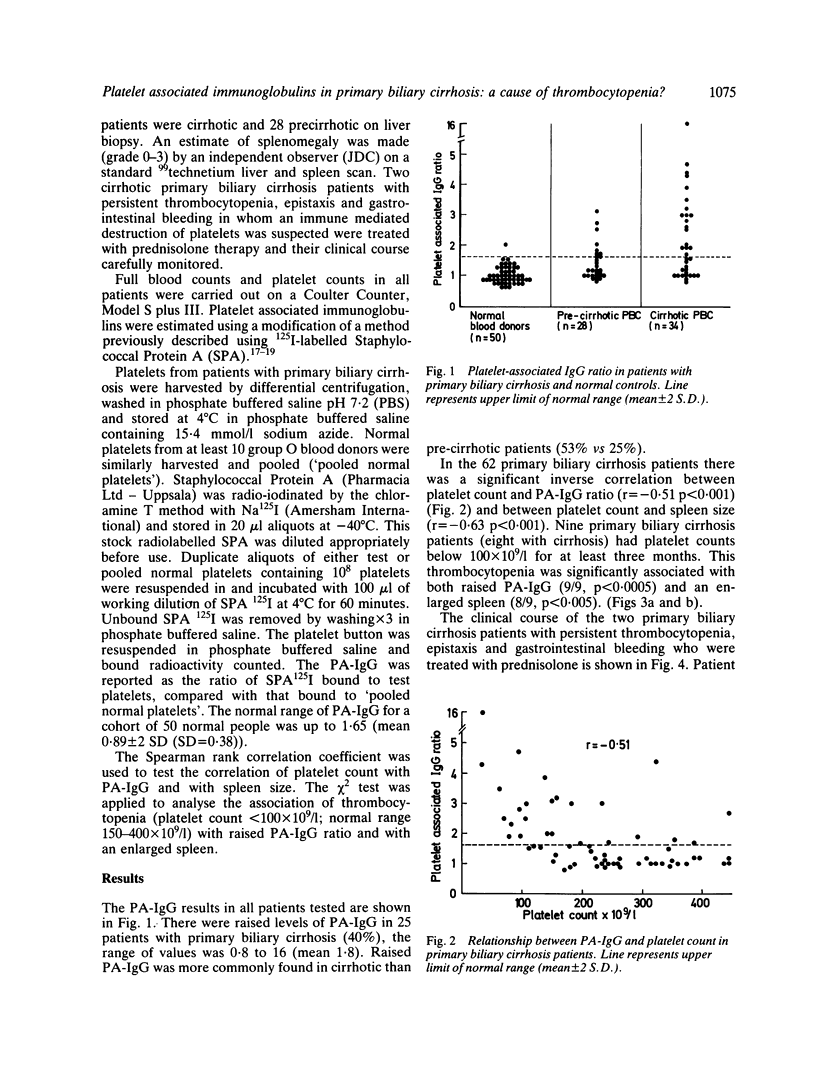
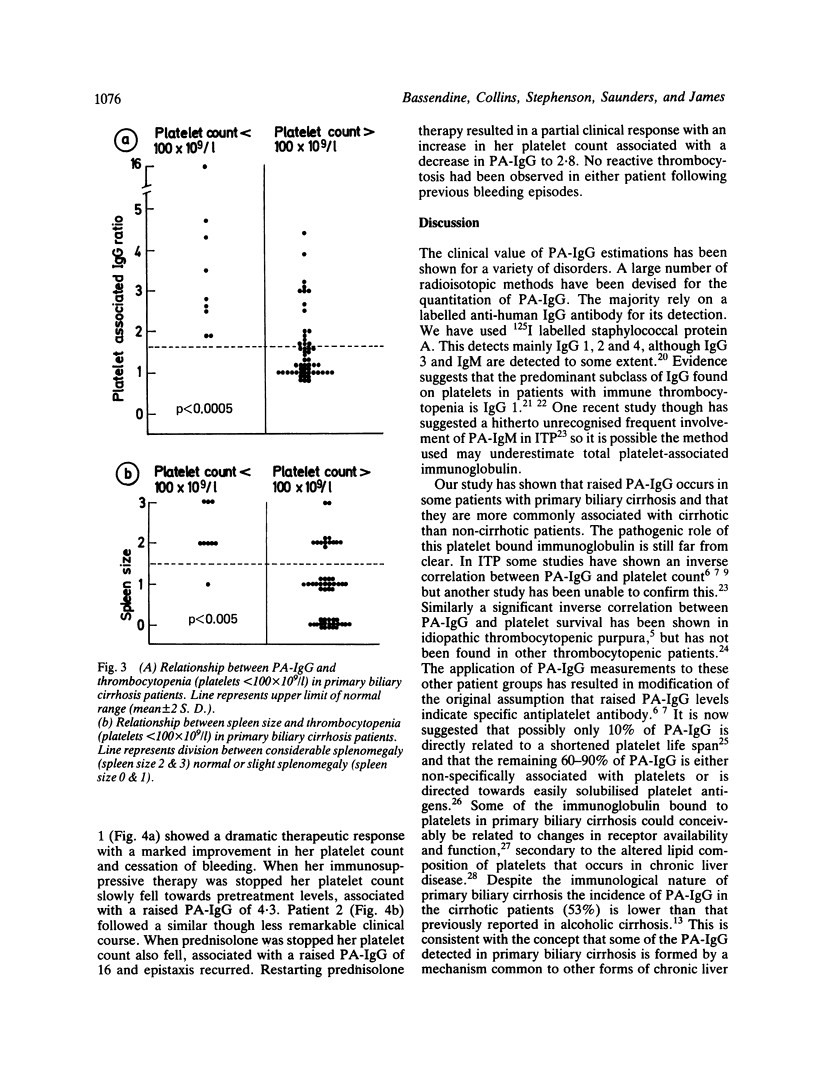
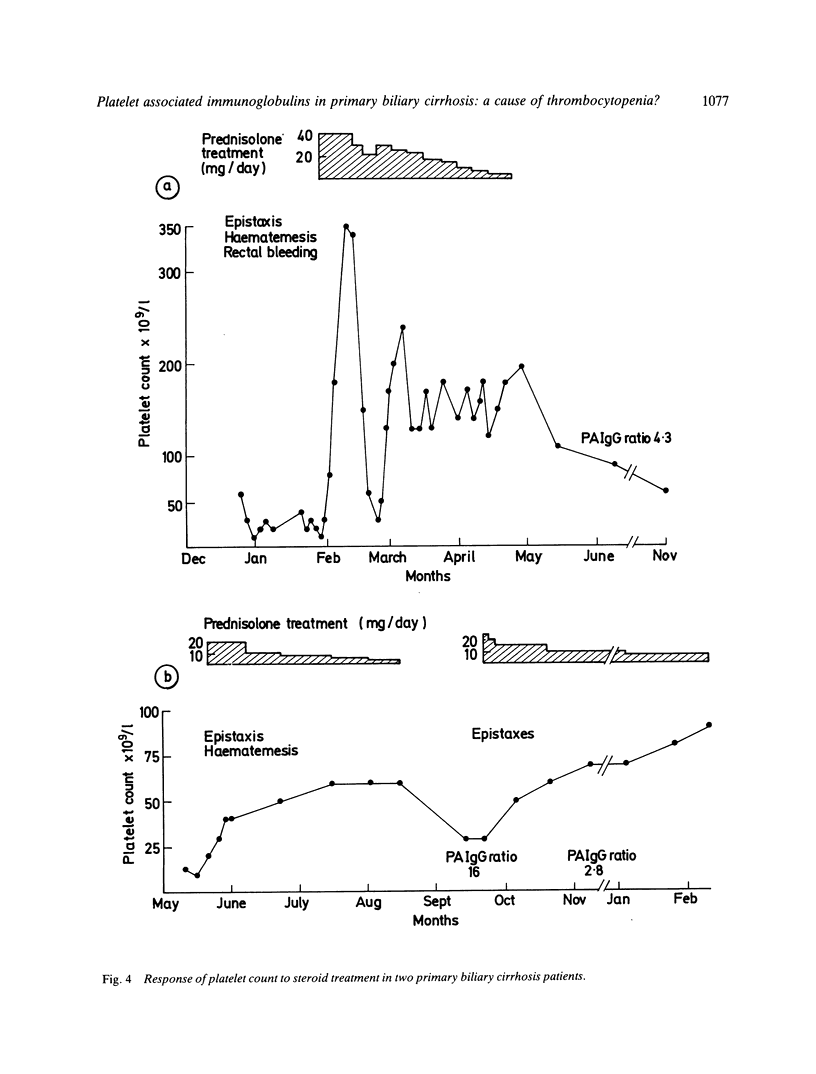
Thrombocytopenia in cirrhotic patients is usually attributed to splenic pooling whereas in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura it is related to platelet bound immunoglobulin (PA-IgG). Since primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is an autoimmune disorder we have undertaken a prospective study to assess the frequency and possible relationship of PA-IgG to thrombocytopenia in this condition. Sixty-two primary biliary cirrhosis patients (28 precirrhotic; 34 cirrhotic) were studied. Twenty-five patients (40%) had raised PA-IgG of whom 18 had cirrhosis. There was a significant inverse correlation between platelet count and PA-IgG (p less than 0.001) and between platelet count and spleen size (p less than 0.001). Thrombocytopenia (platelets less than 100 X 10(9)/l) was found in nine patients (15%); all nine had raised PA-IgG and eight were cirrhotic with an enlarged spleen. Two cirrhotic patients with persistent thrombocytopenia and bleeding episodes were treated with prednisolone and showed a useful therapeutic response. These results suggest that immune mediated platelet destruction and splenic pooling of platelets may both play a part in the thrombocytopenia observed in primary biliary cirrhosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aster R. H. Pooling of platelets in the spleen: role in the pathogenesis of "hypersplenic" thrombocytopenia. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):645–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI105380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrison I. G., Knight I. D., Viola L., Boots M. A., Murray-Lion I. M., Mitchell T. R. Platelet associated immunoglobulins on chronic liver disease. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jun;48(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergh O. J., Solheim B. G. Detection of thrombocyte antibodies by 125I labeled protein A. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Sep;12(3):189–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cines D. B., Schreiber A. D. Immune thrombocytopenia. Use of a Coombs antiglobulin test to detect IgG and C3 on platelets. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 18;300(3):106–111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901183000302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A. Abnormalities of cell-membrane fluidity in the pathogenesis of disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 18;297(7):371–377. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708182970707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Rosse W., Ebbert L. Quantitative determination of antibody in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Correlation of serum and platelet-bound antibody with clinical response. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 30;292(5):230–236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501302920503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach D., Roitt I. M., Walker J. G., Sherlock S. Tissue antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis, active chronic (lupoid) hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis and other liver diseases and their clinical implications. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):237–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymes K., Shulman S., Karpatkin S. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for bound anti-platelet antibody: studies on 45 patients with autoimmune platelet disorders. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Oct;94(4):639–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James O., Macklon A. F., Watson A. J. Primary biliary cirrhosis--a revised clinical spectrum. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1278–1281. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Siskind G. W., Zucker M. B. Studies on the specificity of anti-platelet autoantibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Dec;147(3):715–719. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekomäki Detection of platelet-bound IgG with 125I-labelled staphylococcal protein A. Med Biol. 1977 Apr;55(2):112–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Powers P. J., Carter C. J. A prospective study of the usefulness of the measurement of platelet-associated IgG for the diagnosis of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):1050–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernoff L. M., Blake K. C., Shackleton D. Influence of the amount of platelet-bound IgG on platelet survival and site of sequestration in autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):730–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi R., Leone G., Fedeli G., Storti S., Laghi F., Bizzi B. Platelet-associated IgG in acute and chronic hepatic diseases. Scand J Haematol. 1980 Nov;25(5):417–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1981.tb01423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmark R., Thorén-Tolling K., Sjöquist J. Binding of immunoglobulins to protein A and immunoglobulin levels in mammalian sera. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Aug 12;62(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luiken G. A., McMillan R., Lightsey A. L., Gordon P., Zevely S., Schulman I., Gribble T. J., Longmire R. L. Platelet-associated IgG in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1977 Aug;50(2):317–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacSween R. N., Horne C. H., Moffat A. J., Hughes H. M. Serum protein levels in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Sep;25(9):789–792. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.9.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1981 May 7;304(19):1135–1147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198105073041904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Eckhardt C., Mueller-Eckhardt G., Kayser W., Voss R. M., Wegner J., Küenzlen E. Platelet associated IgG, platelet survival, and platelet sequestration in thrombocytopenic states. Br J Haematol. 1982 Sep;52(1):49–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb03860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nel J. D., Stevens K., Mouton A., Pretorius F. J. Platelet-bound IgM in autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. S., Hutton R. A., Day R. C., Bruckdorfer K. R., McIntyre N. Platelet lipid composition and platelet aggregation in human liver disease. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):423–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Cosgrove L., Firkin B. G., Tew D. Relationship of raised platelet IgG in thrombocytopenia to total platelet protein content. Br J Haematol. 1981 Oct;49(2):293–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb07226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Adams J. P., Yount W. J. Subclasses of IgG antibodies in immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITPO). Br J Haematol. 1980 Sep;46(1):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb05940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. H., Weston M. J., Langley P. G., White Y., Williams R. Platelet function in chronic liver disease: relationship to disease severity. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Mar;24(3):197–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01308429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN N. R., MARDER V. J., HILLER M. C., COLLIER E. M. PLATELET AND LEUKOCYTE ISOANTIGENS AND THEIR ANTIBODIES: SEROLOGIC PHYSIOLOGIC AND CLINICAL STUDIES. Prog Hematol. 1964;4:222–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K. A., Slichter S. J., Harker L. A. Immune-mediated platelet destruction and thrombocytopenia in patients with solid tumours. Br J Haematol. 1982 May;51(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb07285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Axelson J., Maglott J. G., LoBuglio A. F. Quantification of platelet-bound IgG by 125I-Staphylococcal protein A in immune thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombocytopenic disorders. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von dem Borne A. E., Helmerhorst F. M., van Leeuwen E. F., Pegels H. G., von Riesz E., Engelfriet C. P. Autoimmune thrombocytopenia: detection of platelet autoantibodies with the suspension immunofluorescence test. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jun;45(2):319–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb07151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


