Abstract
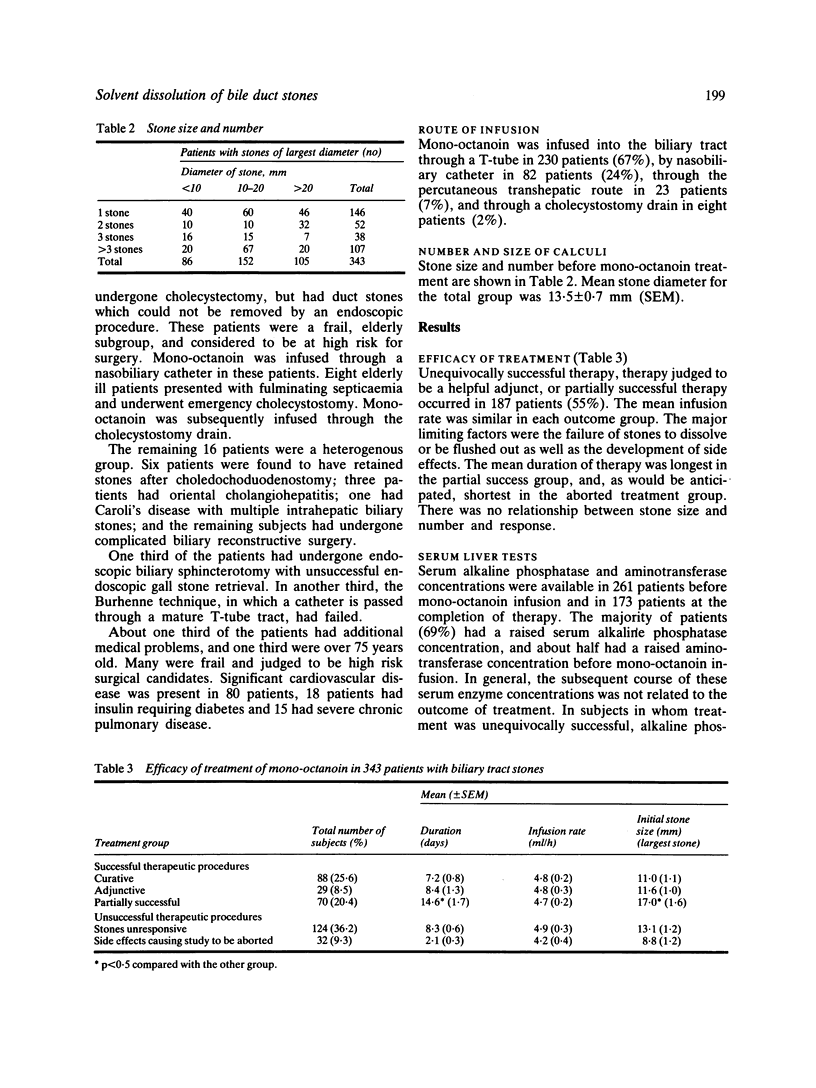
The efficacy and safety of mono-octanoin, a cholesterol solvent for the direct dissolution of stones in the biliary tract, was assessed by collating case reports on 343 patients provided by 222 physicians who used the material between 1977 and 1983. Most patients had previously undergone cholecystectomy, with common duct exploration, the majority within the preceding six weeks. In most, sphincterotomy was impossible or if carried out, had not induced stone passage. Stone dissolution was considered preferable to surgery, especially in patients who were frail, elderly, or had multiple medical problems. Treatment was unequivocally successful in 88 patients (26%) and was a valuable adjunct to interventional treatment in another 29 subjects (8%). In 70 patients (20%), calculi became smaller, but remained within the biliary tree. Thus, mono-octanoin was judged to have been useful in 54% of patients. Treatment was ineffective in 124 cases (36%). In the remaining 32 patients (9%), treatment was aborted because of side effects. Such side effects were common, occurring in 67% of cases, and in 41% of patients they were multiple. Abdominal pain was the most common complication. Other side effects reported were nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea. Side effects were usually dose related and responded to reduction in infusion rate. Side effects were life threatening in 12 patients (5%), but there were no permanent sequelae and no deaths occurred. These data indicate that mono-octanoin is moderately effective, generally second line, but sometimes first line, treatment for retained biliary duct calculi.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Admirand W. H., Way L. Medical treatment of retained gallstones. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1972;85:382–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen M. J., Borody T. J., Bugliosi T. F., May G. R., LaRusso N. F., Thistle J. L. Rapid dissolution of gallstones by methyl tert-butyl ether. Preliminary observations. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 24;312(4):217–220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501243120406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus J. B. Importance of viscosity in the dissolution rate of cholesterol in monooctanoin solutions. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Jul;73(7):906–910. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus J. B. Unusual cholesterol solubility in water/glyceryl-1-monooctanoate solutions. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Mar;71(3):370–372. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton D. C., Gill B. S., Taylor R. M., James O. The removal of retained gallstones from the common bile duct: experience with sodium cholate infusion and the Burhenne catheter. Br J Surg. 1975 Jul;62(7):520–523. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
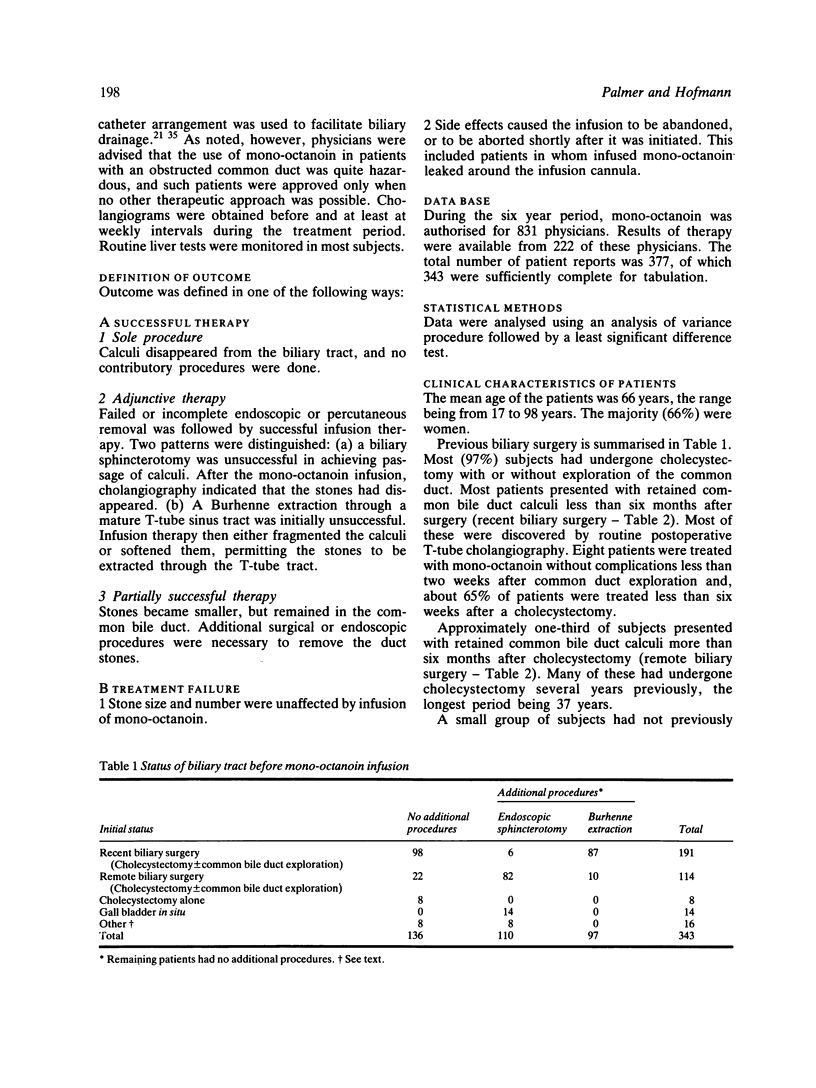
- Catt P. B., Hogg D. F., Clunie G. J., Hardie I. R. Retained biliary calculi: removal by a simple non-operative technique. Ann Surg. 1974 Aug;180(2):247–251. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197408000-00021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree T. S., Dykstra R., Kelly J., Preshaw R. M. Necrotizing choledochomalacia after use of monooctanoin to dissolve bile-duct stones. Can J Surg. 1982 Nov;25(6):644–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H. Management of stones in the biliary tree. Gut. 1983 Jul;24(7):599–608. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.7.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. L., Shah Y., Prakongpan S., Kwan K. H., Higuchi W. I., Hofmann A. F. Cholesterol solubility in organic solvents. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Sep;68(9):1090–1097. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadacz T. R. The effect of monooctanoin on retained common duct stones. Surgery. 1981 May;89(5):527–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner B. Experiences with the use of intracholedochal heparinized saline for the treatment of retained common duct stones. Ann Surg. 1973 Feb;177(2):240–244. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197302000-00021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Schmack B., Thistle J. L., Babayan V. K. Clinical experience with monooctanoin for dissolution of bile duct stones:" an uncontrolled multicenter trial. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Oct;26(10):954–955. doi: 10.1007/BF01309504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett L. N., Balfour T. W., Bell G. D., Knapp D. R., Rose D. H. Intraductal infusion of mono-octanoin: experience in 24 patients with retained common-duct stones. Lancet. 1981 Jan 10;1(8211):68–70. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansford C., Mehta S., Kern F., Jr The treatment of retained stones in the common bile duct with sodium cholate infusion. Gut. 1974 Jan;15(1):48–51. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Baumgärtel H. Chemical dissolution of common bile duct stones. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;152:193–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Baumgärtel H. Gallstone dissolution in the biliary tract: in vitro investigations on inhibiting factors and special dissolution agents. Am J Gastroenterol. 1982 Apr;77(4):222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Baumgärtel H., Wurbs D. Auflösung von Cholesterin-Gallengangssteinen mit einer modifizierten Capmul 8210-Emulsion und einer EDTA-Gallensalzlösung. Leber Magen Darm. 1980 Oct;10(5):284–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Sieratzki J., Klempa I., Baumgärtel H., Lang S., Siede W., Hübner K., Classen M. Investigations on the toxicity of bile salt solutions, Capmul 8210 and a bile salt-EDTA solution for common bile duct perfusion in dogs. Digestion. 1984;30(1):23–32. doi: 10.1159/000199087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack E., Crummy A. B., Babayan V. K. Percutaneous transhepatic dissolution of common bile duct stones. Surgery. 1981 Oct;90(4):584–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack E., Patzer E. M., Crummy A. B., Hofmann A. F., Babayan V. K. Retained biliary tract stones. Nonsurgical treatment with capmul 8210, a new cholesterol gallstone dissolution agent. Arch Surg. 1981 Mar;116(3):341–344. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380150059016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack E., Saito C., Goldfarb S., Carlson G. L., Hofmann A. F. Local toxicity of T-tube-infused cholate in the rhesus monkey. Surg Forum. 1977;28:408–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minuk G. Y., Hoofnagle J. H., Jones E. A. Systemic side effects from the intrabiliary infusion of monooctanoin for the dissolution of gallstones. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1982 Apr;4(2):133–135. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198204000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWABE A. D., COZZETTO F. J., BENNETTLR, MELLINKOFF S. M. Estimation of fat absorption by monitoring of expired radio-active carbon dioxide after feeding a radioactive fat. Gastroenterology. 1962 Mar;42:285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRICKLER J. H., ADKINS D. C., RICE C. O. Ether flush treatment of retained postoperative common duct stones; a local survey. Minn Med. 1954 Jul;37(7):490–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhagen R. M., Pertsemlidis D. Monooctanoin dissolution of retained biliary stones in high risk patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;78(11):756–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teplick S. K., Haskin P. H. Monooctanoin perfusion for in vivo dissolution of biliary stones. A series of 11 patients. Radiology. 1984 Nov;153(2):379–383. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.2.6484170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Carlson G. L., Hofmann A. F., LaRusso N. F., MacCarty R. L., Flynn G. L., Higuchi W. I., Babayan V. K. Monooctanoin, a dissolution agent for retained cholesterol bile duct stones: physical properties and clinical application. Gastroenterology. 1980 May;78(5 Pt 1):1016–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Jablonski P., Watts J. M. Dissolution of stones in the common bile duct with bile-salt solutions. Aust N Z J Surg. 1974 Nov;44(4):336–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1974.tb03899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tritapepe R., Di Padova C., Pozzoli M., Rovagnati P., Montorsi W. The treatment of retained biliary stones with monooctanoin: report of 16 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1984 Sep;79(9):710–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uribe M., Uscanga L., Farca S., Sanjurjo J. L., LaGarriga J., Ortíz J. H. Dissolution of cholesterol ductal stones in the biliary tree with medium-chain glycerides. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Jul;26(7):636–640. doi: 10.1007/BF01367677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco N., Braghetto I., Csendes A. Treatment of retained common bile duct stones: a prospective controlled study comparing monooctanoin and heparin. World J Surg. 1983 Mar;7(2):266–270. doi: 10.1007/BF01656158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venu R. P., Geenen J. E., Toouli J., Hogan W. J., Kozlov N., Stewart E. T. Gallstone dissolution using mono-octanoin infusion through an endoscopically placed nasobiliary catheter. Am J Gastroenterol. 1982 Apr;77(4):227–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way L. W., Admirand W. H., Dunphy J. E. Management of choledocholithiasis. Ann Surg. 1972 Sep;176(3):347–359. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197209000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way L. W., Admirand W. H., Dunphy J. E. Management of choledocholithiasis. Ann Surg. 1972 Sep;176(3):347–359. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197209000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzel L., Wiederholt J., Wolbergs E. Dissolution of retained duct stones by perfusion with monooctanoin via a Teflon catheter introduced endoscopically. Gastrointest Endosc. 1981 May;27(2):63–65. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(81)73151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosiewitz U., Schenk J., Sabinski F., Schmack B. Investigations on common bile duct stones. Digestion. 1983;26(1):43–52. doi: 10.1159/000198867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vanSonnenberg E., Schiffman H. R., Casola G., Talner L. B., Reznek R. H. Simplified solvent infusion and drainage in closed systems: double-lumen, single-catheter method. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 Feb;144(2):259–260. doi: 10.2214/ajr.144.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


