Abstract
Neurotensin is a tridecapeptide located mainly in the distal small intestine. The present study was carried out in order to investigate the neurotensin response after proximal small intestinal resection in the rat. After resection, the median plasma concentration of neurotensin like immunoreactivity (NTLI) was unchanged compared with sham operated rats. Intragastric instillation of fat increased the plasma concentration of NTLI from 45 pmol/l (34-63) in sham operated rats to 92 pmol/l (46-121) in resected rats. No significant increase in the plasma concentration of NTLI was found after intragastric instillation of amino acids or glucose. The tissue concentration of NTLI increased significantly in the jejunum and ileum after proximal small intestinal resection, while the number of immunoreactive neurotensin cells was unchanged. This study shows that the adaptive responses in the distal small intestine after proximal small intestinal resection also involve the neurotensin producing cells.
Full text
PDF

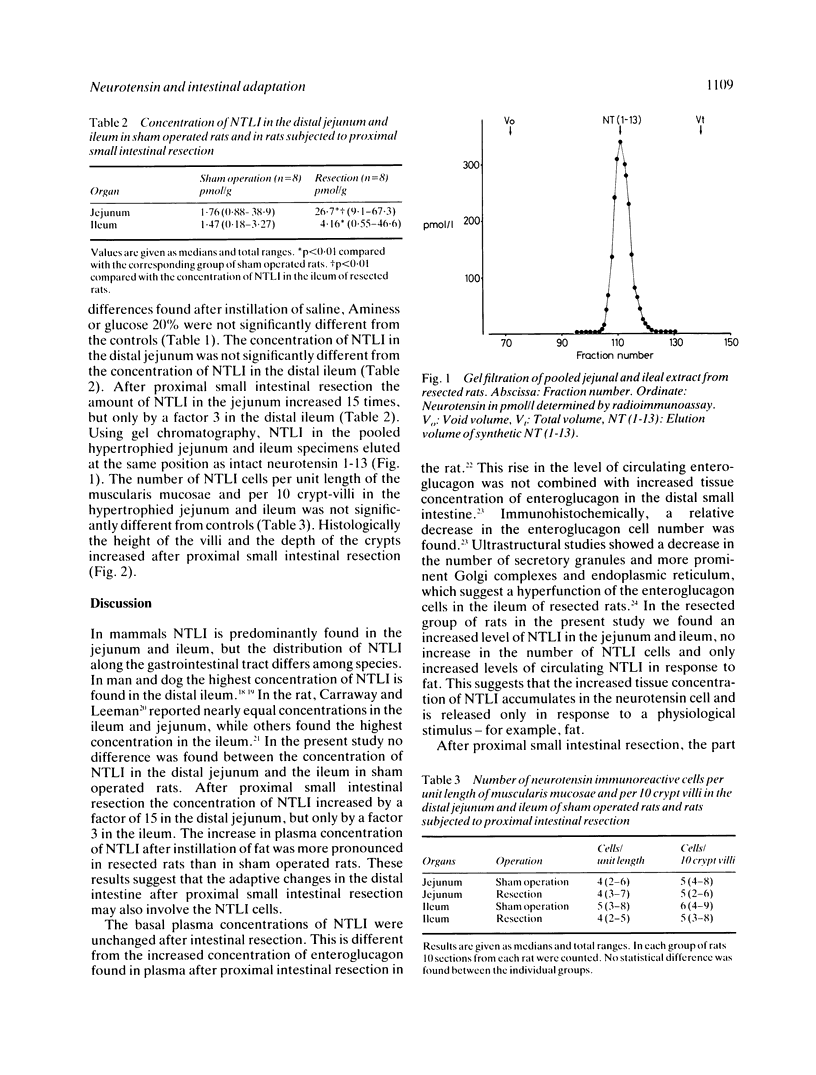


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann G. G. Influence of bile and pancreatic secretions on the size of the intestinal villi in the rat. Am J Anat. 1971 Oct;132(2):167–177. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001320204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH C. C., EVANS K. T., MENZIES T., STREET D. F. Intestinal hypertrophy following partial resection of the small bowel in the rat. Br J Surg. 1959 Jan;46(198):403–410. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004619821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A. M., Griffiths C. J., Morris J. F., Polak J. M. Enteroglucagon cell hyperfunction in rat small intestine after gut resection. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine, and stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7045–7052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clain J. E., Go V. L., Malagelada J. R. Inhibitory role of the distal small intestine on the gastric secretory response to meals in man. Gastroenterology. 1978 Apr;74(4):704–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Booth C. C. Structural and functional changes following small intestinal resection in the rat. Clin Sci. 1967 Feb;32(1):139–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H., Greeley G. H., Jr, Mate L., Sakamoto T., Townsend C. M., Jr, Thompson J. C. Distribution of neurotensin in the canine gastrointestinal tract. Surgery. 1985 Mar;97(3):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman E. J., Dowling R. H., McNaughton J., Peters T. J. Effects of oral versus intravenous nutrition on intestinal adaptation after small bowel resection in the dog. Gastroenterology. 1976 May;70(5 PT1):712–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. F., Hammer R. A., Leeman S. E. Elevation of plasma neurotensin during lipid perfusion of rat small intestine. Peptides. 1981;2 (Suppl 2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(81)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher D. R., Shulkes A., Bladin P. H., Booth D., Hardy K. J. Cholinergic inhibition of meal stimulated plasma neurotensin like immunoreactivity in man. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 29;33(9):863–869. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher D. R., Shulkes A., Bladin P. H., Hardy K. J. The effect of atropine on bombesin and gastrin releasing peptide stimulated gastrin, pancreatic polypeptide and neurotensin release in man. Regul Pept. 1983 Sep;7(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigerio B., Ravazola M., Ito S., Buffa R., Capella C., Solcia E., Orci L. Histochemical and ultrastructural identification of neurotensin cells in the dog ileum. Histochemistry. 1977 Oct 22;54(2):123–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00489670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson M. H., Cullen J., Dowling R. H. Intestinal structure and function after small bowel by-pass in the rat. Clin Sci. 1972 Dec;43(6):731–742. doi: 10.1042/cs0430731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Górnacz G. E., Al-Mukhtar M. Y., Ghatei M. A., Sagor G. R., Wright N. A., Bloom S. R. Pattern of cell proliferation and enteroglucagon response following small bowel resection in the rat. Digestion. 1984;29(2):65–72. doi: 10.1159/000199012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst Pedersen J., Fahrenkrug J. Neurotensin-like immunoreactivities in human plasma: feeding responses and metabolism. Peptides. 1986 Jan-Feb;7(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Ito S., Shibata A. Radioimmunoassay of neurotensin and the distribution and concentration of gut neurotensin in rat and dog. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1980 Feb;130(2):129–137. doi: 10.1620/tjem.130.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard K. Resection of the small intestine in rats. IV. Adaptation of gastro-intestinal motility. Acta Chir Scand. 1967;133(5):407–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. H., Stadil F., Fahrenkrug J. Preparation of 125I-(Tyr 3)- and 125I-(Tyr 11)- neurotensin for radioimmunoassay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1983 Oct;43(6):483–491. doi: 10.1080/00365518309168435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Sullivan S. N., Bloom S. R., Buchan A. M., Facer P., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Specific localisation of neurotensin to the N cell in human intestine by radioimmunoassay and immunocytochemistry. Nature. 1977 Nov 10;270(5633):183–184. doi: 10.1038/270183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke M., Almasan K., Carraway R., Helmstaedter V., Forssmann W. G. Distribution patterns of neurotensin-like immunoreactive cells in the gastro-intestinal tract of higher vertebrates. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;205(3):383–395. doi: 10.1007/BF00232280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosell S., Rökaeus A. The effect of ingestion of amino acids, glucose and fat on circulating neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (NTLI) in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Nov;107(3):263–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagor G. R., Al-Mukhtar M. Y., Ghatei M. A., Wright N. A., Bloom S. R. The effect of altered luminal nutrition on cellular proliferation and plasma concentrations of enteroglucagon and gastrin after small bowel resection in the rat. Br J Surg. 1982 Jan;69(1):14–18. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800690106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Hökfelt T., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Rehfeld J. F., Brown M., Elde R., Goldstein M., Said S. Distribution of peptide- and catecholamine-containing neurons in the gastro-intestinal tract of rat and guinea-pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Neuroscience. 1980;5(4):689–744. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Håkanson R., Hammer R. A., Alumets J., Carraway R., Leeman S. E., Zimmerman E. A. Immunohistochemical localization of neurotensin in endocrine cells of the gut. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Mar 16;178(3):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00218696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E., Rosell S. The effect of duodenal administration of fatty acids, triolein, liquid paraffin and lecithin on plasma neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (p-NTLI) in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Mar;117(3):439–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb00018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



