Abstract
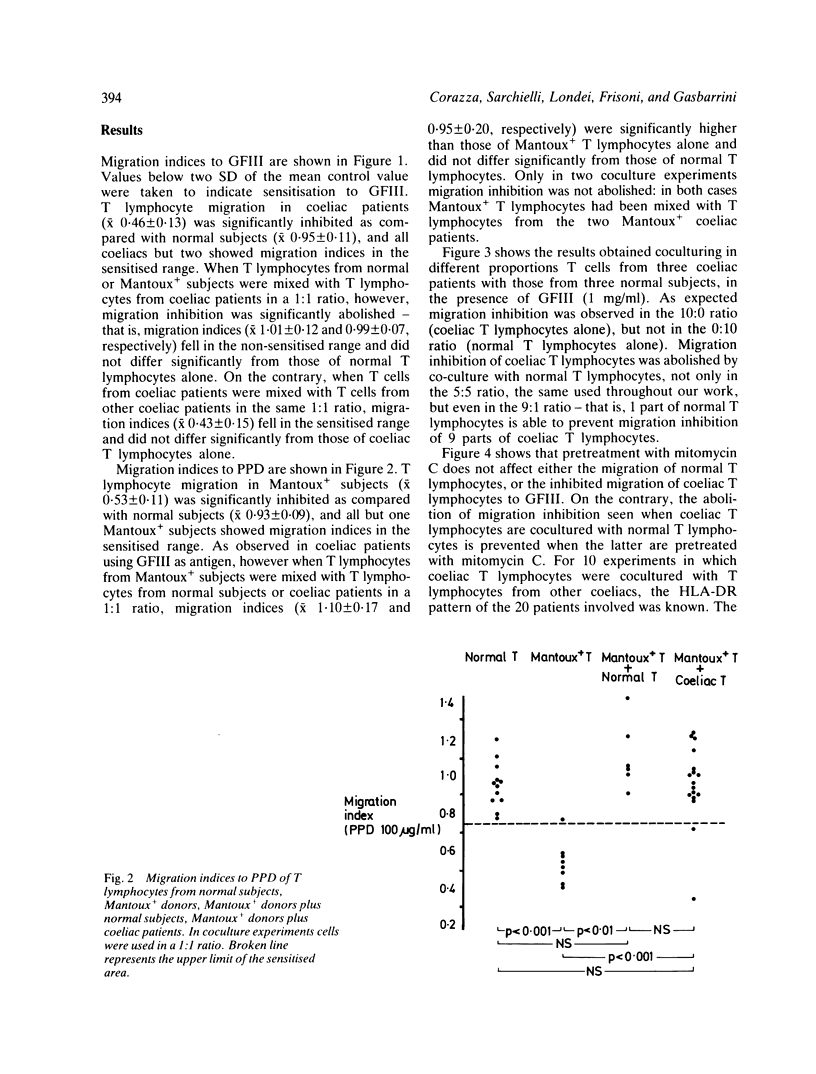
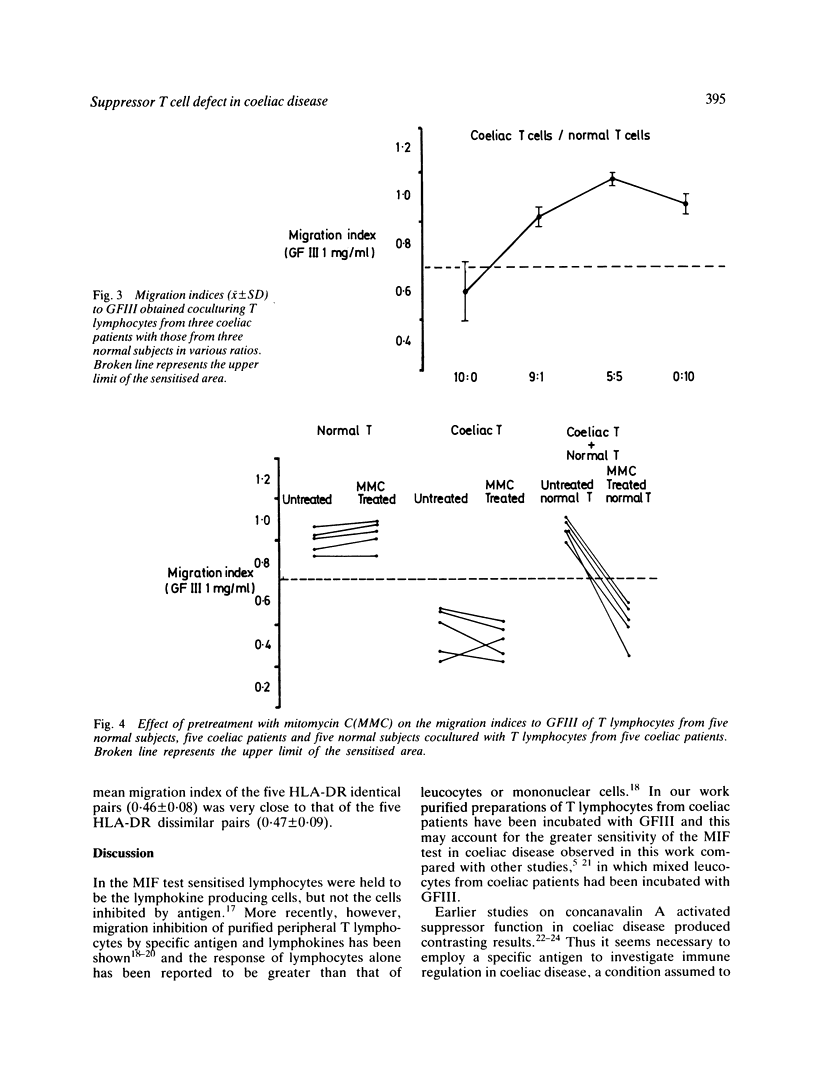
A T lymphocyte direct migration inhibition factor test has been used to investigate the function of the specific suppressor T cell population controlling the immune response to gluten in coeliac disease. The test has been carried out in 21 adult coeliac patients, 22 Mantoux- healthy controls and eight Mantoux+ donors using gluten fraction III and purified protein derivative, as antigens. All coeliacs, but two, were Mantoux-. When gluten fraction III was used a significant migration inhibition was observed in coeliac patients compared to controls; such migration inhibition was abrogated by coculturing in a 1:1 ratio coeliac T cells with T cells from controls or Mantoux+ donors. On the contrary, the addition to coeliac T cells of T lymphocytes from other coeliacs did not abolish migration inhibition to gluten. Pretreatment of normal T cells with mitomycin C prevented their abrogating activity on migration inhibition of coeliac T lymphocytes. When purified protein derivative was used as antigen a significant migration inhibition was observed in Mantoux+ donors compared with healthy subjects and such migration inhibition was abolished by co-culturing T cells from Mantoux+ donors with those from Mantoux- controls and coeliac patients. Our results show that coeliac T cells, while retaining their ability to suppress the immune response to purified protein derivative, cannot suppress the immune response to gluten and are consistent with the hypothesis that a gluten specific suppressor T cell dysfunction, rather than a generalised T lymphocyte defect, may play a role in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman N. E., Ksiazek J., Yoshida T., Cohen S. Lymphoid sources of murine migration inhibition factor. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):825–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkholm M., Holm G., Mellstedt H. No effect of delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity testing (Multitest) on blood lymphocyte counts and functions. Acta Med Scand. 1983;214(5):399–401. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1983.tb08614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen A. W., Losowsky M. S. Cell-mediated immunity to gluten fraction III in adult coeliac disease. Gut. 1978 Feb;19(2):126–131. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen A. W., Losowsky M. S. Comparison of a leucocyte adherence test with the leucocyte migration inhibition test and skin reactivity to PPD. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Mar;31(3):408–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen J. E. Polymorphonuclear leucocytes in the specific antigen-induced inhibition of the in vitro migration of human peripheral leucocytes. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Jul-Aug;1-2(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1970.tb08005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrum K. C., Salvatierra O., Cullen B. L., Perkins H. A., Hanes D. M., Fudenberg H. H. Leukocyte migration inhibitory factor (LIF) as an indicator of mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC) reactivity. Transplant Proc. 1977 Mar;9(1):97–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazza G. R., Frazzoni M., Gasbarrini G. Jejunal intraepithelial lymphocytes in coeliac disease: are they increased or decreased? Gut. 1984 Feb;25(2):158–162. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazza G. R., Rawcliffe P. M., Frisoni M., Sarchielli P., Londei M., Campieri M., Lazzari R., Gasbarrini G. Specificity of leucocyte migration inhibition test in coeliac disease. A reassessment using different gluten subfractions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Apr;60(1):117–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazza G. R., Tabacchi P., Frisoni M., Londei M., Bastia D., Gasbarrini G. T-lymphocyte subsets in adult coeliac disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jul;65(1):89–90. doi: 10.1042/cs0650089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazza G. R., Tabacchi P., Frisoni M., Prati C., Gasbarrini G. DR and non-DR Ia allotypes are associated with susceptibility to coeliac disease. Gut. 1985 Nov;26(11):1210–1213. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.11.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas A. P. The binding of a glycopeptide component of wheat gluten to intestinal mucosa of normal and coeliac human subjects. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Dec 1;73(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZER A. C., FLETCHER R. F., ROSS C. A., SHAW B., SAMMONS H. G., SCHNEIDER R. Gluten-induced enteropathy: the effect of partially digested gluten. Lancet. 1959 Sep 5;2(7097):252–255. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Strober W. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy: synthesis of antigliadin antibody in vitro. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):947–952. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M. Update on gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Am J Med. 1979 Dec;67(6):1085–1096. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., MacDonald T. T., McClure J. P., Holden R. J. Cell-mediated immunity to gliadin within the small-intestinal mucosa in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1975 Apr 19;1(7912):895–897. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91689-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. A., Rajaraman K. A link between helper and suppressor factors and the lymphokines migration inhibition factor and migration stimulation factor. Cell Immunol. 1981 Apr;59(2):448–454. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk D., Zembala M. Migration inhibition of T lymphocytes from human peripheral blood by specific antigen and lymphokines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 May;32(2):333–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly J. A., Waksman B. H. Immunologic suppression after oral administration of antigen. I. Specific suppressor cells formed in rat Peyer's patches after oral administration of sheep erythrocytes and their systemic migration. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1878–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Hanson D. G. Inhibition of specific immune responses by feeding protein antigens. IV. Evidence for tolerance and specific active suppression of cell-mediated immune responses to ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2344–2350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngan J., Kind L. S. Suppressor T cells for IgE and IgG in Peyer's patches of mice made tolerant by the oral administration of ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):861–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrelly C., McKeever U., Feighery C., Weir D. G. Increased concanavalin A induced suppression in treated and untreated coeliac disease. Gut. 1984 Jun;25(6):644–648. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.6.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita N., Kidd A., Row V. V., Volpé R. Sensitization of T-lymphocytes in Graves' and Hashimoto's diseases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Aug;51(2):316–320. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-2-316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita N., Row V. V., Volpe R. Suppressor T-lymphocyte deficiency in Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Mar;52(3):528–533. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-3-528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita N., Topliss D., Lewis M., Row V. V., Volpé R. T-lymphocyte sensitization in Graves' and Hashimoto's diseases confirmed by an indirect migration inhibition factor test. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Mar;52(3):523–527. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-3-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignata C., Troncone R., Monaco G., Ciriaco M., Farris E., Carminati G., Auricchio S. Impaired suppressor activity in children affected by coeliac disease. Gut. 1985 Mar;26(3):285–290. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. A., Bullen A., Field H., Simpson F. G., Losowsky M. S. Suppressor cell activity, splenic function and HLA B8 status in man. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 Nov;9(2):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Nishimura Y., Muto M., Ohta N. HLA-linked genes controlling immune response and disease susceptibility. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:51–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Bofill M., Jewell D. P. Lymphocyte subpopulations in the human small intestine. The findings in normal mucosa and in the mucosa of patients with adult coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):219–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B. Stimulation of autologous and allogeneic human T cells by B cells occurs through separate B-cell antigen systems. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 15;36(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dutton R. W. Negative allogeneic effects in vitro. I. Allogeneic T cells markedly suppress the secondary antibody-forming cell response. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2262–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR K. B., TRUELOVE S. C., THOMSON D. L., WRIGHT R. An immunological study of coeliac disease and idiopathic steatorrhoea. Serological reactions to gluten and milk proteins. Br Med J. 1961 Dec 30;2(5269):1727–1731. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5269.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Bernoco D., Park M. S., Ozturk G., Iwaki Y. Microdroplet testing for HLA-A, -B, -C, and -D antigens. The Phillip Levine Award Lecture. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;69(2):103–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., Parrott M. V. The induction of tolerance to a soluble protein antigen by oral administration. Immunology. 1974 Oct;27(4):631–639. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento S., Hegarty J. E., Bottazzo G., Macchia E., Williams R., Eddleston A. L. Antigen specific suppressor cell function in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1984 Jun 2;1(8388):1200–1204. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91691-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M., Douglas A. P. An alternative mechanism for gluten toxicity in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1976 Mar 13;1(7959):567–569. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90361-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


