Abstract
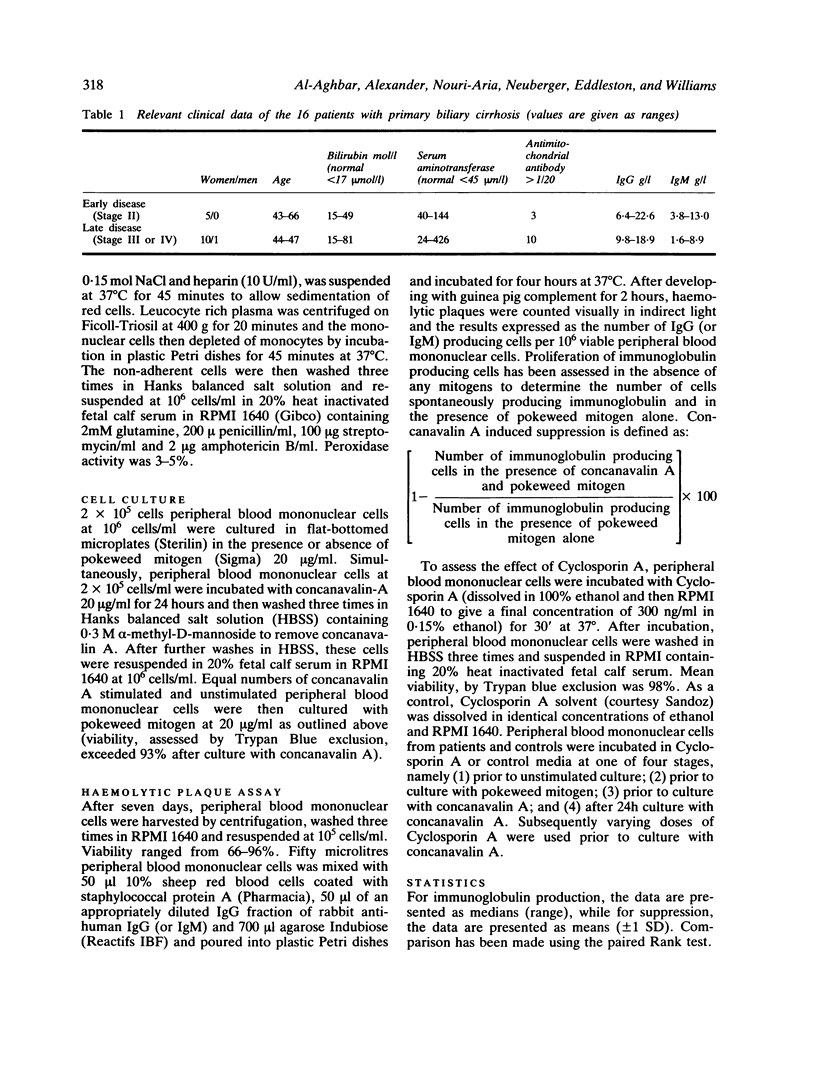
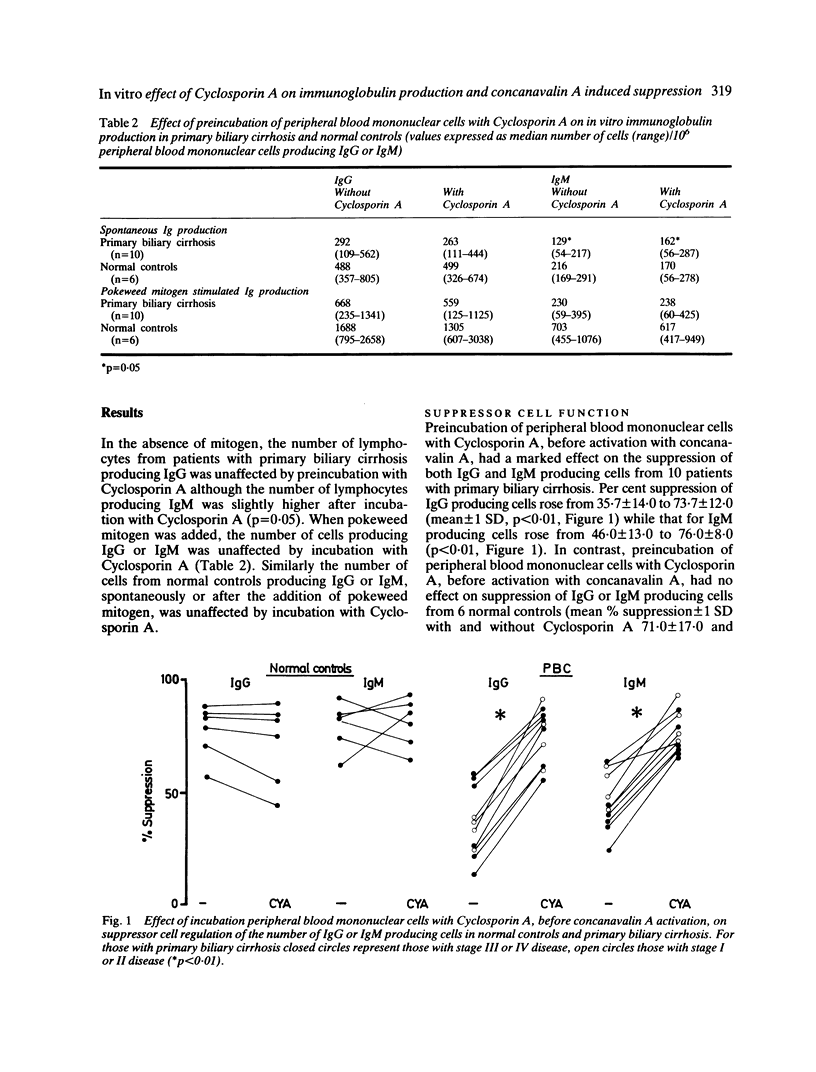
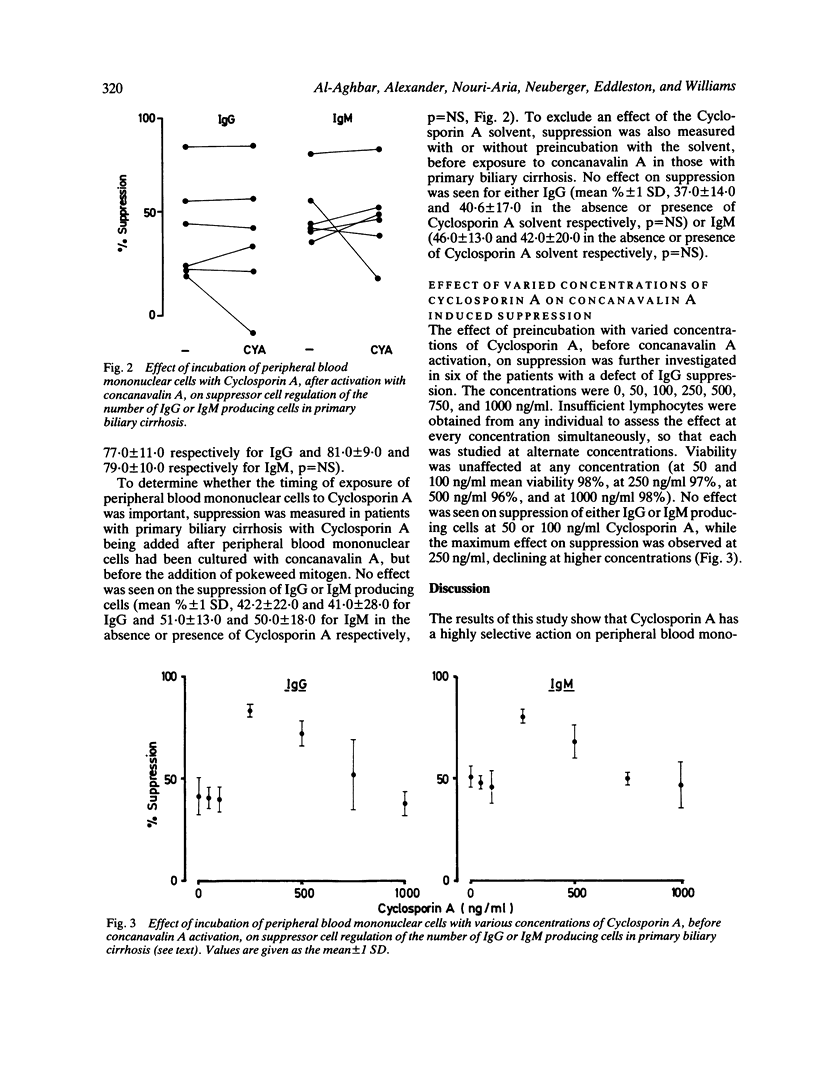
The in vitro effect of Cyclosporin A on the regulation of immunoglobulin production was investigated in 16 patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. A significant improvement in concanavalin A induced suppression of IgG and IgM producing cells was observed after prior incubation of mononuclear cells with 300 ng/ml Cyclosporin A for 30 minutes. No effect was seen on spontaneous or pokeweed mitogen induced immunoglobulin production, nor on con A induced suppression if Cyclosporin A was added after 24 hours. Incubation of mononuclear cells with a variable dose of Cyclosporin A showed an effect only at 250-500 ng/ml. Higher and lower doses had no effect. This dose dependent effect of Cyclosporin A is likely to be related to a differential inhibitory effect on T helper and T suppressor cells and may underlie the clinical benefit being observed in current clinical trials.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. C., Pounder R. E. Cyclosporin for Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1984 Apr 21;1(8382):902–903. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F., Feurer C., Magnée C., Stähelin H. Effects of the new anti-lymphocytic peptide cyclosporin A in animals. Immunology. 1977 Jun;32(6):1017–1025. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunjes D., Hardt C., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Cyclosporin A mediates immunosuppression of primary cytotoxic T cell responses by impairing the release of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):657–661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARMAN C. T., GIANSIRACUSA J. E. Effect of steroid therapy on the clinical and laboratory features of primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1955 Feb;28(2):193-207; discussion, 208-15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y., Rolles K., White D. J., Thiru S., Evans D. B., McMaster P., Dunn D. C., Craddock G. N., Henderson R. G., Aziz S. Cyclosporin A initially as the only immunosuppressant in 34 recipients of cadaveric organs: 32 kidneys, 2 pancreases, and 2 livers. Lancet. 1979 Nov 17;2(8151):1033–1036. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92440-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. O., Allison A. C., Samcewicz B. Experimental erythrocyte autoimmunity prevented by suppressor T cells in mice treated with Cyclosporin-A. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Jul;28(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote J., Desmet V. J., Gedigk P., Korb G., Popper H., Poulsen H., Scheuer P. J., Schmid M., Thaler H., Uehlinger E. A classification of chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1968 Sep 14;2(7568):626–628. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90710-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallgren H. M., Kersey J. H., Dubey D. P., Yunis E. J. Lymphocyte subsets and integrated immune function in aging humans. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 May;10(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. D., Tutschka P. J. Effect of cyclosporin A on human lymphocyte responses in vitro. I. CsA allows for the expression of alloantigen-activated suppressor cells while preferentially inhibiting the induction of cytolytic effector lymphocytes in MLR. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2601–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howat H. T., Ralston A. J., Varley H., Wilson J. A. The late results of long-term treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis by corticosteroids. Rev Int Hepatol. 1966;16(2):227–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Elson C. O., Jones E. A., Strober W. Abnormal regulation of immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):242–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. E., Benzie C. R. Effects of cyclosporin A on the metabolism of unstimulated and mitogen-activated lymphocytes. Immunology. 1983 May;49(1):153–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkl A., Klaus G. G. Selective effects of cyclosporin A on functional B cell subsets in the mouse. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2526–2531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L. Cyclosporin A and dexamethasone suppress T cell responses by selectively acting at distinct sites of the triggering process. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2828–2833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. B., Sepersky R. A., Brown K. M., Goldberg M. J., Kaplan M. M. Genetic abnormalities of immunoregulation in primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Med. 1983 Jul;75(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Yachie A., Ohzeki S., Nagaoki T., Taniguchi N. Cyclosporin A does not prevent expression of Tac antigen, a probable TCGF receptor molecule, on mitogen-stimulated human T cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2737–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Butler J. L., Kehrl J. H., Falkoff R. J., Fauci A. S. Selective suppression of an early step in human B cell activation by cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):690–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Kehrl J. H., Butler J. L., Fauci A. S. Sequential requirements for cell cycle progression of resting human B cells after activation by anti-Ig. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):176–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri-Aria K. T., Donaldson P. T., Hegarty J. E., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. HLA A1-B8-DR3 and suppressor cell function in first-degree relatives of patients with autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(3):235–241. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Palestine A. G., Rook A. H., Scher I., Wacker W. B., Gery I. Treatment of intraocular inflammatory disease with cyclosporin A. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):235–238. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Möller G. Cyclosporin A blocks receptors for HLA-DR antigens on T cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):792–794. doi: 10.1038/290792a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebuck A. S., Stiller C. R., Braude A. C., Laupacis A., Cohen R. D., Chapman K. R. Cyclosporin for pulmonary sarcoidosis. Lancet. 1984 May 26;1(8387):1174–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91411-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routhier G., Epstein O., Janossy G., Thomas H. C., Sherlock, Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Effects of cyclosporin A on suppressor and inducer T lymphocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1980 Dec 6;2(8206):1223–1226. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92481-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Iwatsuki S., Klintmalm G., Schröter G. P., Weil R., 3rd, Koep L. J., Porter K. A. Liver transplantation, 1980, with particular reference to cyclosporin-A. Transplant Proc. 1981 Mar;13(1 Pt 1):281–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller C. R., Dupré J., Gent M., Jenner M. R., Keown P. A., Laupacis A., Martell R., Rodger N. W., von Graffenried B., Wolfe B. M. Effects of cyclosporine immunosuppression in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1362–1367. doi: 10.1126/science.6367043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. S., Heacock E. H., Collins K. H., Hutchinson I. F., Tilney N. L., Mannick J. A. Suppressive effects of cyclosporin A on the induction of alloreactivity in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., McGregor A. M., Ludgate M., Beck L., Mills P. V., Lazarus J. H., Hall R. Cyclosporin improves Graves' ophthalmopathy. Lancet. 1983 Aug 27;2(8348):486–489. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90514-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. J., Plumb A. M., Pawelec G., Brons G. Cyclosporin A: an immunosuppressive agent preferentially active against proliferating T cells. Transplantation. 1979 Jan;27(1):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


