Abstract
Abnormalities of gut endocrine responses, as well as changes in the number of different endocrine cell types, have been reported convincingly in coeliac patients. Nevertheless, no estimation of total numbers of gut endocrine cells has yet been made in well defined groups of coeliacs. In this study, we have visualised all endocrine cell types in jejunal biopsies from coeliac patients with active and quiescent disease as well as in controls, using a monoclonal antibody to chromogranin. This protein was purified originally from bovine adrenal medulla and is known to be a reliable marker for all endocrine cells of the gut. The following groups were considered: (a) nine coeliacs with active illness, (b) 10 coeliacs under gluten-free diet, (c) eight coeliacs receiving gluten challenge, (d) five non-coeliacs (controls). Histological (haematoxylin and eosin) and immunocytochemical (peroxidase anti-peroxidase) stains were applied to 3 micron paraffin sections. Quantitative estimation of endocrine cell density was made using four different methods in order to evaluate the results fully (number of cells/mm2, number of cells/visual field, number of cells/8 crypts-villi, number of cells/unit of length of muscularis mucosae). In patient groups (a) and (c), coeliacs with active disease and coeliacs on gluten challenge diet respectively, a significantly higher number of endocrine cells was observed in comparison with normal controls (group d). In group (b) patients, coeliacs on gluten-free diet, no significant changes in the number of endocrine cells were observed in comparison with controls. Our results show that a significant increase in endocrine cell density exists in coeliacs with active illness (groups a and c), in comparison with controls. This condition is resolved in coeliacs receiving a gluten-free diet (group b).
Full text
PDF


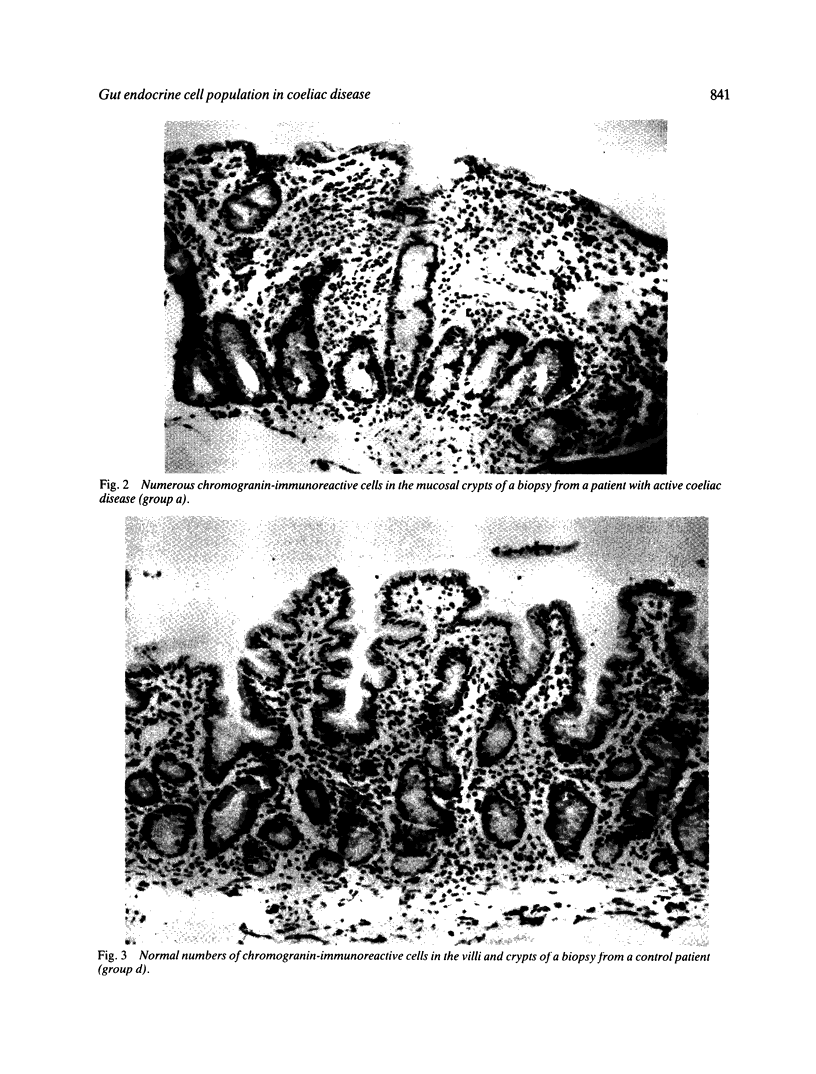


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besterman H. S., Bloom S. R., Sarson D. L., Blackburn A. M., Johnston D. I., Patel H. R., Stewart J. S., Modigliani R., Guerin S., Mallinson C. N. Gut-hormone profile in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1978 Apr 15;1(8068):785–788. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92994-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Comline R. S., Schneider F. H., Silver M., Smith A. D. Secretion of a chromaffin granule protein, chromogranin, from the adrenal gland after splanchnic stimulation. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):58–59. doi: 10.1038/215058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth C. C. Enterocyte in coeliac disease. 1. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 26;3(5725):725–731. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5725.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A. M., Grant S., Brown J. C., Freeman H. J. A quantitative study of enteric endocrine cells in celiac sprue. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Nov;3(5):665–671. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198411000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J., Bryant M. G., Bloom S. R., Peters T. J. Gastrointestinal regulatory peptide storage granule abnormalities in jejunal mucosal diseases. Gut. 1984 Jun;25(6):636–643. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.6.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facer P., Bishop A. E., Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S., Hennessy R. J., Polak J. M. Chromogranin: a newly recognized marker for endocrine cells of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1366–1373. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90657-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilander A. F., Dotevall G., Lindstedt G., Lundberg P. A. Plasma enteroglucagon related to malabsorption in coeliac disease. Gut. 1984 Jun;25(6):629–635. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.6.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S. Specific endocrine tissue marker defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6635661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N., Haeney M. R. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. VI--Proliferative response of small intestinal epithelial lymphocytes distinguishes gluten- from non-gluten-induced enteropathy. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Feb;36(2):149–160. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. III. Quantitative analyses of epithelial lymphocytes in the small intestine of human control subjects and of patients with celiac sprue. Gastroenterology. 1980 Sep;79(3):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. IV--The predictive value of raised mitotic indices among jejunal epithelial lymphocytes in the diagnosis of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. J Clin Pathol. 1982 May;35(5):517–525. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.5.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Burton D., Deftos L. J. Immunoreactive human chromogranin A in diverse polypeptide hormone producing human tumors and normal endocrine tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Nov;57(5):1084–1086. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-5-1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor F. A., McLoughlin J. C., Buchanan K. D. Impaired immunoreactive secretin release in coeliac disease. Br Med J. 1977 Mar 26;1(6064):811–811. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6064.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Pearse A. G., Van Noorden S., Bloom S. R., Rossiter M. A. Secretin cells in coeliac disease. Gut. 1973 Nov;14(11):870–874. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.11.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider F. H., Smith A. D., Winkler H. Secretion from the adrenal medulla: biochemical evidence for exocytosis. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):94–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölund K., Alumets J., Berg N. O., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Duodenal endocrine cells in adult coeliac disease. Gut. 1979 Jul;20(7):547–552. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.7.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölund K., Alumets J., Berg N. O., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Enteropathy of coeliac disease in adults: increased number of enterochromaffin cells the duodenal mucosa. Gut. 1982 Jan;23(1):42–48. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. Purification and properties of an acidic protein from chromaffin granules of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):483–492. doi: 10.1042/bj1030483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Lloyd R. V. Detection of chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells with a monoclonal antibody. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):458–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





