Abstract
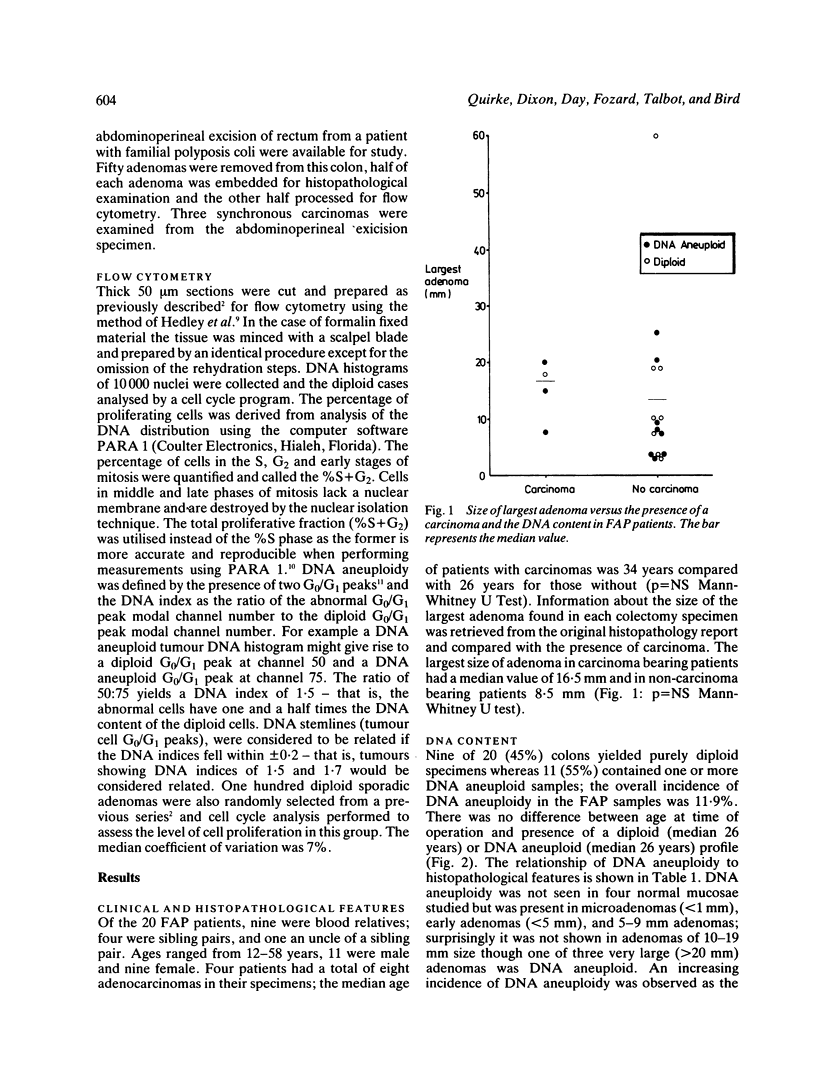
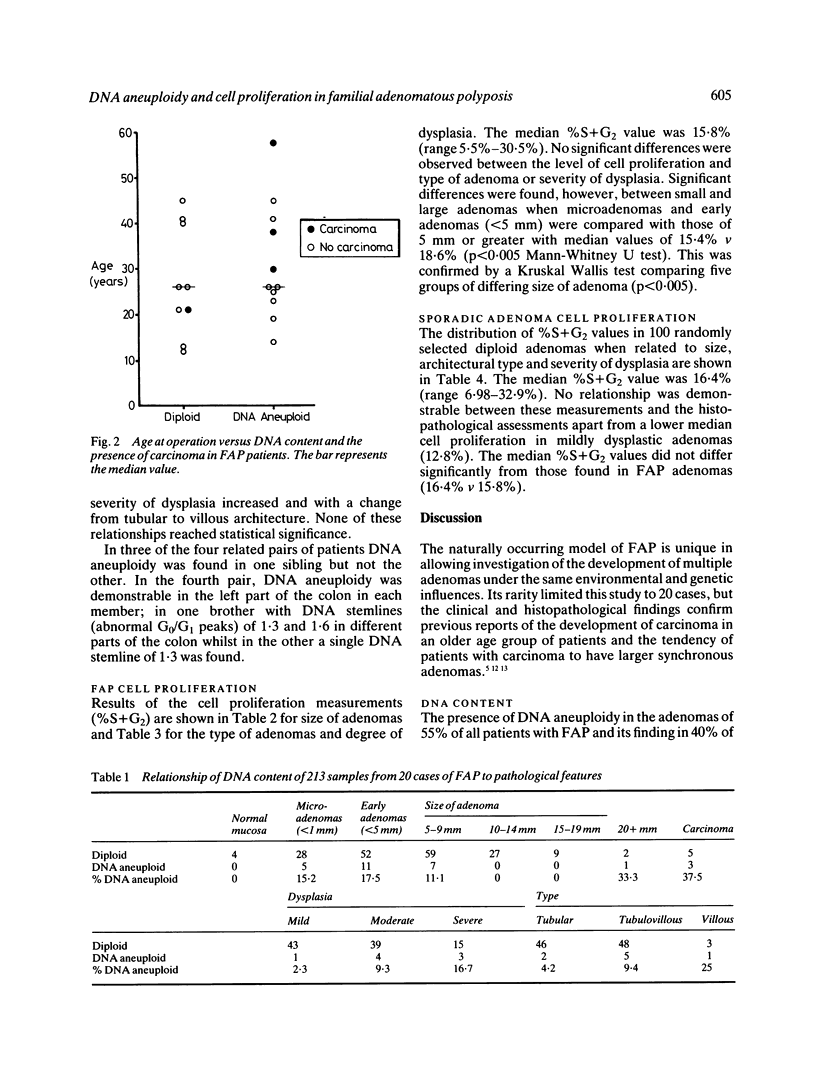
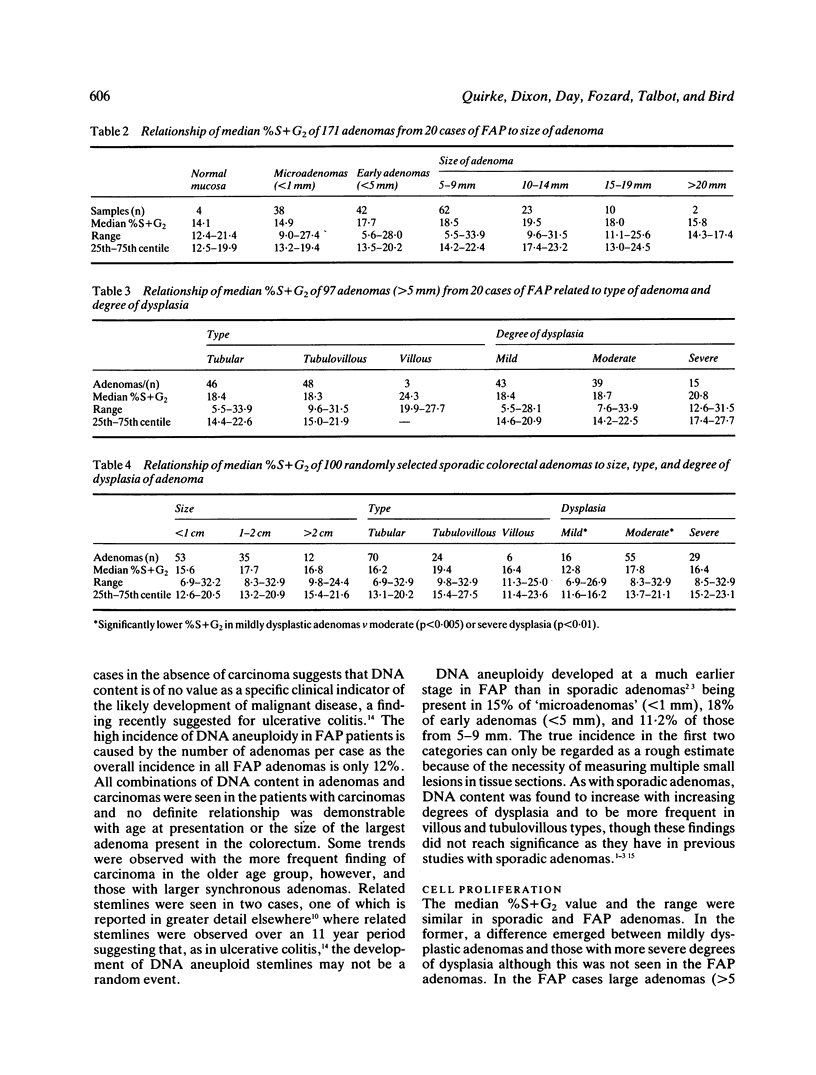
Two hundred and thirteen samples from 20 patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) were investigated by flow cytometry and the results compared with 100 sporadic adenomas. Eleven of the 20 (55%) yielded one or more DNA aneuploid samples with an overall incidence within FAP adenomas of 12%. Despite a similar level of DNA aneuploidy in sporadic adenomas, it was commonly detected at a smaller polyp size. The degree of cell proliferation was found to be similar in the two groups (median %S+G2 15.8% v 16.4%) but larger FAP adenomas demonstrated a higher level of cell proliferation than smaller adenomas. DNA aneuploidy had no value as a predictor of a synchronous carcinoma and appeared to be an early change in the development of carcinoma in these patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown L. J., Smeeton N. C., Dixon M. F. Assessment of dysplasia in colorectal adenomas: an observer variation and morphometric study. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Feb;38(2):174–179. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.2.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danes B. S., Deschner E. E. Detection of in vitro tetraploidy in heritable colon cancer syndromes. Confirmation by three different assays. Cancer. 1984 Oct 1;54(7):1353–1359. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841001)54:7<1353::aid-cncr2820540720>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danes B. S. Increased tetraploidy: cell-specific for the Gardner gene in the cultured cell. Cancer. 1976 Nov;38(5):1983–1988. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197611)38:5<1983::aid-cncr2820380520>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund G., Lindström C. Histopathological analysis of benign polyps in patients with carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Gut. 1974 Aug;15(8):654–663. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.8.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. B., Quirke P., Dixon M. F., Giles G. R., Bird C. C. DNA aneuploidy in ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1986 Dec;27(12):1414–1418. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.12.1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh H. S., Jass J. R. DNA content and the adenoma-carcinoma sequence in the colorectum. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Apr;39(4):387–392. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.4.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W., Rugg C. A., Musgrove E. A. Method for analysis of cellular DNA content of paraffin-embedded pathological material using flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Nov;31(11):1333–1335. doi: 10.1177/31.11.6619538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi F., Morson B. C. Pathology of colorectal adenomas: a colonoscopic survey. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Aug;35(8):830–841. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.8.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozuka S. Premalignancy of the mucosal polyp in the large intestine: I. Histologic gradation of the polyp on the basis of epithelial pseudostratification and glandular branching. Dis Colon Rectum. 1975 Sep;18(6):483–493. doi: 10.1007/BF02587217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Iwama T., Ustunomiya J., Aoki N., Suzuki S. Radiological features of familial polyposis coli: grouping by polyp profusion. Br J Radiol. 1984 Mar;57(675):217–221. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-57-675-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto T., Bussey H. J., Morson B. C. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirke P., Dixon M. F., Clayden A. D., Durdey P., Dyson J. E., Williams N. S., Bird C. C. Prognostic significance of DNA aneuploidy and cell proliferation in rectal adenocarcinomas. J Pathol. 1987 Apr;151(4):285–291. doi: 10.1002/path.1711510408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirke P., Fozard J. B., Dixon M. F., Dyson J. E., Giles G. R., Bird C. C. DNA aneuploidy in colorectal adenomas. Br J Cancer. 1986 Apr;53(4):477–481. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider S. H., Mazzullo H. A., Davis M. B., Delhanty J. D. Familial polyposis coli: growth characteristics of karyotypically variable cultured fibroblasts, response to epidermal growth factor and the tumour promoter 12-0-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. J Med Genet. 1986 Apr;23(2):131–144. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H., Wildner G. P., Jacobasch K. H., Heinz U., Schaelicke W. Characterization of human adenomatous polyps of the colorectal bowel by means of DNA distribution patterns. Oncology. 1985;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1159/000225996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ingh H. F., Griffioen G., Cornelisse C. J. Flow cytometric detection of aneuploidy in colorectal adenomas. Cancer Res. 1985 Jul;45(7):3392–3397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


