Abstract
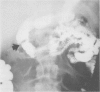
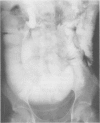
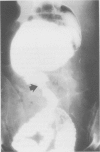
Three cases are described of end stage chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction successfully treated by subtotal enterectomy and home parenteral nutrition (HPN). In all three patients prior use of drugs to stimulate gastrointestinal motility, antibiotics to suppress bacterial overgrowth and surgical bypass of dilated bowel had failed to alleviate the symptoms of chronic intestinal obstruction. Similarly parenteral nutrition combined with restriction of oral intake, although improving nutrition did not relieve symptoms. The treatment of end stage chronic pseudo-obstruction should relieve intestinal obstruction and correct nutritional deficiency. In our experience this is best achieved by subtotal enterectomy, restoration of continuity by end-to-end anastomosis and total parenteral nutrition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anuras S., Shirazi S., Faulk D. L., Gardner G. D., Christensen J. Surgical treatment in familial visceral myopathy. Ann Surg. 1979 Mar;189(3):306–310. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197903000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton W. T. Radical enterectomy for hereditary megaduodenum. Arch Surg. 1968 Apr;96(4):549–553. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330220065012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL C. A., TOMIYASU U., MELLINKOFF S. M. Nearly fatal pseudo-obstruction of the small intestine. A case report of its relief by subtotal resection of the small bowel. Gastroenterology. 1961 May;40:698–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., Mann L. L., Berquist W. E., Ament M. E., Fonkalsrud E. W., DenBesten L. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Management with total parenteral nutrition and a venting enterostomy. Arch Surg. 1985 May;120(5):614–618. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390290090015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Deitch E. A. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. A surgical approach. Ann Surg. 1980 Dec;192(6):752–761. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198012000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Leon S. H., Krishnamurthy S. Intestinal pseudoobstruction caused by a new form of visceral neuropathy: palliation by radical small bowel resection. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1152–1156. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Rohrmann C. A., Chaffee R. G., Brand D. L., Delaney J. H., Young J. H. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. A report of 27 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):173–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner E., Jeejeebhoy K. N. Successful management of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction with home parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Mar-Apr;9(2):173–178. doi: 10.1177/0148607185009002173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]