Abstract
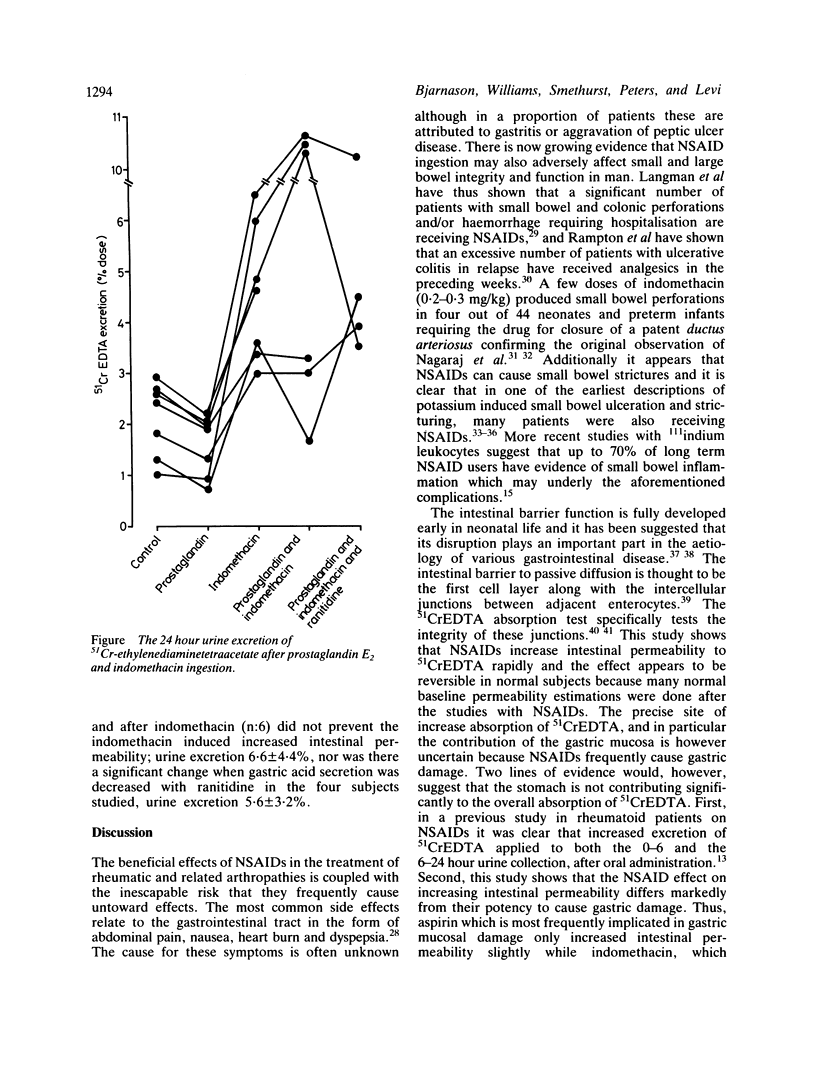
Intestinal permeability was estimated in healthy subjects after ingestion of aspirin (1.2+1.2 g), ibuprofen (400+400 mg) and indomethacin (75+50 mg) at midnight and an hour before starting a 51chromium labelled ethylenediaminetetraacetate absorption test. Intestinal permeability increased significantly from control levels following each drug and the effect was related to drug potency to inhibit cyclooxygenase. Intestinal permeability increased to a similar extent after oral and rectal administration of indomethacin showing that the effect is systemically mediated. Prostaglandin E2 decreased intestinal permeability significantly but failed to prevent the indomethacin induced increased intestinal permeability. These studies show that non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs disrupt the intestinal barrier function in man and suggest that the morphological correlates of the damage may reside at the level of the intercellular junctions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpan G., Eyal F., Vinograd I., Udassin R., Amir G., Mogle P., Glick B. Localized intestinal perforations after enteral administration of indomethacin in premature infants. J Pediatr. 1985 Feb;106(2):277–281. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeley L., Kendall M. J. Effect of aspirin on renal clearance of 125I-diatrizoate. Br Med J. 1971 Mar 27;1(5751):707–708. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5751.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste G. L., Morris R. G. Penetration of cefotaxime into pancreatic juice. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):588–589. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K. J. Acute effects of acetylsalicylic acid on renal function in normal man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Jan 3;11(2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00562902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., O'Morain C., Levi A. J., Peters T. J. Absorption of 51chromium-labeled ethylenediaminetetraacetate in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):318–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Levi A. J. Intestinal permeability: clinical correlates. Dig Dis. 1986;4(2):83–92. doi: 10.1159/000171140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Veall N. A persistent defect in intestinal permeability in coeliac disease demonstrated by a 51Cr-labelled EDTA absorption test. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):323–325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Wise R. J. The leaky gut of alcoholism: possible route of entry for toxic compounds. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):179–182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Williams P., So A., Zanelli G. D., Levi A. J., Gumpel J. M., Peters T. J., Ansell B. Intestinal permeability and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet. 1984 Nov 24;2(8413):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92739-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie D. A., Cook P. G., Bauer B. J., Dagle G. E. Indomethacin-induced intestinal lesions in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;17(3):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Cheung G., Lyster D. M. Prevention of aspirin-induced faecal blood loss by prostaglandin E2. Gut. 1980 Jul;21(7):602–606. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.7.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., McCready D. R., Clark L., Sevelius H. Protection against aspirin-induced antral and duodenal damage with enprostil. A double-blind endoscopic study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 2):382–386. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Pollett J. M. Prostaglandin E2 prevents aspirin and indomethacin damage to human gastric mucosa. Surg Forum. 1976;27(62):400–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronquist A. G., Mackenzie J., Smith T. A high resolution bulk-sample counter with variable geometry. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1975 Feb;26(2):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(75)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Brightmore T. Idiopathic and drug-induced ulceration of the small intestine. Br J Surg. 1970 Feb;57(2):134–139. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800570213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donker A. J., Arisz L., Brentjens J. R., van der Hem G. K., Hollemans H. J. The effect of indomethacin on kidney function and plasma renin activity in man. Nephron. 1976;17(4):288–296. doi: 10.1159/000180733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang W. F., Broughton A., Jacobson E. D. Indomethacin-induced intestinal inflammation. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Sep;22(9):749–760. doi: 10.1007/BF01694504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. H., Cardelli R. M., Stamler F. W. Small intestinal ulcers and intestinal flora in rats given indomethacin. Am J Pathol. 1969 Feb;54(2):237–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Kwiecień N., Obtułowicz W., Polański M., Kopp B., Oleksy J. Comparison of prostaglandin E2 and ranitidine in prevention of gastric bleeding by aspirin in man. Gut. 1983 Feb;24(2):89–93. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.2.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman M. J., Morgan L., Worrall A. Use of anti-inflammatory drugs by patients admitted with small or large bowel perforations and haemorrhage. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Feb 2;290(6465):347–349. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6465.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Trier J. S. Structural abnormalities of jejunal epithelial cell membranes in celiac sprue. Lab Invest. 1980 Sep;43(3):254–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Anti-inflammatory agents as inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis in man. Med Clin North Am. 1981 Jul;65(4):713–757. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31495-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. A., Jacobson E. D. Gastrointestinal cytoprotection by prostaglandins. Gut. 1979 Jan;20(1):75–87. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muther R. S., Bennett W. M. Effects of aspirin on glomerular filtration rate in normal humans. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):386–387. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NSAID and the leaky gut. Lancet. 1985 Jan 26;1(8422):218–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraj H. S., Sandhu A. S., Cook L. N., Buchino J. J., Groff D. B. Gastrointestinal perforation following indomethacin therapy in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Dec;16(6):1003–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(81)80865-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoptolemos J. P., Locke T. J. Recurrent small bowel obstruction associated with phenylbutazone. Br J Surg. 1983 Apr;70(4):244–245. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W. Barrier function of epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):G275–G288. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.4.G275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainsford K. D. An analysis of the gastro-intestinal side-effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, with particular reference to comparative studies in man and laboratory species. Rheumatol Int. 1982;2(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00541263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampton D. S., McNeil N. I., Sarner M. Analgesic ingestion and other factors preceding relapse in ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1983 Mar;24(3):187–189. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.3.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A. An intestinal disease produced experimentally by a prostaglandin deficiency. Gastroenterology. 1975 Oct;69(4):1045–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A. Effects of prostaglandins on the stomach and the intestine. Prostaglandins. 1974 Jun 25;6(6):523–532. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert M., Fillastre J. P., Berger H., Malandain H. Effect of intravenous infusion of acetylsalicyclic acid on renal function. Br Med J. 1972 May 20;2(5811):466–467. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5811.466-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh H., Guth P. H., Grossman M. I. Role of bacteria in gastric ulceration produced by indomethacin in the rat: cytoprotective action of antibiotics. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):483–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saverymuttu S. H., Peters A. M., Lavender J. P., Pepys M. B., Hodgson H. J., Chadwick V. S. Quantitative fecal indium 111-labeled leukocyte excretion in the assessment of disease in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1333–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturges H. F., Krone C. L. Ulceration and stricture of the jejunum in a patient on long-term indomethacin therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1973 Feb;59(2):162–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udall J. N., Pang K., Fritze L., Kleinman R., Walker W. A. Development of gastrointestinal mucosal barrier. I. The effect of age on intestinal permeability to macromolecules. Pediatr Res. 1981 Mar;15(3):241–244. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198103000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J. Uptake and transport of macromolecules by the intestine. Possible role in clinical disorders. Gastroenterology. 1974 Sep;67(3):531–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshe J. J., Venuto R. C. Acute oliguric renal failure induced by indomethacin: possible mechanism. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jul;91(1):47–49. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. W., Veall N., Purkiss P. Oxalate dynamics and removal rates during haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in patients with primary hyperoxaluria and severe renal failure. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 May;66(5):591–597. doi: 10.1042/cs0660591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. W., Veall N., Purkiss P. Sequential studies of oxalate dynamics in primary hyperoxaluria. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Dec;65(6):627–633. doi: 10.1042/cs0650627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wax J., Clinger W. A., Varner P., Bass P., Winder C. V. Relationship of the enterohepatic cycle to ulcerogenesis in the rat small bowel with flufenamic acid. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jun;58(6):772–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J. Temporal relationship between cyclooxygenase inhibition, as measured by prostacyclin biosynthesis, and the gastrointestinal damage induced by indomethacin in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jan;80(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


