Abstract
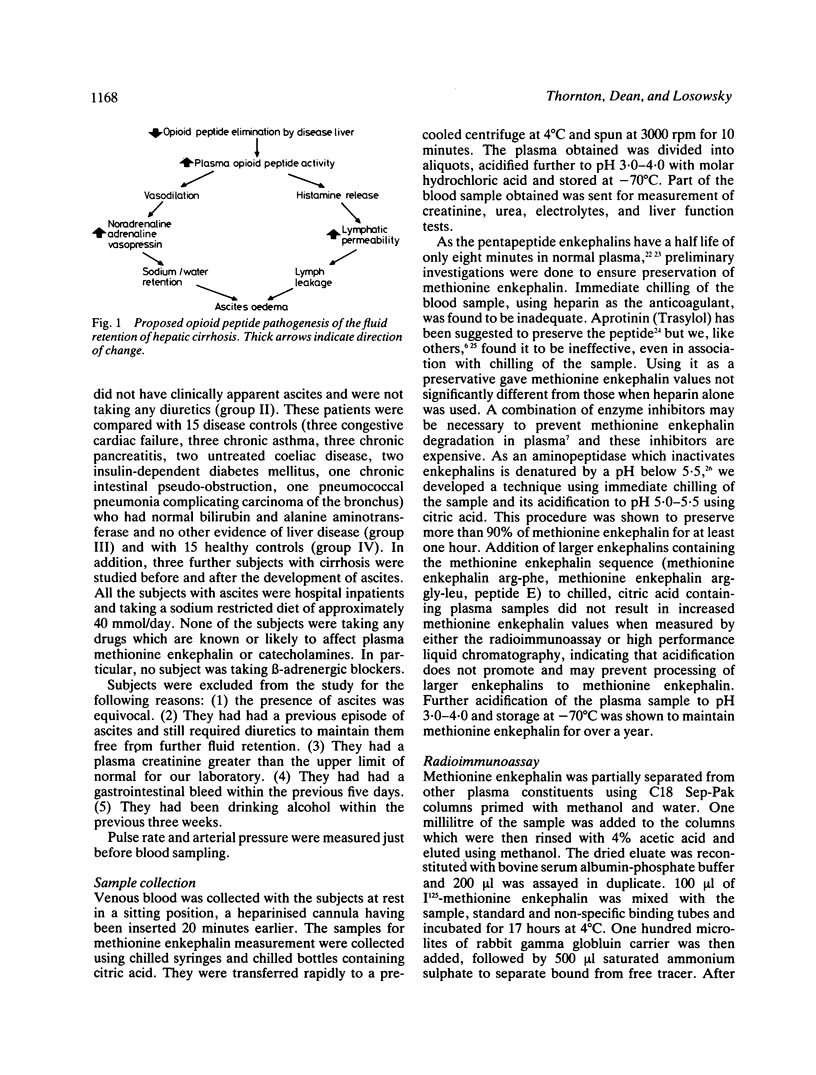
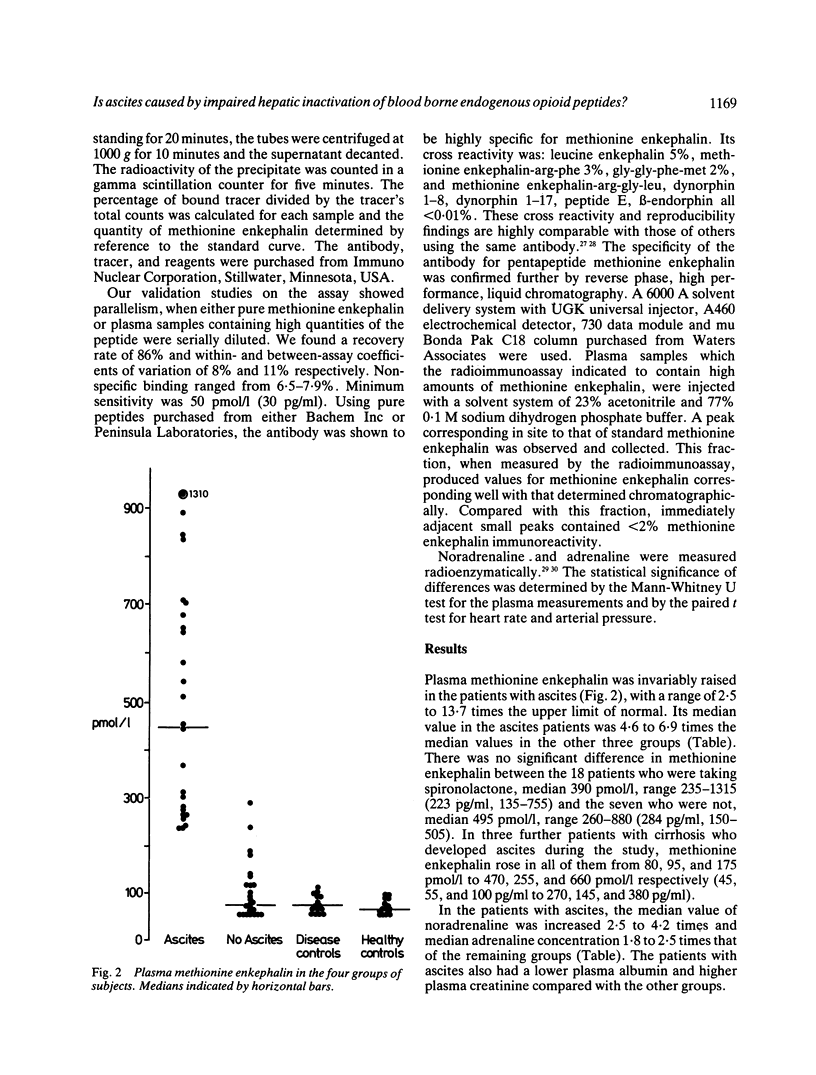
Methionine enkephalin and catecholamines were measured in carefully collected plasma samples from 25 patients with cirrhosis and ascites, and 25 with cirrhosis without ascites, 15 disease and 15 healthy controls. Methionine enkephalin was invariably raised in the ascites group, the median value being 4.6-6.9 times that of the other three groups. Similarly, in the ascites group, median noradrenaline was increased 2.5-4.2 and median adrenaline 1.8-2.5 times that of the other groups. Plasma methionine enkephalin is considerably raised in patients with cirrhotic ascites and has actions which could enable it to be an initiating factor of ascites formation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloyo V. J., Mousa S. A., Van Loon G. R. Stabilization of methionine-enkephalin in human and rat blood. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 7;39(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. T., Altura B. M., Quirion R. Identification of benzomorphan-kappa opiate receptors in cerebral arteries which subserve relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;82(2):459–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barger A. C., Herd J. A. The renal circulation. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 4;284(9):482–490. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103042840907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi M., Trevisani F., Santini C., Zoli G., Baraldini M., Ligabue A., Gasbarrini G. Plasma norepinephrine, weak neurotransmitters, and renin activity during active tilting in liver cirrhosis: relationship with cardiovascular homeostasis and renal function. Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):56–64. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D. G., Van Putten V. J., Schrier R. W. Potential role of increased sympathetic activity in impaired sodium and water excretion in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 16;307(25):1552–1557. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212163072504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blendis L. M., Sole M. J., Campbell P., Lossing A. G., Greig P. D., Taylor B. R., Langer B. The effect of peritoneovenous shunting on catecholamine metabolism in patients with hepatic ascites. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):143–148. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R., Erdelyi E., Barchas J. D. Opioid peptides in human plasma: evidence for multiple forms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Apr;54(4):715–720. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-4-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R., McArdle W. Breakdown of small enkephalin derivatives and adrenal peptide E by human plasma. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 15;35(6):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casale T. B., Bowman S., Kaliner M. Induction of human cutaneous mast cell degranulation by opiates and endogenous opioid peptides: evidence for opiate and nonopiate receptor participation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jun;73(6):775–781. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaminade M., Foutz A. S., Rossier J. Co-release of enkephalins and precursors with catecholamines by the perfused cat adrenal in-situ. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernow B., Lake C. R., Teich S., Mougey E. H., Meyerhoff J., Casey L. C., Fletcher J. R. Hemorrhagic hypotension increases plasma beta-endorphin concentrations in the nonhuman primate. Crit Care Med. 1986 May;14(5):505–507. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198605000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement-Jones V., Lowry P. J., Rees L. H., Besser G. M. Development of a specific extracted radioimmunoassay for methionine enkephalin in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. J Endocrinol. 1980 Aug;86(2):231–243. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0860231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement-Jones V., Lowry P. J., Rees L. H., Besser G. M. Met-enkephalin circulates in human plasma. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):295–297. doi: 10.1038/283295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coletti-Previero M. A., Mattras H., Descomps B., Previero A. Purification and substrate characterization of a human enkephalin-degrading aminopeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 15;657(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Paterson S. J., McKnight A. T., Magnan J., Kosterlitz H. W. Dynorphin and dynorphin are ligands for the kappa-subtype of opiate receptor. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):79–81. doi: 10.1038/299079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Isotope-derivative measurements of plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine in man. Diabetes. 1976 Nov;25(11):1071–1082. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.11.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Zürcher Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engeland W. C., Bereiter D. F., Gann D. S. Sympathetic control of adrenal secretion of enkephalins after hemorrhage in awake dogs. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):R341–R348. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.251.2.R341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. Deranged sodium homeostasis in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1979 Mar;76(3):622–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell L. D., Harrison T. S., Demers L. M. Immunoreactive met-enkephalin in the canine adrenal; response to acute hypovolemic stress. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Sep;173(4):515–518. doi: 10.3181/00379727-173-41680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMBOS E. A., HULET W. H., BOPP P., GOLDRINGW, BALDWIN D. S., CHASIS H. Reactivity of renal and systemic circulations to vasoconstrictor agents in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:203–217. doi: 10.1172/JCI104472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A., Clement-Jones V. Opiate receptors: enkephalins and endorphins. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Mar;12(1):31–56. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(83)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. H., Davis D., Gunnells J. C., Shand D. G. Plasma norepinephrine in the evaluation of baroreceptor function in humans. Hypertension. 1982 Jul-Aug;4(4):566–571. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.4.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanbauer I., Kelly G. D., Saiani L., Yang H. Y. [Met5]-enkephalin-like peptides of the adrenal medulla: release by nerve stimulation and functional implications. Peptides. 1982 May-Jun;3(3):469–473. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Ramme D., Starke K. Inhibition of neuroeffector transmission in the rabbit mesenteric artery by [Met5]enkephalin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 8;107(3):397–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imura H., Kato Y., Nakai Y., Nakao K., Tanaka I., Jingami H., Koh T., Yoshimasa T., Tsukada T., Suda M. Endogenous opioids and related peptides: from molecular biology to clinical medicine. The Sir Henry Dale lecture for 1985. J Endocrinol. 1985 Nov;107(2):147–157. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1070147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONTOS H. A., SHAPIRO W., MAUCK H. P., PATTERSON J. L., Jr GENERAL AND REGIONAL CIRCULATORY ALTERATIONS IN CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER. Am J Med. 1964 Oct;37:526–535. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller U., Gerber P. P., Bühler F. R., Stauffacher W. Role of the splanchnic bed in extracting circulating adrenaline and noradrenaline in normal subjects and in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Jul;67(1):45–49. doi: 10.1042/cs0670045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew M. Renal changes in cirrhosis. Gut. 1972 Sep;13(9):748–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.9.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake C. R., Ziegler M. G., Kopin I. J. Use of plasma norepinephrine for evaluation of sympathetic neuronal function in man. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 1;18(11):1315–1325. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINI G. A., HAGEMANN J. E. Uber Fingernagelveränderungen bei Lebercirrhose als Folge veränderter peripherer Durchblutung. Klin Wochenschr. 1956 Jan 1;34(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01494896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY J. F., DAWSON A. M., SHERLOCK S. Circulatory changes in chronic liver disease. Am J Med. 1958 Mar;24(3):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90322-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKechnie K., Dean H. G., Furman B. L., Parratt J. R. Plasma catecholamines during endotoxin infusion in conscious unrestrained rats: effects of adrenal demedullation and/or guanethidine treatment. Circ Shock. 1985;17(1):85–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Nakai Y., Oki S., Horii K., Imura H. Presence of immunoreactive beta-endorphin in normal human plasma: a concomitant release of beta-endorphin with adrenocorticotropin after metyrapone administration. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1395–1398. doi: 10.1172/JCI109261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasanisi F., Sloan L., Rubin P. C. Cardiovascular properties of metkephamid, a delta opioid receptor agonist, in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Feb;68(2):209–213. doi: 10.1042/cs0680209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Sullivan S. N., Facer P., Pearse A. G. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the human gastrointestinal tract. Lancet. 1977 May 7;1(8019):972–974. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring-Larsen H., Hesse B., Henriksen J. H., Christensen N. J. Sympathetic nervous activity and renal and systemic hemodynamics in cirrhosis: plasma norepinephrine concentration, hepatic extraction, and renal release. Hepatology. 1982 May-Jun;2(3):304–310. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscetti G., Possenti R., Bassano E., Roda L. G. Mechanisms of leu-enkephalin hydrolysis in human plasma. Neurochem Res. 1985 Oct;10(10):1393–1404. doi: 10.1007/BF00964980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder S. W., Eng J. Radioimmunoassay of leucine-enkephalin-like substance in human and canine plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Feb;52(2):367–369. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTHE C. M., NICKEL J. F., BRADLEY S. E. The effect of epinephrine (USP), l-epinephrine, and l-norepinephrine on glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow, and the urinary excretion of sodium, potassium, and water in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1952 May;31(5):499–506. doi: 10.1172/JCI102634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. W., Berl T., Anderson R. J. Osmotic and nonosmotic control of vasopressin release. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):F321–F332. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.4.F321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Elfvin L. G., Elde R. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in nerve terminals in sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla and in adrenal medullary gland cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Aug;103(4):475–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatney C. H., Cohen R. M., Cohen M. R., Imagawa D. K. Endogenous opioid activity in clinical hemorrhagic shock. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1985 Jun;160(6):547–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Grossman A., Gaillard R., Clement-Jones V., Ratter S., Mallinson J., Lowry P. J., Besser G. M., Rees L. H. Studies on circulating met-enkephalin and beta-endorphin: normal subjects and patients with renal and adrenal disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1981 Sep;15(3):291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1981.tb00668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama K., Furuta H. Histamine release induced by dynorphin-(1-13) from rat mast cells. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;35(3):247–252. doi: 10.1254/jjp.35.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett I., Esler M., Burke F., Leonard P., Dudley F. Total and renal sympathetic nervous system activity in alcoholic cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(6):639–648. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Hotta K., Matsuda T. Effect of methionine-enkephalin on the spontaneous electrical and mechanical activity of the smooth muscle of the rat portal vein. Life Sci. 1984 Mar 5;34(10):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90304-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEPPA R., WOMACK N. A. Humoral control of hepatic lymph flow. Surgery. 1963 Jul;54:37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelis R., Mansour E. J., Capone R. J., Mason D. T. The cardiovascular effects of morphine. The peripheral capacitance and resistance vessels in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1247–1258. doi: 10.1172/JCI107869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


