Abstract
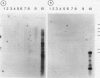
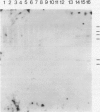
A mycobacterial aetiology for Crohn's disease (CD) has been suggested. Slow growing mycobacteria indistinguishable from M paratuberculosis, the causative agent of enteritis in ruminants (Johne's disease) have been isolated from CD tissues. We have used cloned genomic DNA probes derived from a CD isolated mycobacteria strain Ben, to investigate the presence of mycobacterial DNA sequences in CD tissues. DNA was extracted from total tissue from 17 CD and four control gut specimens. DNA was digested with restriction endonucleases, electrophoresed and transferred to nylon membranes by Southern blotting and hybridised to radiolabelled DNA probes. No mycobacterial DNA was detected in any tissue sample studied. Reconstitution experiments with known numbers of in vitro cultured mycobacteria showed sensitive detection of mycobacterial DNA. DNA extracted from mouse liver, infected with M lepraemurium revealed a strong hybridisation signal and showed the applicability of the experimental approach to the detection of mycobacterial DNA in naturally infected tissues. The results do not provide evidence for the involvement of mycobacteria in the pathogenesis of CD but do not exclude the possibility of low levels of infection in subsets of intestinal cells with spheroplast or cell wall deficient forms of mycobacteria.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baess I. Determination and re-examination of genome sizes and base ratios on deoxyribonucleic acid from mycobacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Aug;92(4):209–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeken W. L. Transmissible agents in inflammatory bowel disease: 1980. Med Clin North Am. 1980 Nov;64(6):1021–1035. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsheim M. R., Darwish R. Z., Watson W. C., Schieven B. Bacterial L-form isolation from inflammatory bowel disease patients. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):364–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham W. R., Lennard-Jones J. E., Stanford J. L., Bird R. G. Mycobacteria as a possible cause of inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1978 Sep 30;2(8092 Pt 1):693–696. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S., Thayer W. R., Jr, Coutu J. A. Characteristics of an unclassified Mycobacterium species isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):966–971. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.966-971.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Thayer W. R., Coutu J. A. Spheroplastic phase of mycobacteria isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):357–363. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.357-363.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Thayer W. R., Merkal R. S., Coutu J. A. Possible role of mycobacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. I. An unclassified Mycobacterium species isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Dec;29(12):1073–1079. doi: 10.1007/BF01317078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitnick G. Is Crohn's disease a mycobacterial disease after all? Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Dec;29(12):1086–1088. doi: 10.1007/BF01317080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W. Aetiology of regional enteritis. Lancet. 1968 May 25;1(7552):1144–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Markesich D. C., Yoshimura H. H. Mycobacteria and inflammatory bowel disease. Results of culture. Gastroenterology. 1987 Feb;92(2):436–442. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J. Epidemiological aspects of Crohn's disease: a review of the literature. Gut. 1984 Aug;25(8):886–899. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.8.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R. J., Hermon-Taylor J. Determination of genome size and DNA homology between an unclassified Mycobacterium species isolated from patients with Crohn's disease and other mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jan;133(1):211–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-1-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. Crohn's disease-isolated mycobacteria are identical to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, as determined by DNA probes that distinguish between mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):796–801. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.796-801.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Thompson J., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. The use of DNA probes identifying restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms to examine the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R., Kvach J. T., Mounts P. Isolation and restriction endonuclease analysis of mycobacterial DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):541–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D. S., Allen W. M. Chronic mycobacterial enteritis in ruminants as a model of Crohn's disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Nov;65(11):998–1001. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kruiningen H. J., Chiodini R. J., Thayer W. R., Coutu J. A., Merkal R. S., Runnels P. L. Experimental disease in infant goats induced by a Mycobacterium isolated from a patient with Crohn's disease. A preliminary report. Dig Dis Sci. 1986 Dec;31(12):1351–1360. doi: 10.1007/BF01299814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura H. H., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K., Merkal R. S. Investigation of association of mycobacteria with inflammatory bowel disease by nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):45–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.45-51.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]