Abstract
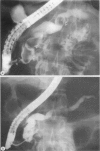
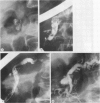
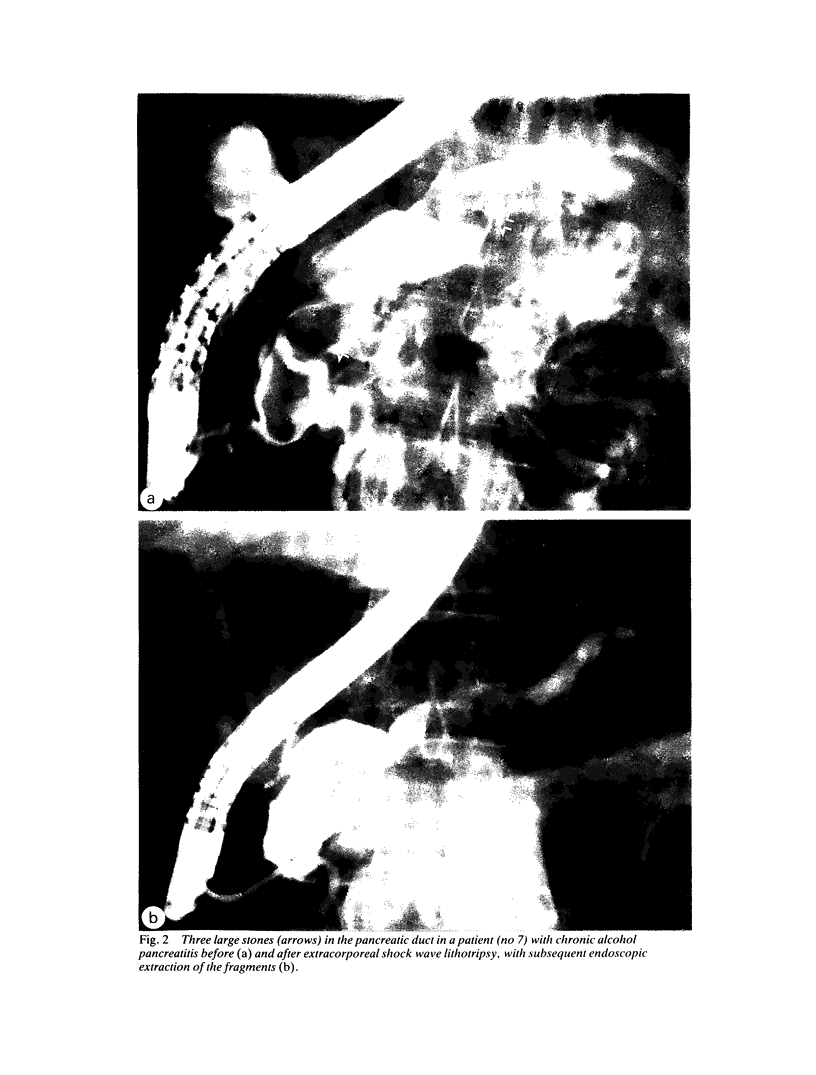
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy of pancreatic stones was performed in eight patients with chronic pancreatitis and a dilated duct system harbouring stones 5 to 20 mm (means 10 (SD) 5 mm) in diameter. After endoscopic sphincterotomy of the pancreatic orifice the stones were disintegrated by shock waves under fluoroscopic control using a kidney lithotripter (Dornier HM3). The procedure was well tolerated by all but one patient, who had a mild pancreatitic attack immediately after lithotripsy. Clearance of the pancreatic duct systems from the larger stones was achieved in seven of eight patients. Half of the patients showed no improvement in the intensity and frequency of pain. The other patients had a marked amelioration of symptoms, however, both immediately and during a mean follow up interval of 11 (eight) months. A selective combined approach by endoscopy and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for the treatment of pancreatic stones seems promising.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammann R. W., Akovbiantz A., Largiader F., Schueler G. Course and outcome of chronic pancreatitis. Longitudinal study of a mixed medical-surgical series of 245 patients. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann R. W., Muench R., Otto R., Buehler H., Freiburghaus A. U., Siegenthaler W. Evolution and regression of pancreatic calcification in chronic pancreatitis. A prospective long-term study of 107 patients. Gastroenterology. 1988 Oct;95(4):1018–1028. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axon A. T., Classen M., Cotton P. B., Cremer M., Freeny P. C., Lees W. R. Pancreatography in chronic pancreatitis: international definitions. Gut. 1984 Oct;25(10):1107–1112. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.10.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDSON H. A., BULLOCK W. K., MEHL J. W. Chronic pancreatitis and lithiasis; a clinicopathologic study of 62 cases of chronic pancreatitis. Am J Pathol. 1949 Nov;25(6):1227-47, incl 3 pl. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy P., Milan C., Pignon J. P., Baetz A., Bernades P. Mortality factors associated with chronic pancreatitis. Unidimensional and multidimensional analysis of a medical-surgical series of 240 patients. Gastroenterology. 1989 Apr;96(4):1165–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles H. Chronic calcifying pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Aug;20(6):651–659. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbruch T., Holl J., Sackmann M., Werner R., Wotzka R., Paumgartner G. Disintegration of a pancreatic duct stone with extracorporeal shock waves in a patient with chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 1987 Sep;19(5):207–208. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbruch T., Stern M. Fragmentation of bile duct stones by extracorporeal shock waves. A new approach to biliary calculi after failure of routine endoscopic measures. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jan;96(1):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90775-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. U., Lux G. Floating pancreatic duct concrements in chronic pancreatitis. Pain relief by endoscopic removal. Endoscopy. 1985 Jan;17(1):8–10. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]