Abstract
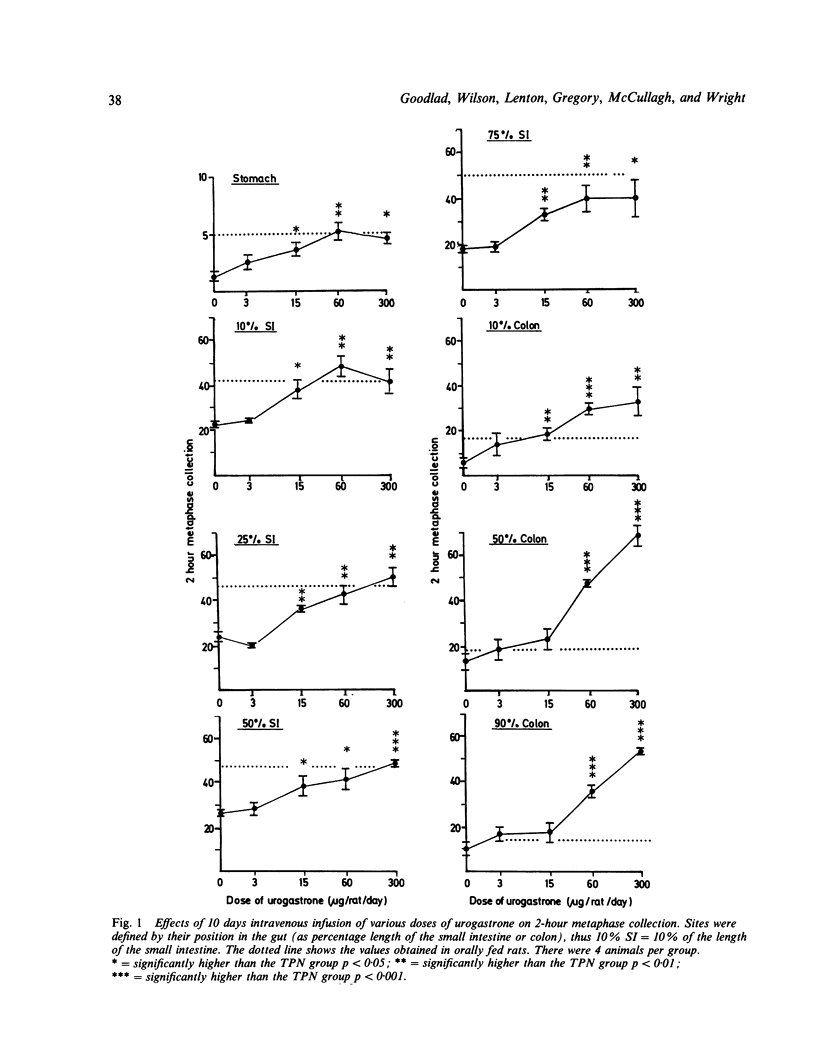
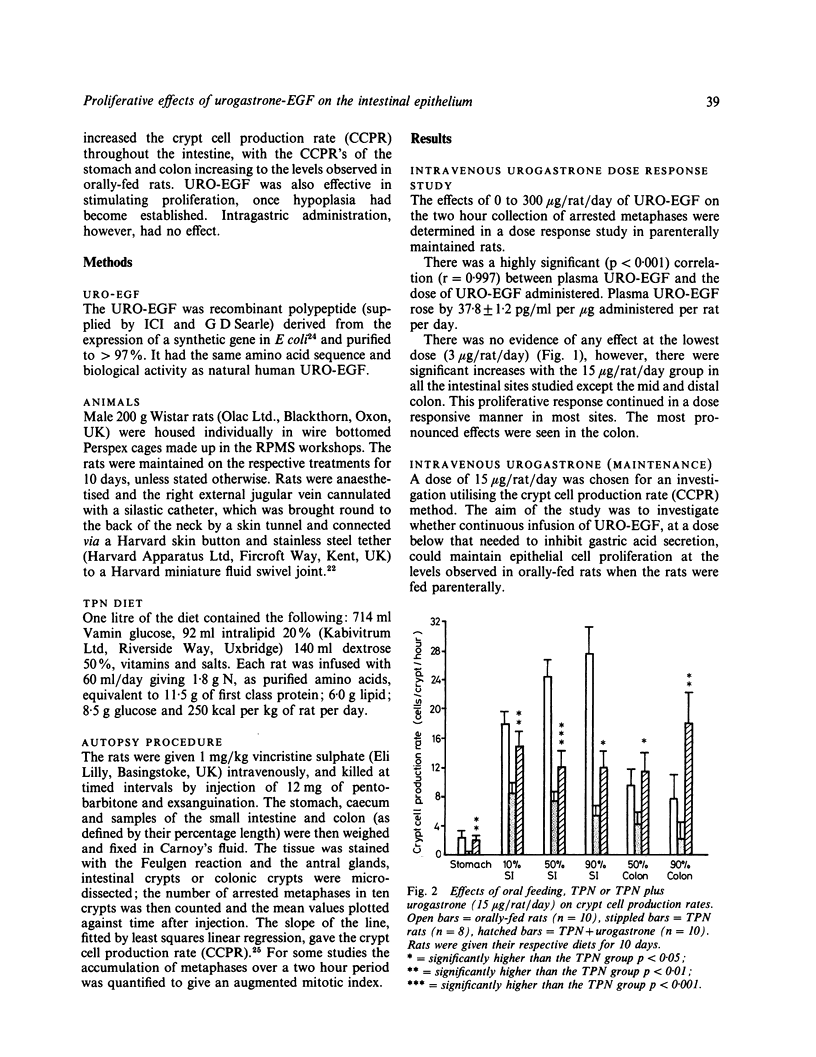
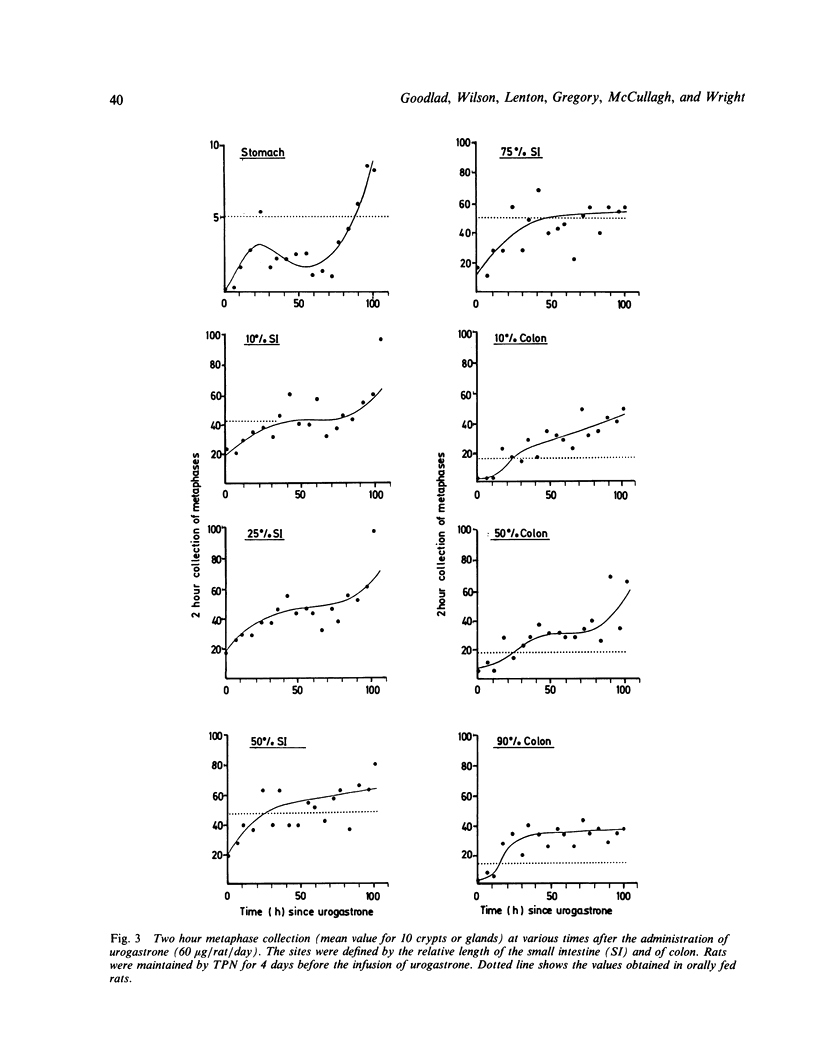
The effects of B-urogastrone/human epidermal growth factor on intestinal epithelial cell proliferation were studied in rats in which intestinal cell proliferation was reduced to a steady state basal level (by maintaining the rats on total parenteral nutrition). Increasing doses of urogastrone progressively raised the two hour collection of metaphases and intestinal weights. The crypt cell production rate was measured in animals maintained parenterally with or without urogastrone, and in rats fed a standard laboratory ration. Continuous infusion of 15 micrograms per rat per day of recombinant beta urogastrone (a dose which has a minimal effect on gastric acid secretion) significantly increased cell proliferation and intestinal tissue weights throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Intravenous infusion of urogastrone was also effective in restoring cell proliferation when it was infused after the intestine had become hypoproliferative. Urogastrone administered through an intragastric cannula thrice daily had no significant effect on either intestinal weight, crypt cell production rate, or metaphase collection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bower J. M., Camble R., Gregory H., Gerring E. L., Willshire I. R. The inhibition of gastric acid secretion by epidermal growth factor. Experientia. 1975 Jul 15;31(7):825–826. doi: 10.1007/BF01938488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. F., Bennett D. C., Smith J. A. Mammalian cell cycles need two random transitions. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):493–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90524-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvert R., Beaulieu J. F., Ménard D. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) accelerates the maturation of fetal mouse intestinal mucosa in utero. Experientia. 1982 Sep 15;38(9):1096–1097. doi: 10.1007/BF01955387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor is a major growth-promoting agent in human milk. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):198–199. doi: 10.1126/science.6968093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot J. G., Payet N., Hugon J. S. Effects of epidermal growth factor (EGF) on adult mouse small intestine in vivo and in organ culture. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1983;74(2):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(83)90595-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembiński A., Gregory H., Konturek S. J., Polański M. Trophic action of epidermal growth factor on the pancreas and gastroduodenal mucosa in rats. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:35–42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman E. J., Aures D., Grossman M. I. Epidermal growth factor stimulates ornithine decarboxylase activity in the digestive tract of mouse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Dec;159(3):400–402. doi: 10.3181/00379727-159-40357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue-Lafitte M. E., Laburthe M., Chamblier M. C., Moody A. J., Rosselin G. Demonstration of specific receptors for EGF--urogastrone in isolated rat intestinal epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 2;114(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodlad R. A., Wilson T. J., Lenton W., Gregory H., McCullough K. G., Wright N. A. Urogastrone-epidermal growth factor is trophic to the intestinal epithelium of parenterally fed rats. Experientia. 1985 Sep 15;41(9):1161–1163. doi: 10.1007/BF01951708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodlad R. A., Wright N. A. The effects of starvation and refeeding on intestinal cell proliferation in the mouse. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;45(1):63–73. doi: 10.1007/BF02889852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H. Isolation and structure of urogastrone and its relationship to epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1975 Sep 25;257(5524):325–327. doi: 10.1038/257325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemann R. F., Stragand J. J. Fasting and refeeding: cell kinetic response of jejunum, ileum and colon. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1977 Jan;10(1):3–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1977.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz P. U., Kasper M., van Noorden S., Polak J. M., Gregory H., Pearse A. G. Immunohistochemical localisation of urogastrone to human duodenal and submandibular glands. Gut. 1978 May;19(5):408–413. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.5.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. A., Dowling R. H. Speed of onset of adaptive mucosal hypoplasia and hypofunction in the intestine of parenterally fed rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Nov;59(5):317–327. doi: 10.1042/cs0590317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard P., Olsen P. S., Poulsen S. S., Nexø E. Epidermal growth factor inhibits cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcers. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1277–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A. P. Postnatal undernutrition: effect of epidermal growth factor on growth and function of the gastrointestinal tract in rats. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Sep;3(4):618–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo C., Ménard D. Influence of epidermal growth factor on the development of suckling mouse intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jul;83(1 Pt 1):28–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuchansky C., Morichau-Beauchant M., Druart F., Tapin J. Cyclic (nocturnal) total parenteral nutrition in hospitalized adult patients with severe digestive diseases. Report of a prospective study. Gastroenterology. 1981 Sep;81(3):433–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Ghishan F. K., Greene H. L., Orth D. N. Effect of mouse epidermal growth factor/urogastrone on the functional maturation of rat intestine. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):940–944. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen P. S., Nexø E. Quantitation of epidermal growth factor in the rat. Identification and partial characterization of duodenal EGF. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Sep;18(6):771–776. doi: 10.3109/00365528309182093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen P. S., Poulsen S. S., Kirkegaard P., Nexø E. Role of submandibular saliva and epidermal growth factor in gastric cytoprotection. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):103–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheving L. A., Yeh Y. C., Tsai T. H., Scheving L. E. Circadian phase-dependent stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, caecum, colon, and rectum of the adult male mouse. Endocrinology. 1980 May;106(5):1498–1503. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-5-1498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheving L. A., Yeh Y. C., Tsai T. H., Scheving L. E. Circadian phase-dependent stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the tongue, esophagus, and stomach of the adult male mouse. Endocrinology. 1979 Dec;105(6):1475–1480. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-6-1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Cook E., Fotheringham I., Pheby S., Derbyshire R., Eaton M. A., Doel M., Lilley D. M., Pardon J. F., Patel T. Chemical synthesis and cloning of a gene for human beta-urogastrone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4467–4482. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


