Abstract
The effects of pressure and temperature on the decay kinetics of the M412 (M) intermediate in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin were studied to provide information about the phase transitions of the purple membrane lipids. The activation volume (delta V++) for the decay of M is expected to be different below and above a phase transition. However, no abrupt change in delta V++ was found from 3.5 degrees to 60 degrees C. But a sharp break was observed in a plot of the logarithm of the rate of M decay vs. pressure. Extrapolation of this break point to standard atmospheric pressure gives a temperature of -42 degrees C, which probably corresponds to the phase transition of the purple membrane lipids. This conclusion is supported by studies of the effect of pressure on the M kinetics of bacteriorhodopsin incorporated into dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles, whose phase transition has previously been characterized.
Full text
PDF

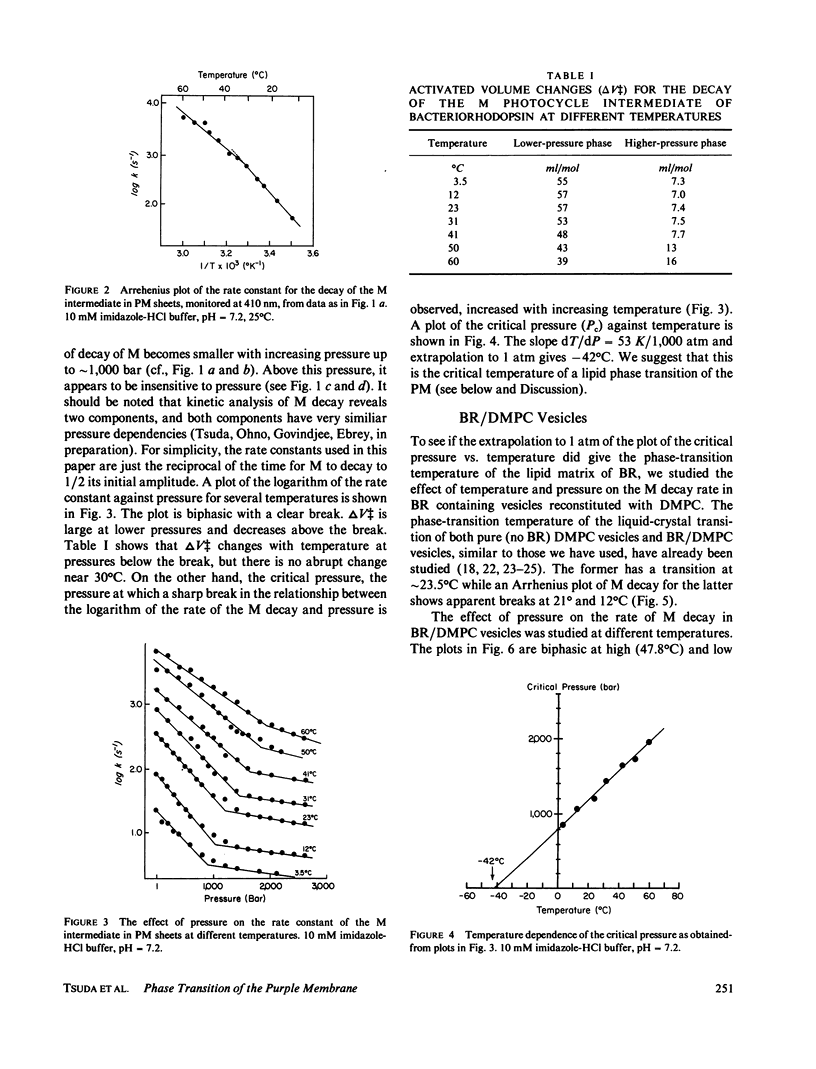
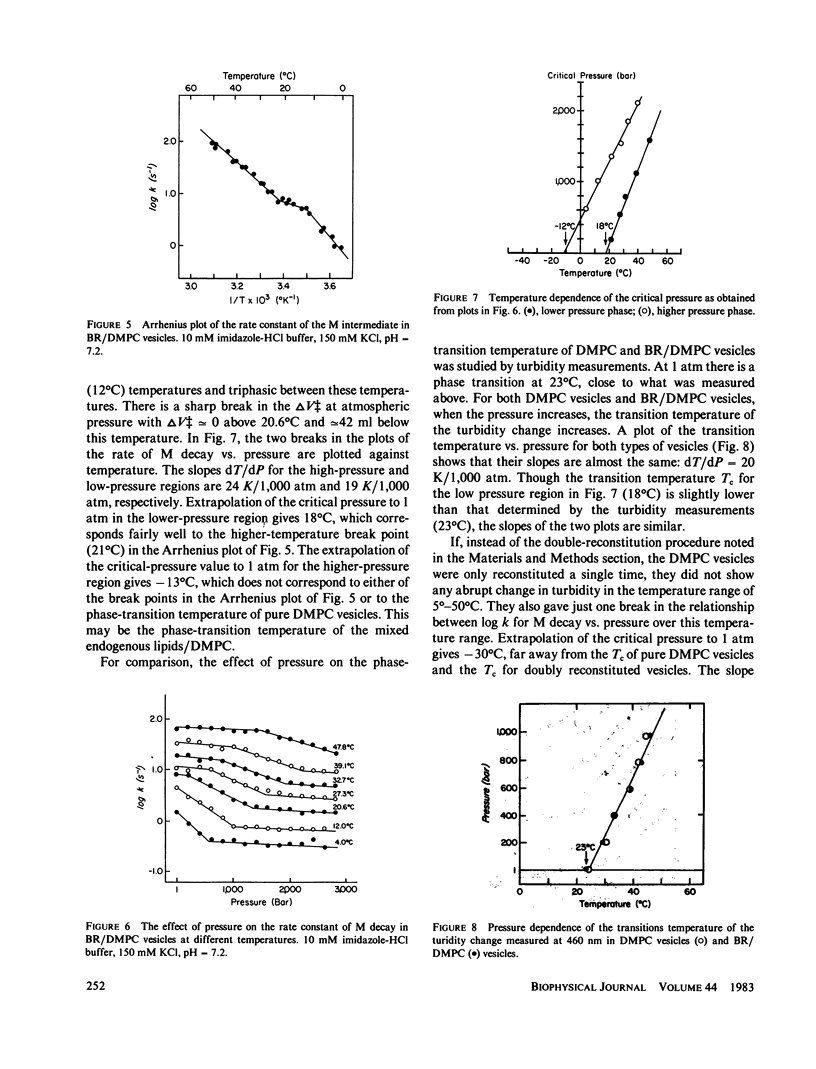


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Caplan S. R. Phospholipid substitution of the purple membrane. The stoichiometry of light-induced proton release by phospholipid-substituted purple membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 8;503(2):362–379. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley S. T., Morton R. A. Recent developments in the molecular biology of extremely halophilic bacteria. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6(2):151–205. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B. M., Cassim J. Y. Improved isolation procedures for the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):161–178. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Barton P. G., Brown D., Kates M. Osmometric and microscopic studies on bilayers of polar lipids from the extreme halophile, Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):202–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Müller U. Temperature-dependent aggregation of bacteriorhodopsin in dipalmitoyl- and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chignell C. F., Chignell D. A. A spin label study of purple membranes from Halobacterium halobium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 6;62(1):136–143. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani H., Danon A., Caplan S. R. Proton and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the polar lipids of Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1626–1631. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heremans K. High pressure effects on proteins and other biomolecules. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1982;11:1–21. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.11.060182.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heremans K., Wuytack F. Pressure effect on the Arrhenius discontinuity in Ca2+-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum: evidence for lipid involvement. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):161–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Blume A., Rehorek M., Dencher N. A. Calorimetric and fluorescence depolarization studies on the lipid phase transition of bacteriorhodopsin--dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7109–7115. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Cherry R. J., Dencher N. A. Lipid--protein interactions in bacteriorhodopsin--dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):840–849. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Sturtevant J. M. Phase transitions of the purple membranes of Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):911–915. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Sherman W. V., Caplan S. R. Kinetic isotope effects in the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys Struct Mech. 1976 Dec 22;2(3):267–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00535372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey H., Petersen N. O., Chan S. I. Physicochemical characterization of 1,2-diphytanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine in model membrane systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 19;555(1):147–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan K. R., Kay R. L., Nagle J. F. The pressure dependence of the lipid bilayer phase transition. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3494–3496. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Ebrey T. G. Effect of high pressure on the absorption spectrum and isomeric composition of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1980 Apr;30(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Shirotani I., Minomura S., Terayama Y. Pressure induced intermediates in the photochemical reaction of squid rhodopsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):989–994. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90953-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


