Abstract
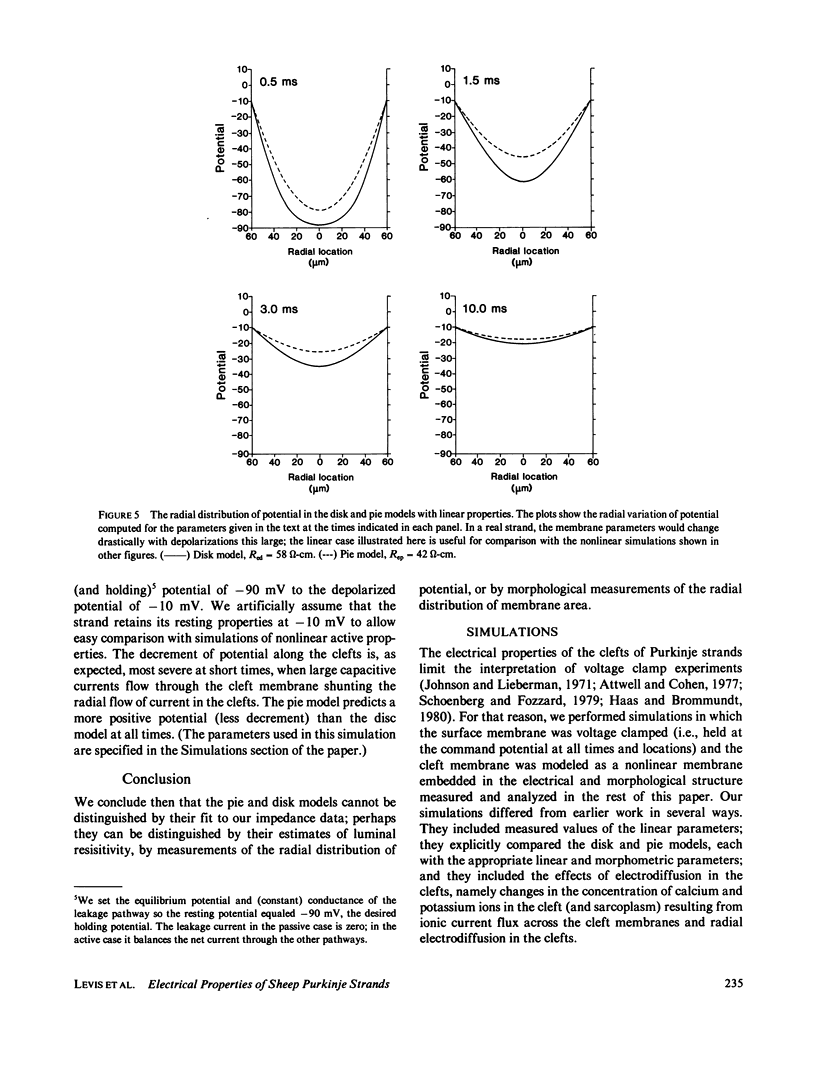
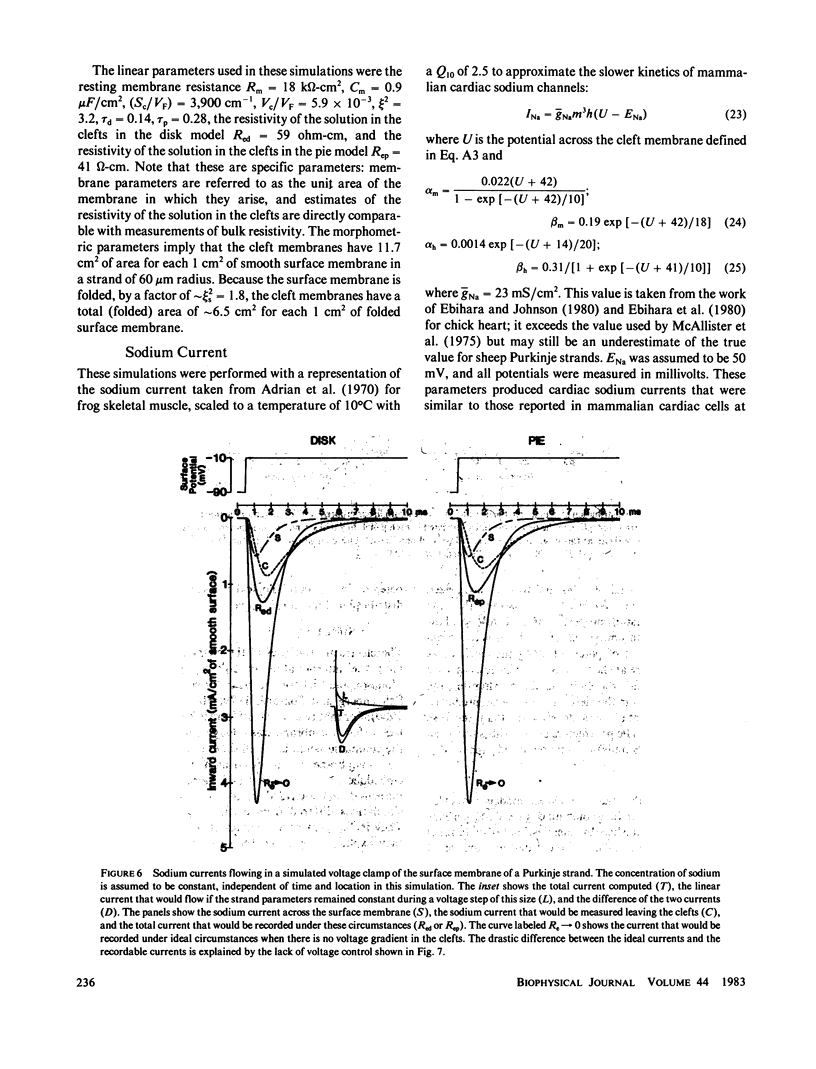
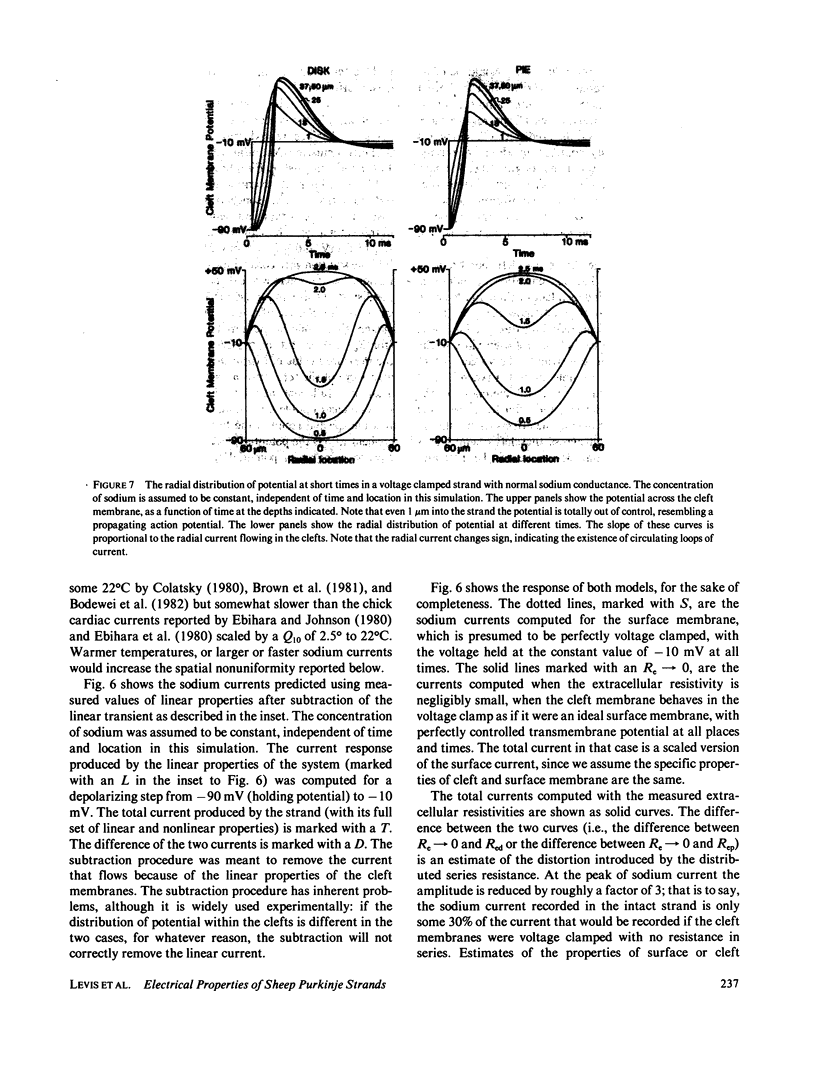
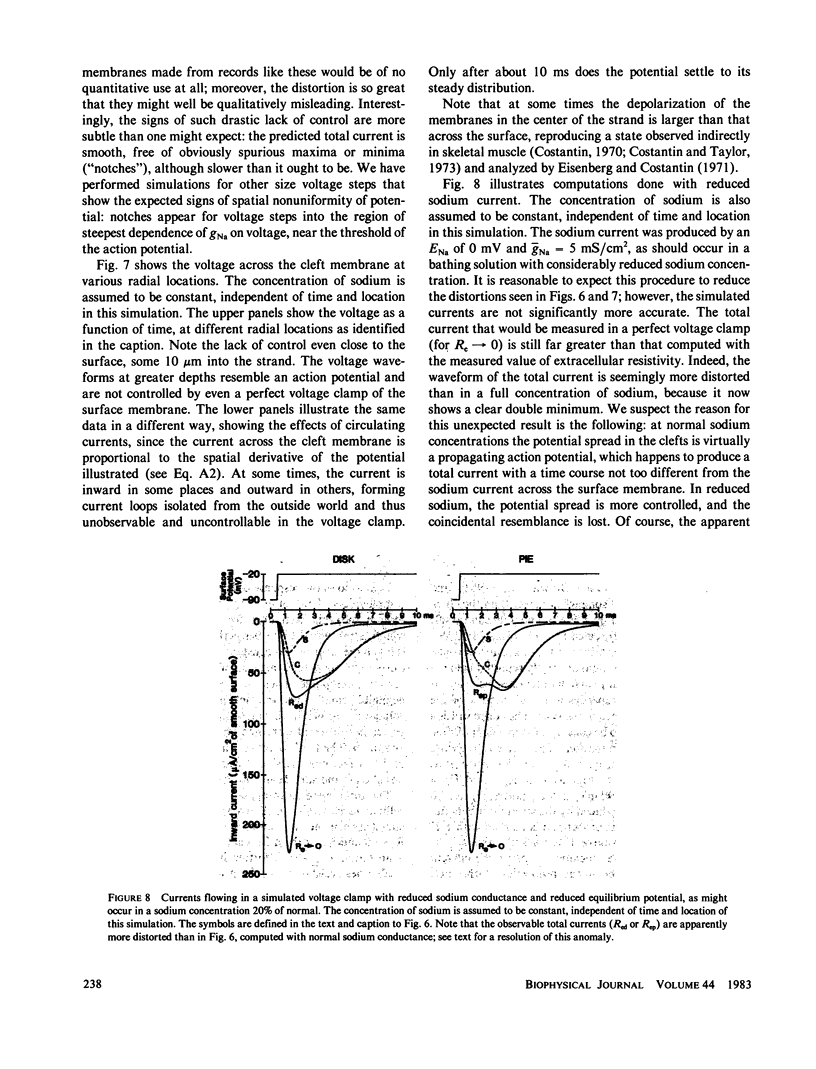
The impedence of sheep Purkinje strands, measured to 3-5 kHz, is interpreted with circuit models based on morphology. The strand is described as a one-dimensional electrical cable. Clefts between myocytes of the strand allow radial current to flow in parallel with current across the outer membrane. A lumped model of the clefts, in which all the cleft membrane is in series with 100 omega-cm2, fits only below 20 Hz. Two distributed models, pie and disk, fit at all frequencies with somewhat different (31%) luminal resistivities, but with similar membrane parameters. Series resistance representing the endothelial sheath is small. Simulations of voltage clamp experiments include measured linear parameters and nonlinear membrane channels, as well as radial variation of cleft concentration, membrane flux, voltage, and current. Cleft potential is drastically nonuniform when sodium current flows. Cleft potential is reasonably uniform when calcium and potassium currents flow, but the calcium and potassium concentrations change markedly, enough to turn off the calcium current, even if the calcium channel did not inactivate. We conclude that physiological current flows produce significant nonuniformities in electrochemical potentials in the clefts of this cardiac preparation.
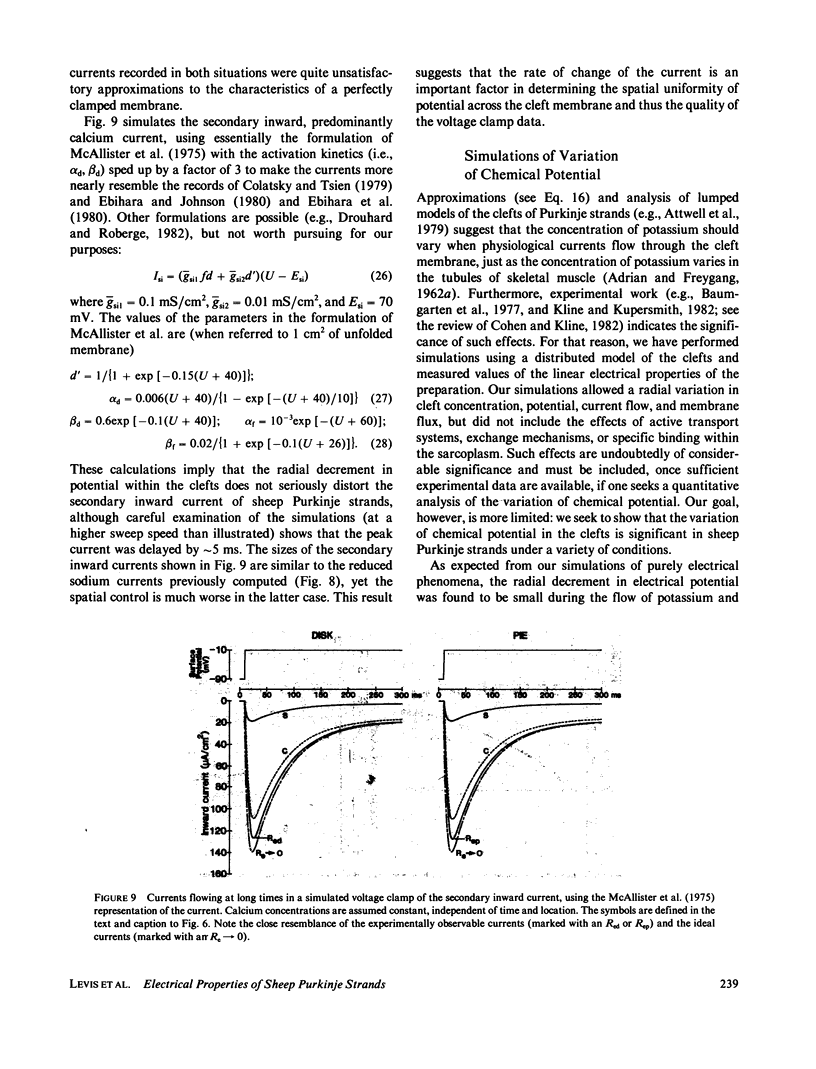
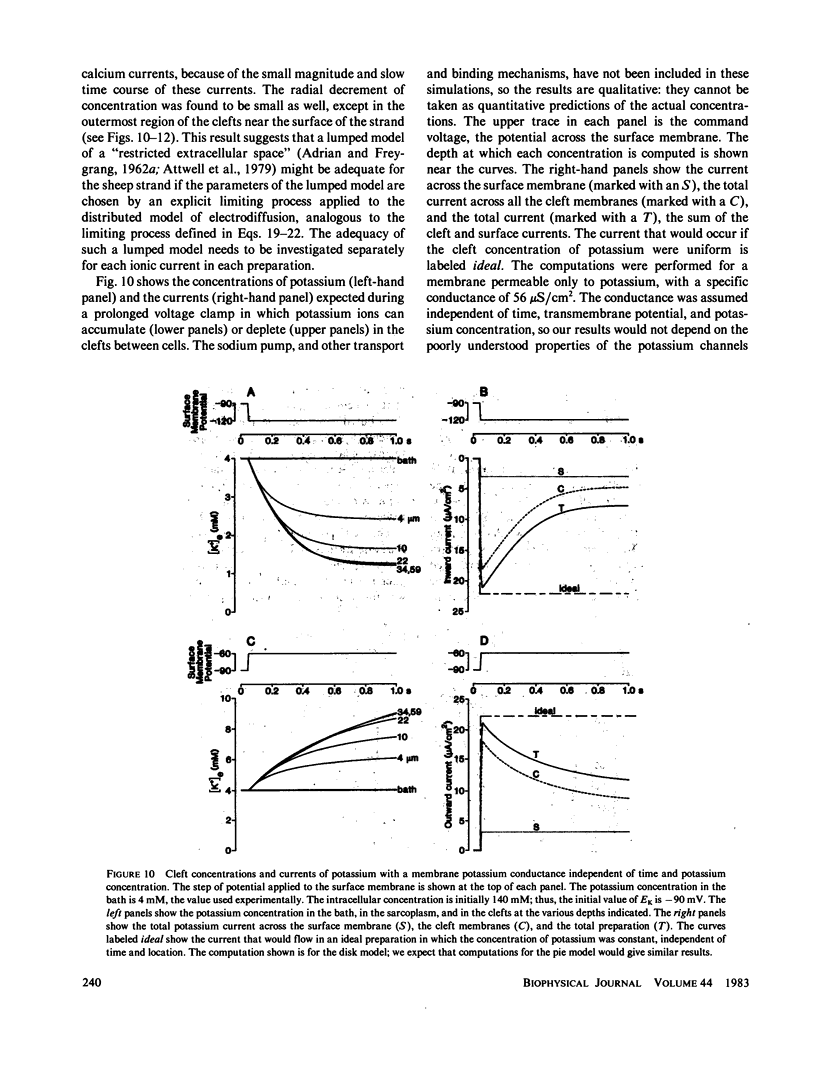
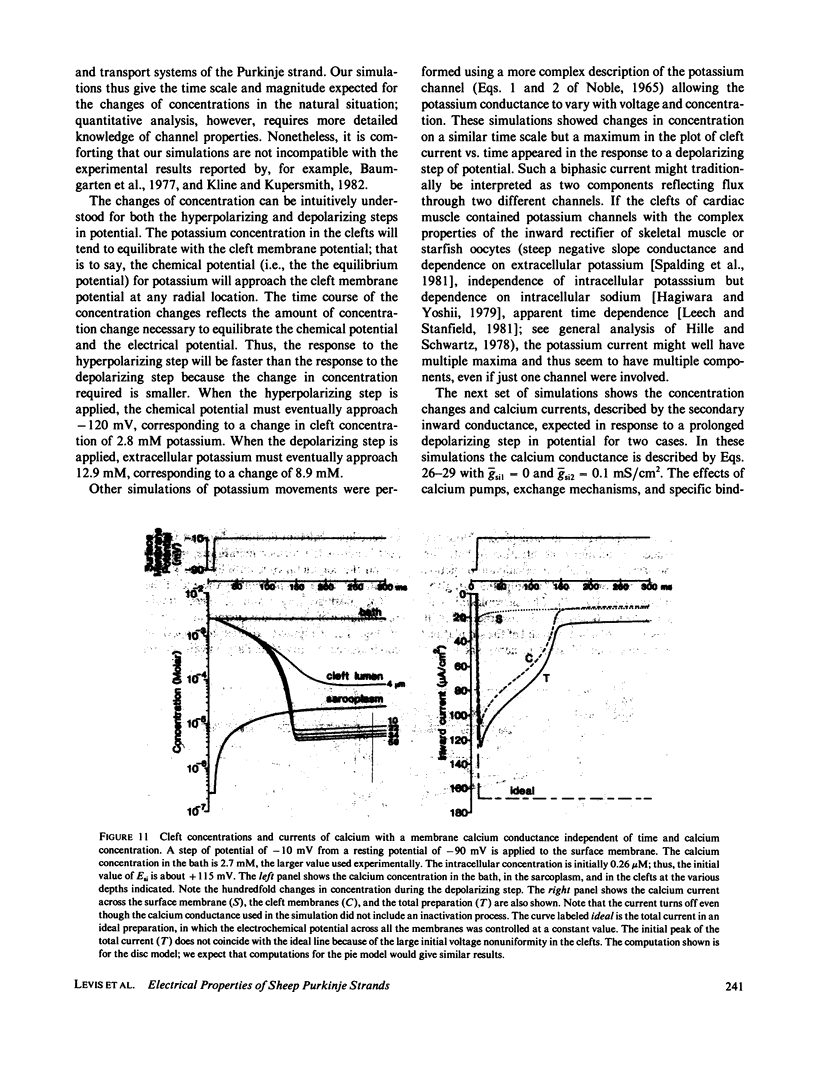
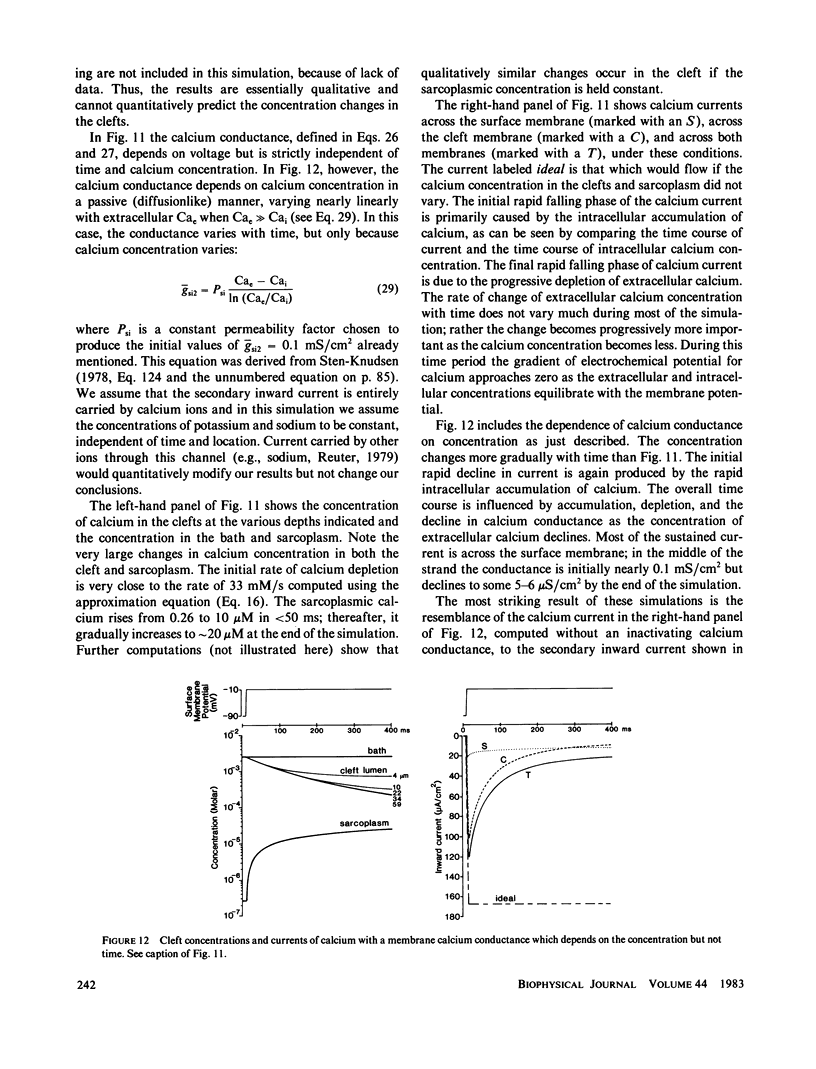
Full text
PDF

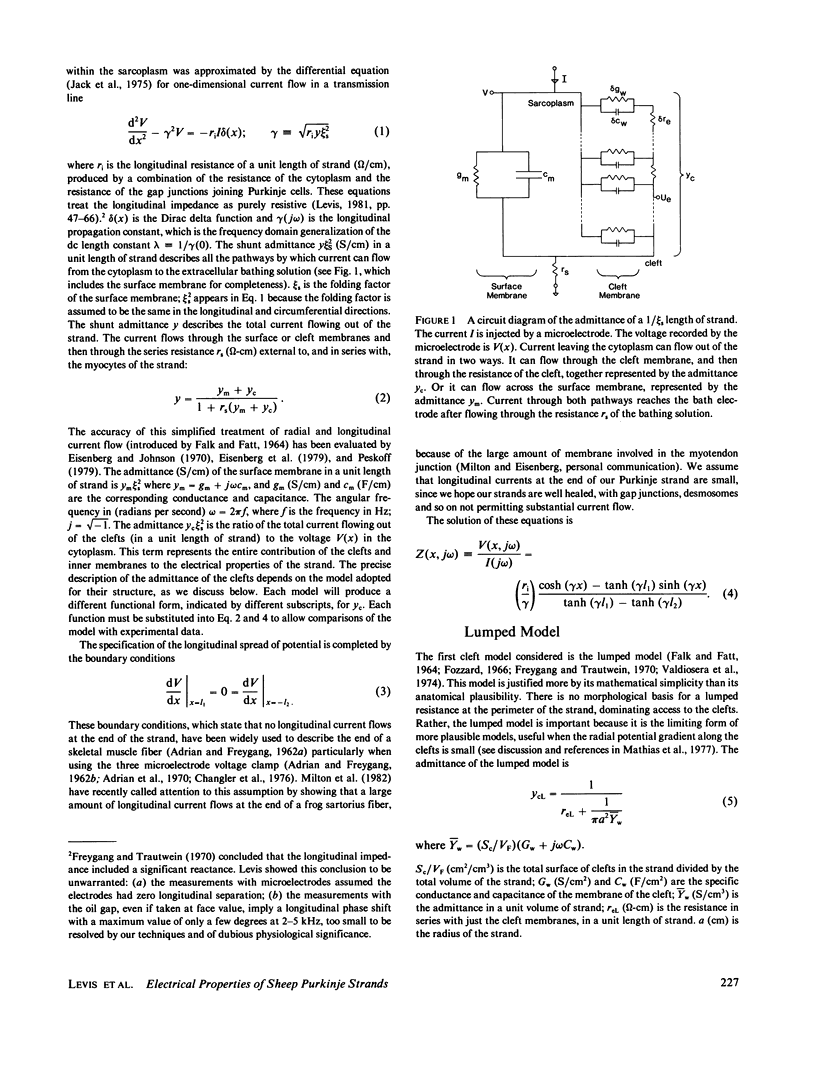

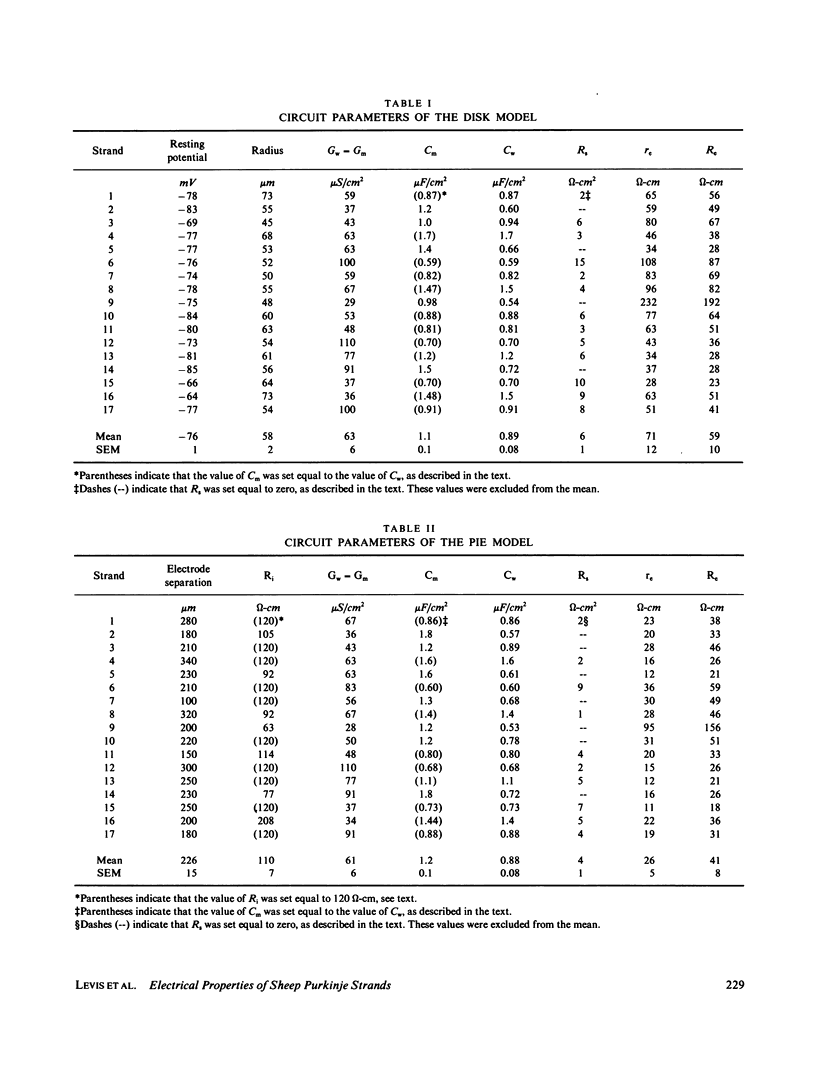


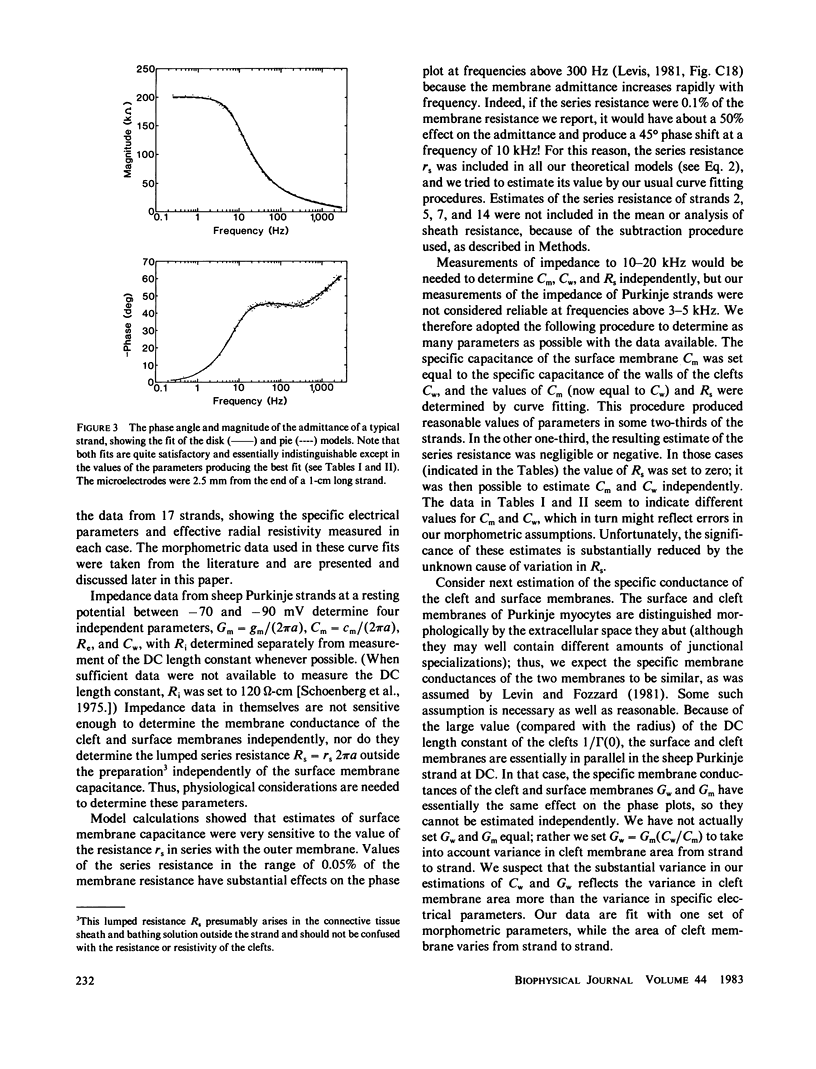
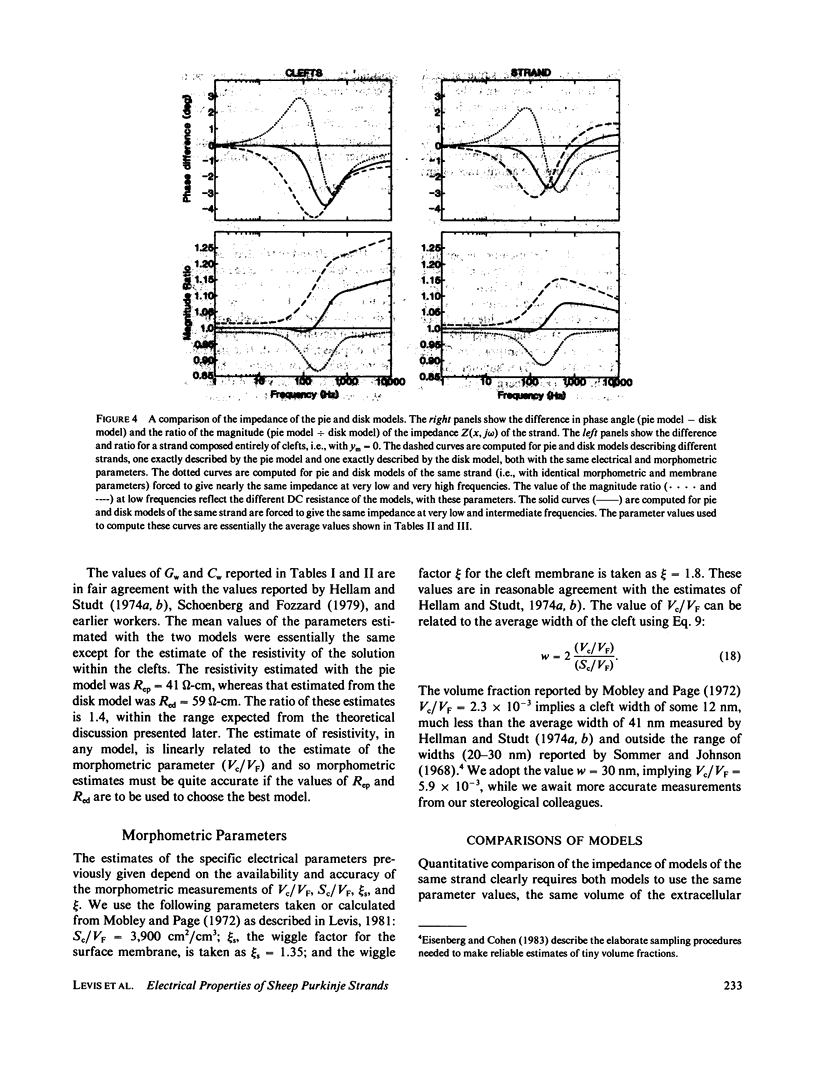







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H., FREYGANG W. H. Potassium conductance of frog muscle membrane under controlled voltage. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163:104–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Membrane capacity measurements on frog skeletal muscle in media of low ion content. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):573–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Costantin L. L., Peachey L. D. Radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):231–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peachey L. D. Reconstruction of the action potential of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):103–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Cohen I. The voltage clamp of multicellular preparations. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1977;31(3):201–245. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(78)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Eisner D., Cohen I. Voltage clamp and tracer flux data: effects of a restricted extra-cellular space. Q Rev Biophys. 1979 Aug;12(3):213–261. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten C. M., Isenberg G., McDonald T. F., Ten Eick R. E. Depletion and accumulation of potassium in the extracellular clefts of cardiac Purkinje fibers during voltage clamp hyperpolarization and depolarization: experiments in sodium-free bathing media. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):149–169. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodewei R., Hering S., Lemke B., Rosenshtraukh L. V., Undrovinas A. I., Wollenberger A. Characterization of the fast sodium current in isolated rat myocardial cells: simulation of the clamped membrane potential. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:301–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennecke R., Lindemann B. Design of a fast voltage clamp for biological membranes, using discontinuous feedback. Rev Sci Instrum. 1974 May;45(5):656–661. doi: 10.1063/1.1686708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Lee K. S., Powell T. Sodium current in single rat heart muscle cells. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:479–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C., Lewis S. A., Diamond J. M. Impedance analysis of a tight epithelium using a distributed resistance model. Biophys J. 1979 May;26(2):291–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85250-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Kline R. K+ fluctuations in the extracellular spaces of cardiac muscle. Evidence from the voltage clamp and extracellular K+ - selective microelectrodes. Circ Res. 1982 Jan;50(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colatsky T. J., Tsien R. W. Electrical properties associated with wide intercellular clefts in rabbit Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colatsky T. J. Voltage clamp measurements of sodium channel properties in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:215–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole K. S. Squid axon membrane: impedance decrease to voltage clamp. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:305–323. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Latorre R. Detection of K+ and Cl-channels from calf cardiac sarcolemma in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):849–852. doi: 10.1038/298849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L., Taylor S. R. Graded activation in frog muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Apr;61(4):424–443. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.4.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The role of sodium current in the radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):703–715. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DECK K. A., TRAUTWEIN W. IONIC CURRENTS IN CARDIAC EXCITATION. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1964 Jun 9;280:63–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00412616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouhard J. P., Roberge F. A. The simulation of repolarization events of the cardiac Purkinje fiber action potential. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1982 Jul;29(7):481–493. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1982.324920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara L., Johnson E. A. Fast sodium current in cardiac muscle. A quantitative description. Biophys J. 1980 Nov;32(2):779–790. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85016-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara L., Shigeto N., Lieberman M., Johnson E. A. The initial inward current in spherical clusters of chick embryonic heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Apr;75(4):437–456. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. L., Brehm P. Calcium-mediated control of Ca and K currents. Fed Proc. 1981 Jun;40(8):2226–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Barcilon V., Mathias R. T. Electrical properties of spherical syncytia. Biophys J. 1979 Jan;25(1):151–180. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85283-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Costantin L. L. The radial variation of potential in the transverse tubular system of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):700–701. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Mathias R. T. Structural analysis of electrical properties of cells and tissues. Crit Rev Bioeng. 1980;4(3):203–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., FATT P. LINEAR ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF STRIATED MUSCLE FIBRES OBSERVED WITH INTRACELLULAR ELECTRODES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:69–123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):341–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calcium and cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:473–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozzard H. A. Heart: excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:201–220. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozzard H. A. Membrane capacity of the cardiac Purkinje fibre. J Physiol. 1966 Jan;182(2):255–267. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freygang W. H., Trautwein W. The structural implications of the linear electrical properties of cardiac Purkinje strands. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Apr;55(4):524–547. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.4.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Divalent cations and the activation kinetics of potassium channels in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):965–996. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Slowing of sodium channel opening kinetics in squid axon by extracellular zinc. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):935–964. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y., Morad M. Measurement of transmembrane potential and current in cardiac muscle: a new voltage clamp method. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):613–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. G., Brommundt G. Influence of intercellular clefts on potential and current distribution in a multifiber preparation. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):327–349. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85098-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Yoshii M. Effects of internal potassium and sodium on the anomalous rectification of the starfish egg as examined by internal perfusion. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:251–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiny J. A., Vergara J. Optical signals from surface and T system membranes in skeletal muscle fibers. Experiments with the potentiometric dye NK2367. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Aug;80(2):203–230. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellam D. C., Studt J. W. A core-conductor model of the cardiac Purkinje fibre based on structural analysis. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):637–660. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellam D. C., Studt J. W. Linear analysis of membrane conductance and capacitance in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):661–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L. Chance and design in electrophysiology: an informal account of certain experiments on nerve carried out between 1934 and 1952. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(1):1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. Analysis of the membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Lieberman M. Heart: excitation and contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:479–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner R. W., Westerfield M., Moore J. W., Stockbridge N. A numerical method to model excitable cells. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):155–170. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85481-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline R. P., Kupersmith J. Effects of extracellular potassium accumulation and sodium pump activation on automatic canine Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:507–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammel E. A theoretical study on the sucrose gap technique as applied to multicellular muscle preparations. I. Saline-sucrose interdiffusion. Biophys J. 1981 Dec;36(3):533–553. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84751-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech C. A., Stanfield P. R. Inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres and its dependence on membrane potential and external potassium. J Physiol. 1981;319:295–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. N., Fozzard H. A. A cleft model for cardiac Purkinje strands. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):383–408. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84902-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Rink T. J., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium in heart muscle at rest and during contraction measured with Ca2+ -sensitive microelectrodes. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):845–850. doi: 10.1038/286845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Ebihara L., Lieberman M., Johnson E. A. Linear electrical properties of passive and active currents in spherical heart cell clusters. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):221–242. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84725-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T. Effect of tortuous extracellular pathways on resistance measurements. Biophys J. 1983 Apr;42(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84368-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Eisenberg R. S., Valdiosera R. Electrical properties of frog skeletal muscle fibers interpreted with a mesh model of the tubular system. Biophys J. 1977 Jan;17(1):57–93. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85627-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Rae J. L., Eisenberg R. S. Electrical properties of structural components of the crystalline lens. Biophys J. 1979 Jan;25(1):181–201. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85284-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Rae J. L., Eisenberg R. S. The lens as a nonuniform spherical syncytium. Biophys J. 1981 Apr;34(1):61–83. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84837-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. E., Noble D., Tsien R. W. Reconstruction of the electrical activity of cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):1–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merickel M. Design of a single electrode voltage clamp. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Feb;2(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A., Page E. The surface area of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):547–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Salama G. Optical probes of membrane potential in heart muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:267–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Gilai A. Action potentials of isolated single muscle fibers recorded by potential-sensitive dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Dec;76(6):729–750. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.6.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Gilai A. Radial propagation of muscle action potential along the tubular system examined by potential-sensitive dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Dec;76(6):751–762. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.6.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. Outward membrane currents activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):205–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peskoff A. Electric potential in cylindrical syncytia and muscle fibers. Bull Math Biol. 1979;41(2):183–192. doi: 10.1007/BF02460877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J. L., Mathias R. T., Eisenberg R. S. Physiological role of the membranes and extracellular space with the ocular lens. Exp Eye Res. 1982 Nov;35(5):471–489. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Properties of two inward membrane currents in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:413–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Stevens C. F., Tsien R. W., Yellen G. Properties of single calcium channels in cardiac cell culture. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):501–504. doi: 10.1038/297501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F. Linear electrical properties of the transverse tubules and surface membrane of skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Nov;56(5):640–671. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.5.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M., Dominguez G., Fozzard H. A. Effect of diameter on membrane capacity and conductance of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Apr;65(4):441–458. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M., Fozzard H. A. The influence of intercellular clefts on the electrical properties of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. Biophys J. 1979 Feb;25(2 Pt 1):217–234. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(79)85287-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. R., Johnson E. A. Cardiac muscle. A comparative study of Purkinje fibers and ventricular fibers. J Cell Biol. 1968 Mar;36(3):497–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding B. C., Senyk O., Swift J. G., Horowicz P. Unidirectional flux ratio for potassium ions in depolarized frog skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):C68–C75. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.1.C68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. E., Bezanilla F., Rojas E. Diffusion models for the squid axon Schwann cell layer. Biophys J. 1980 Jan;29(1):95–117. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85120-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdiosera R., Clausen C., Eisenberg R. S. Measurement of the impedance of frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1974 Apr;14(4):295–315. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85917-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R., Morad M. Intrinsic birefringence signal preceding the onset of contraction in heart muscle. Science. 1981 Aug 7;213(4508):663–666. doi: 10.1126/science.7256266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. A., Goldner M. M. Voltage clamping with a single microelectrode. J Neurobiol. 1975 Jul;6(4):411–422. doi: 10.1002/neu.480060406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


